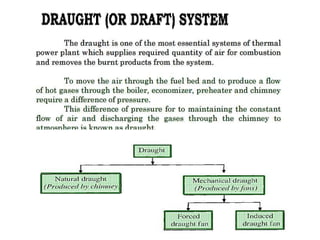
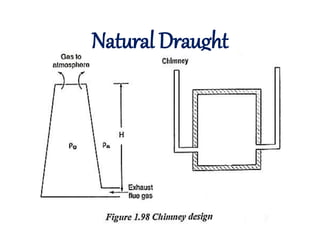
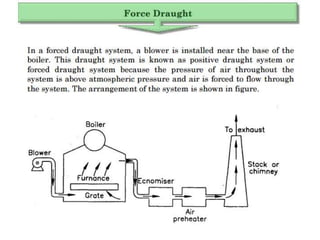
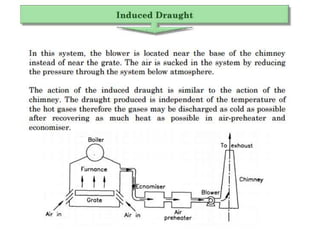
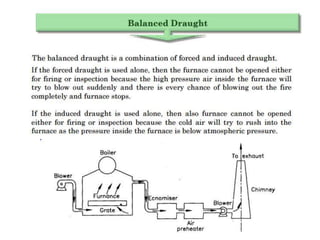
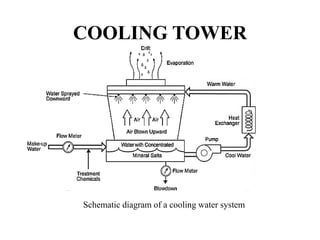
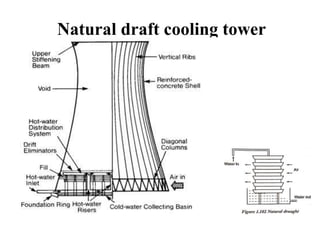
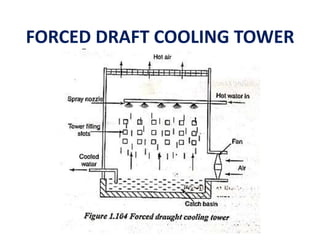
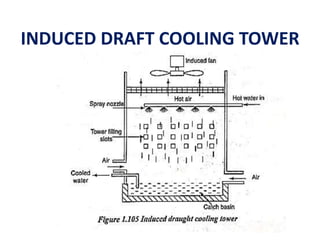
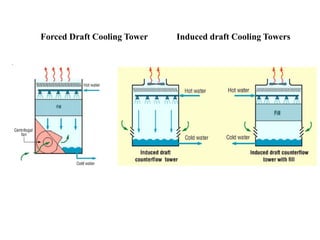
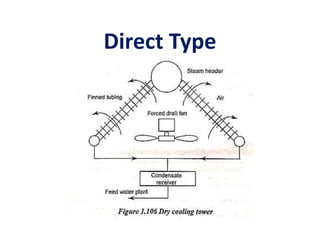
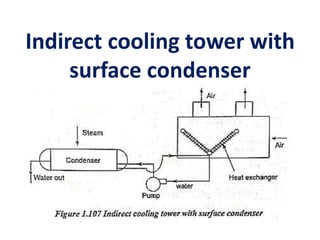
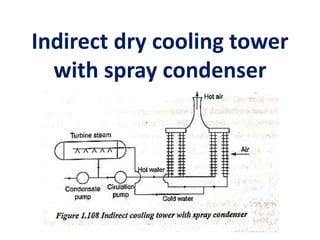
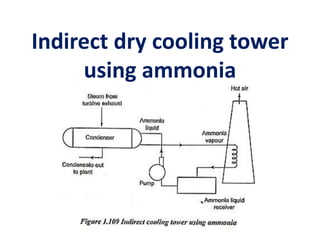
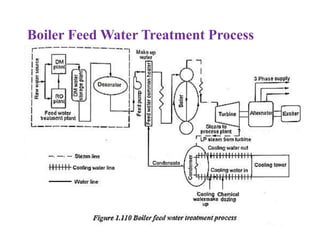
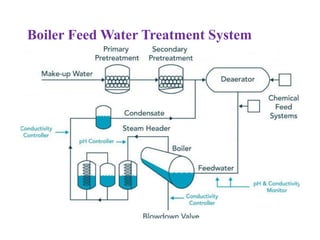
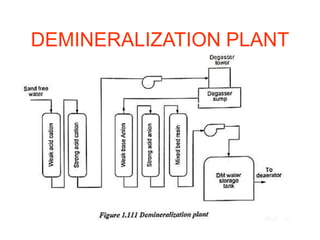
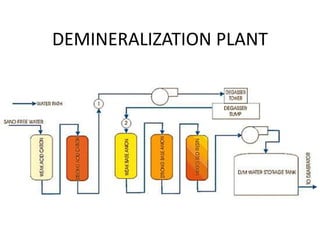
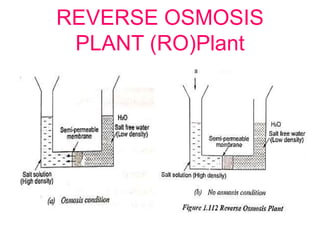
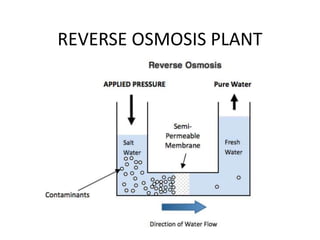
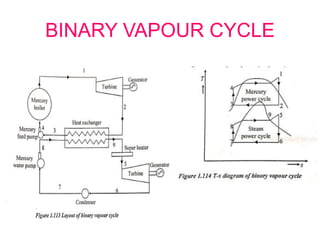
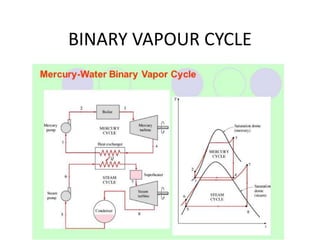
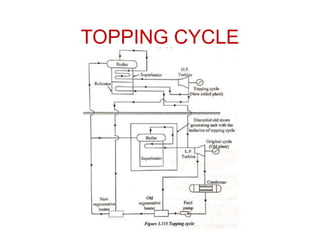
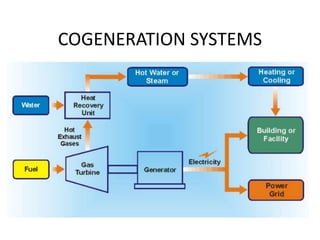
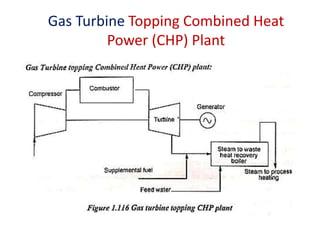
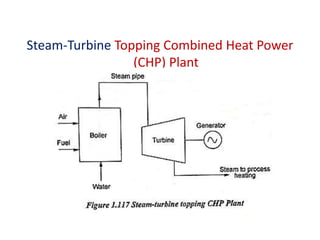
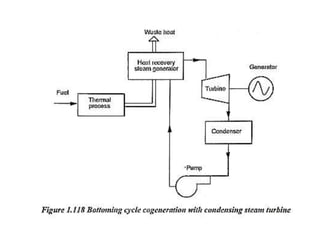
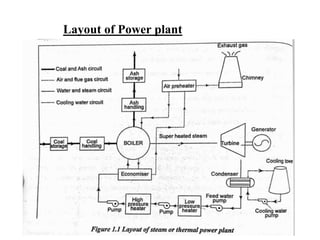
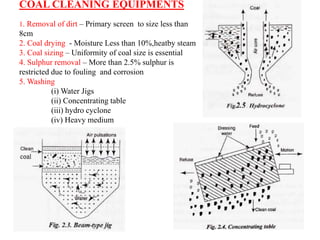
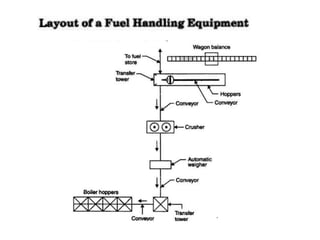
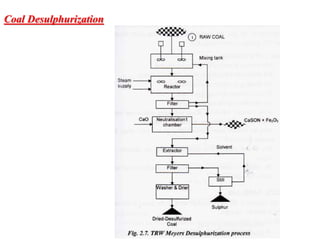
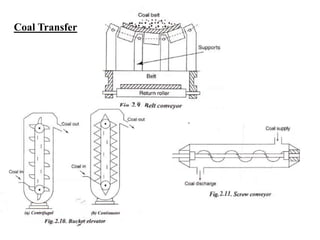
The document covers engineering principles related to steam power plants, focusing on modern coal power plant components including boilers, steam generation processes, and supporting systems like economizers and condensers. It describes various types of boilers, their operational principles, classifications, and their efficiency advantages. Additionally, it discusses the importance of accessories for improved efficiency and the applications of steam turbines and condensers in power generation.






































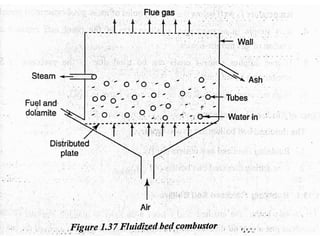




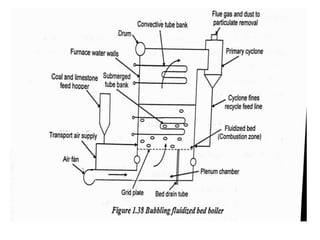
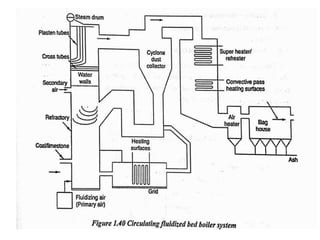
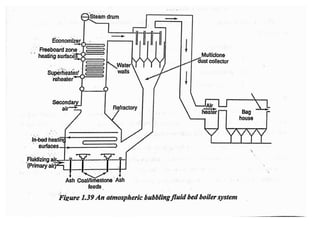
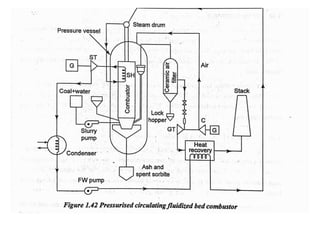
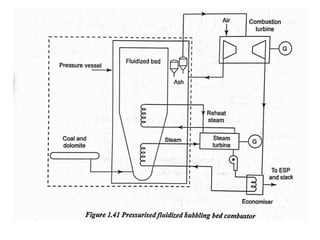
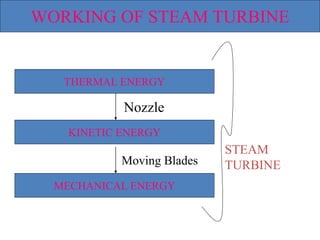

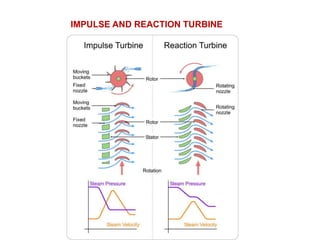


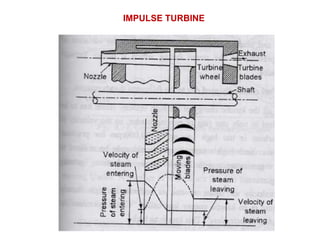
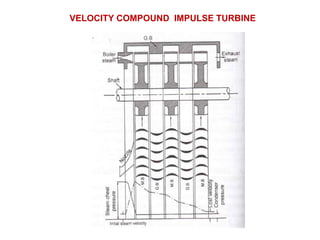
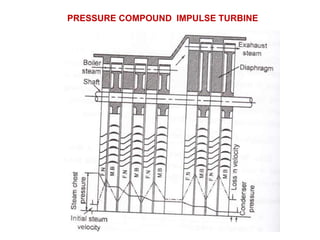
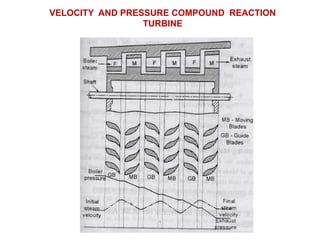

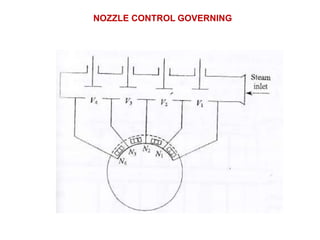
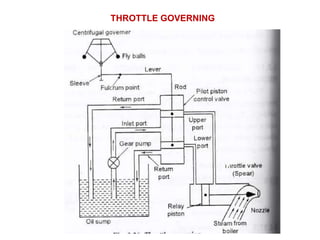
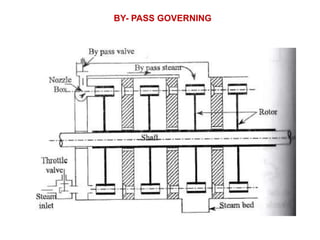


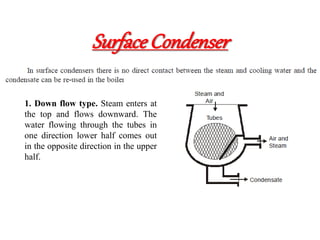
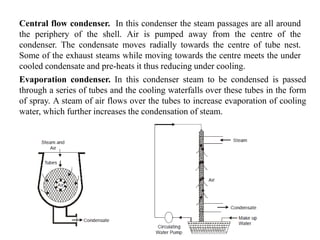
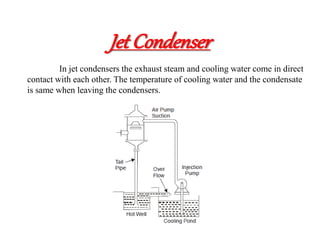

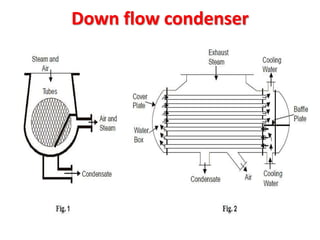

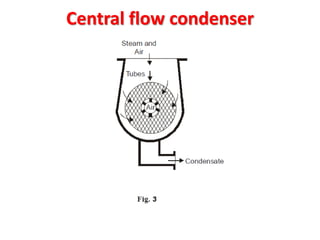

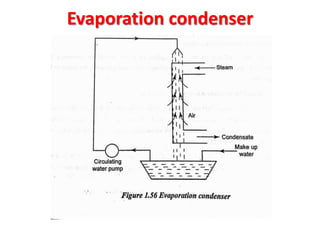



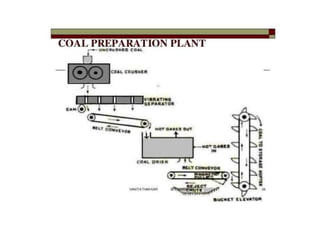
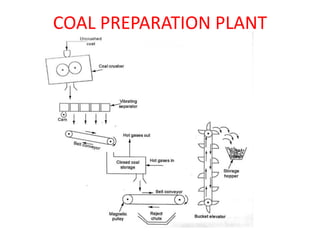
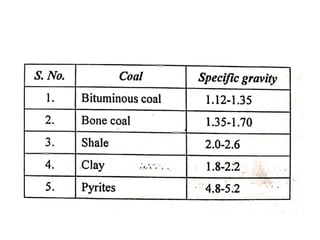


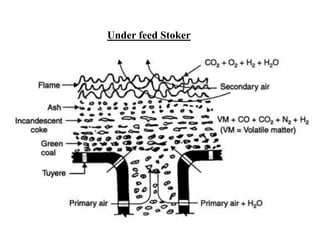
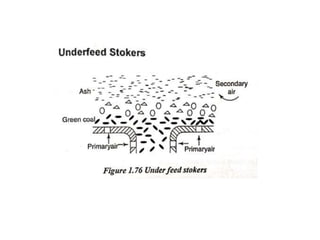
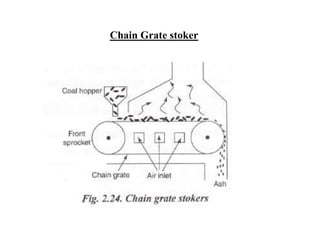
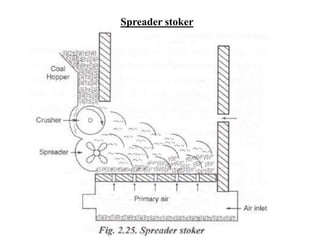
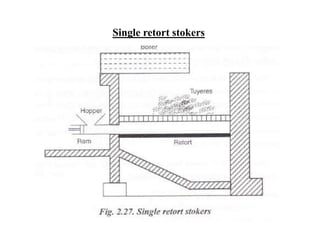
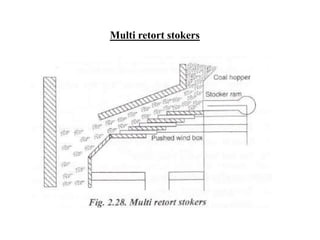


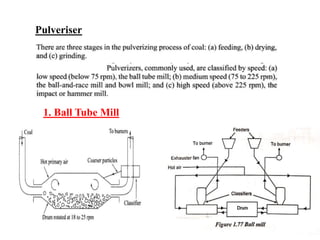
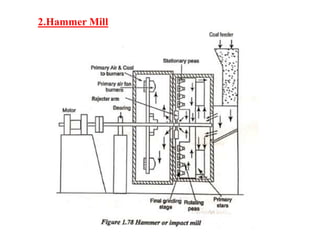
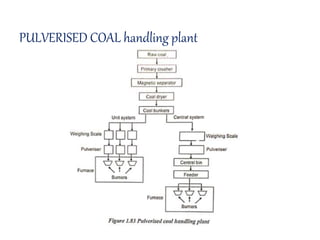

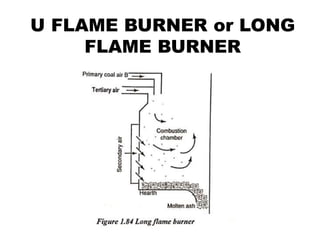
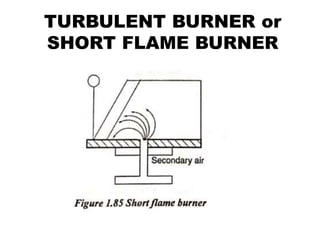

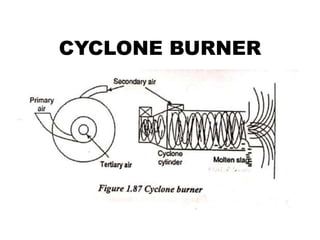


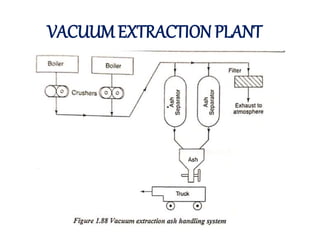
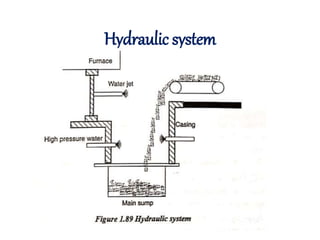
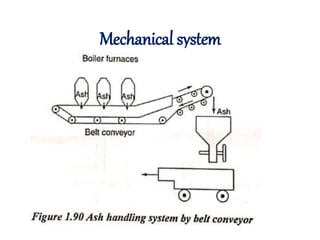
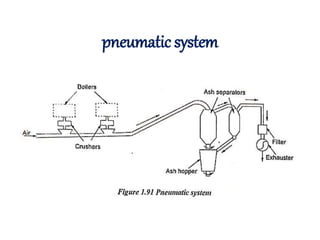
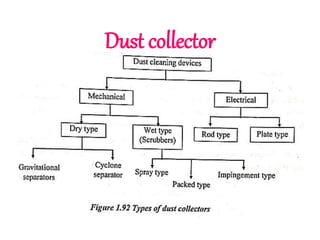

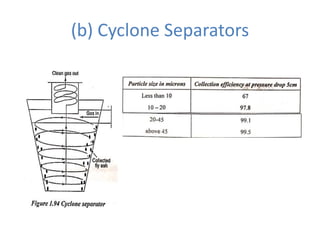
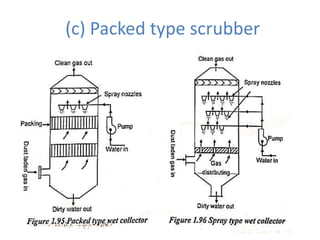

![(e) ElectroStatic precipitator [ESP]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-1-steampowerplant-231005065721-5991dcaa/85/UNIT-1-Steam-Power-Plant-pptx-141-320.jpg)