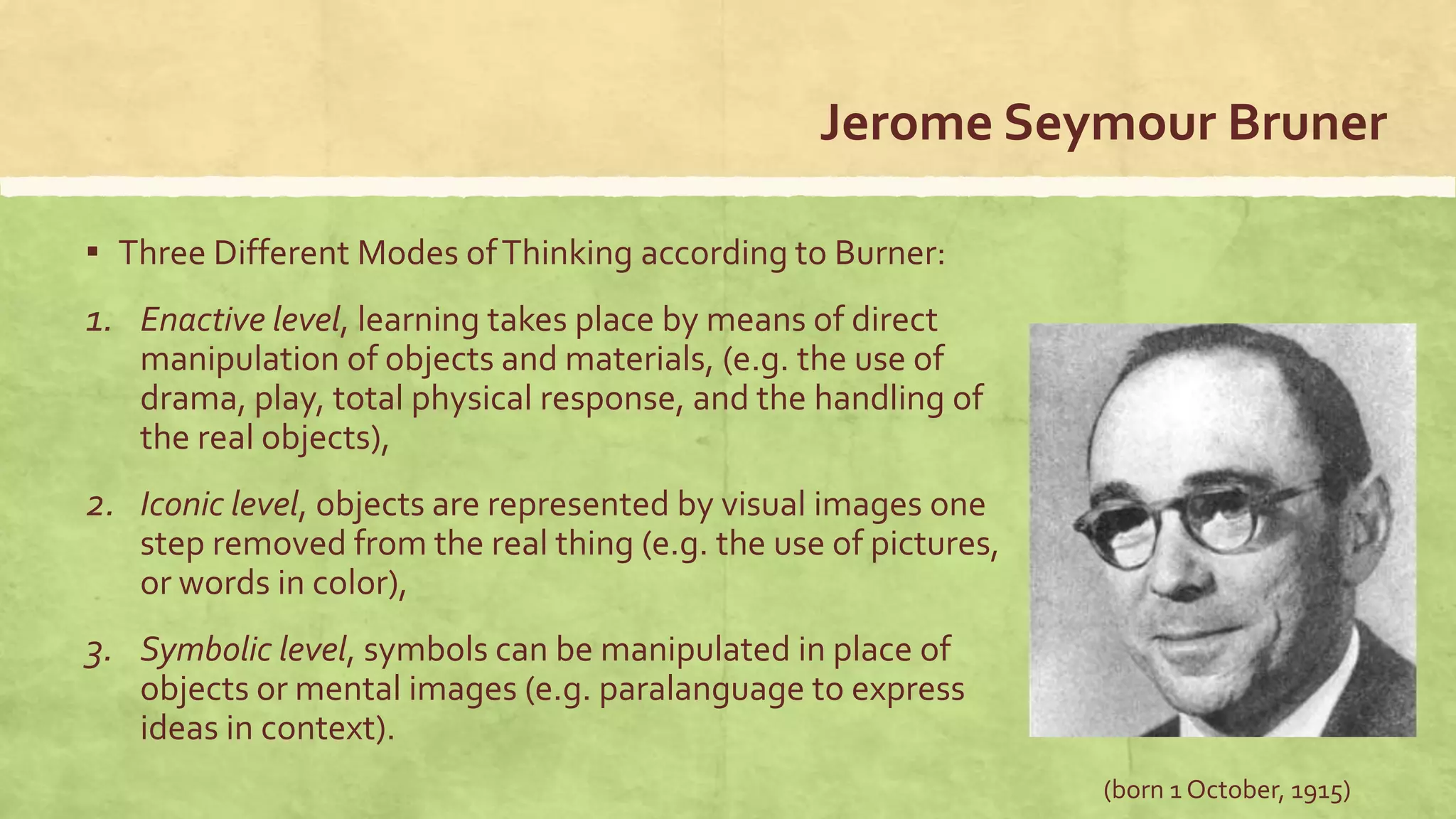
This document provides an overview of educational psychology theories related to behaviorism and cognitive psychology. It discusses early theories like behaviorism proposed by Pavlov and Skinner which viewed learning as stimulus-response conditioning. It also discusses cognitive psychology and how it takes into account mental processes like attention, memory, problem-solving and intelligence, unlike behaviorism. The document compares the teacher-oriented audiolingual method based on behaviorism to cognitive approaches and discusses some weaknesses and strengths of both perspectives in language teaching.