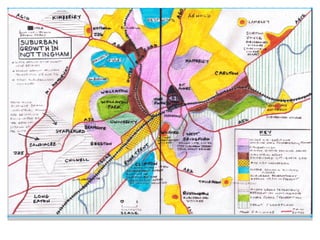
Suburbanisation refers to the movement of people, services, and industries from the centers of inner urban areas to the edges of built-up areas. In the 1800-1900 period, industry could pay the most for city center sites, leading to unplanned housing around factories with few amenities. The middle class began moving to suburbs. Suburban areas continued rapidly expanding in the inter-war and post-war periods due to fewer regulations. Causes of suburbanization include decentralization of jobs to cheaper land prices on the outskirts, deindustrialization causing inner city job losses, attractions of suburban locations like space and amenities, and advances in transportation allowing longer commutes. Consequences can be economic, environmental, or social for both the