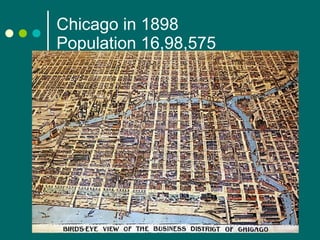
Urbanization refers to the increasing proportion of people living in cities and suburbs. It is closely connected to industrialization, as factories located in cities and drew workers. The main causes of urbanization are the industrial revolution, emergence of large manufacturing centers, job opportunities, and availability of transportation. Chicago's population grew from 15 people in 1820 to over 1.6 million in 1898, reflecting the effects of urbanization. Positive effects include opportunities not available in rural areas and a higher standard of living in cities. However, rapid urbanization also led to issues like overcrowding, lack of sanitation, unemployment, poverty, and increased crime rates.