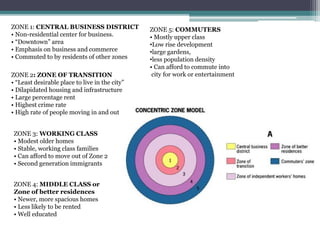
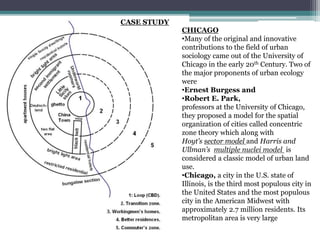
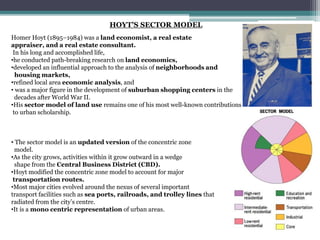
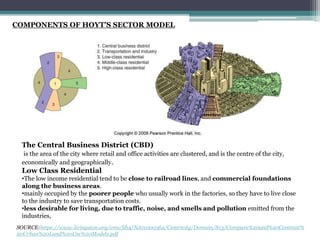
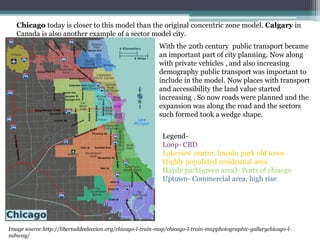
Homer Hoyt proposed the sector model as an update to the concentric zone model. The sector model accounts for major transportation routes radiating out from the central business district. Land uses, such as industrial, commercial, and residential zones, develop along these transportation corridors in wedge-shaped sectors. The model places low-income housing and industry closest to the central business district, with wealthier residential neighborhoods farther out. Examples of cities that generally follow the sector model include Chicago and Calgary.