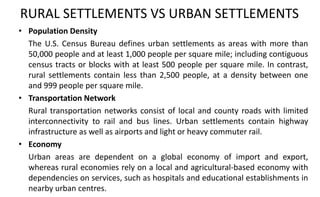
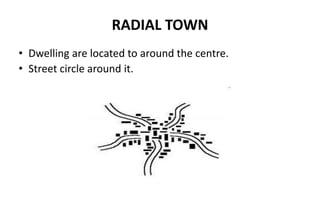
This document discusses types of settlements including rural and urban settlements. Rural settlements typically have smaller populations engaged in farming, fishing or mining, with dispersed, linear or nucleated patterns. Characteristics include villages surrounded by farms and limited services. Urban settlements have larger populations engaged in non-rural activities with a wide range of specialized services in towns and cities. They differ from rural settlements in population density, transportation networks and economies. Settlement patterns can be dispersed, nucleated or linear along transport routes.