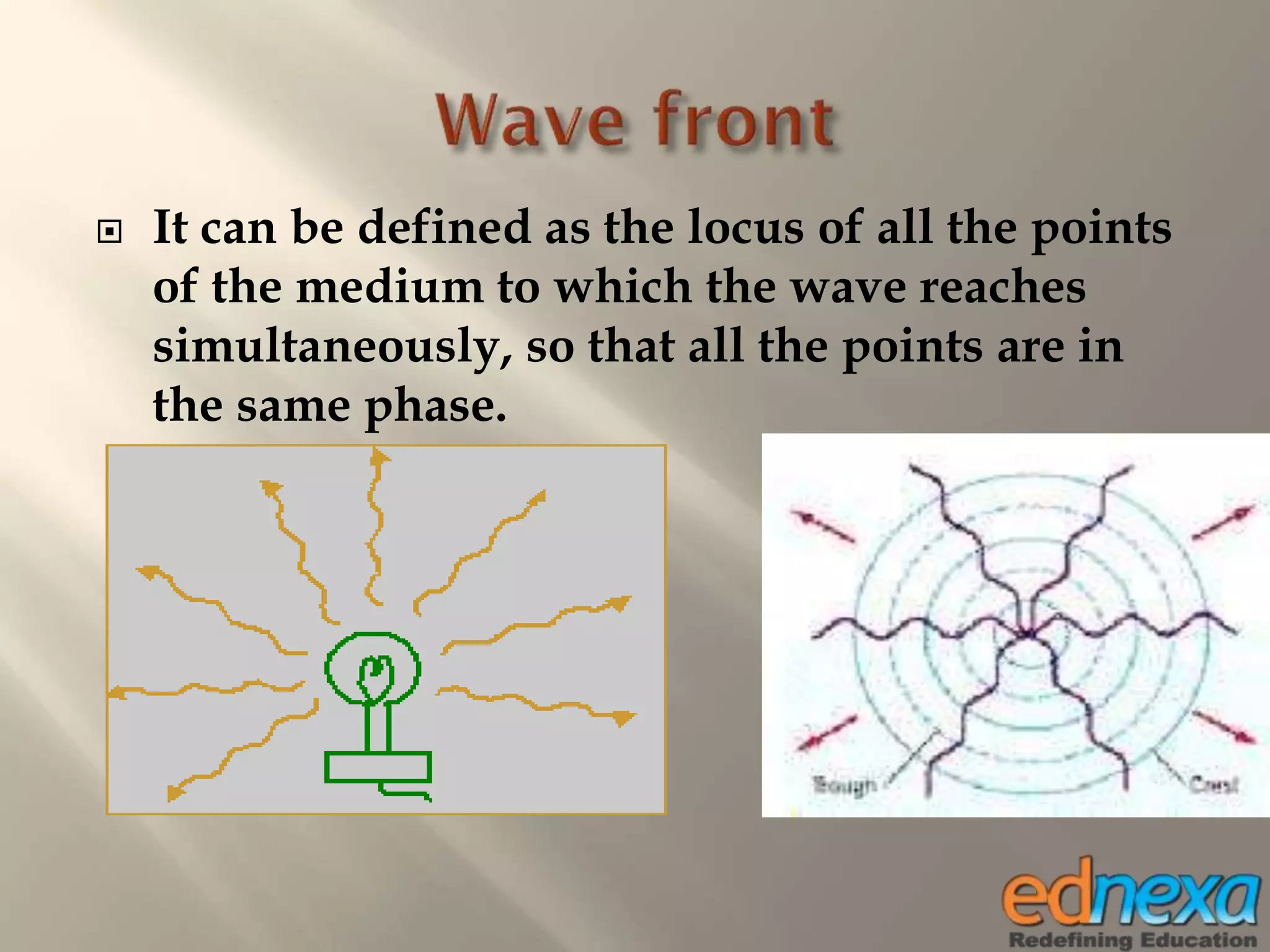
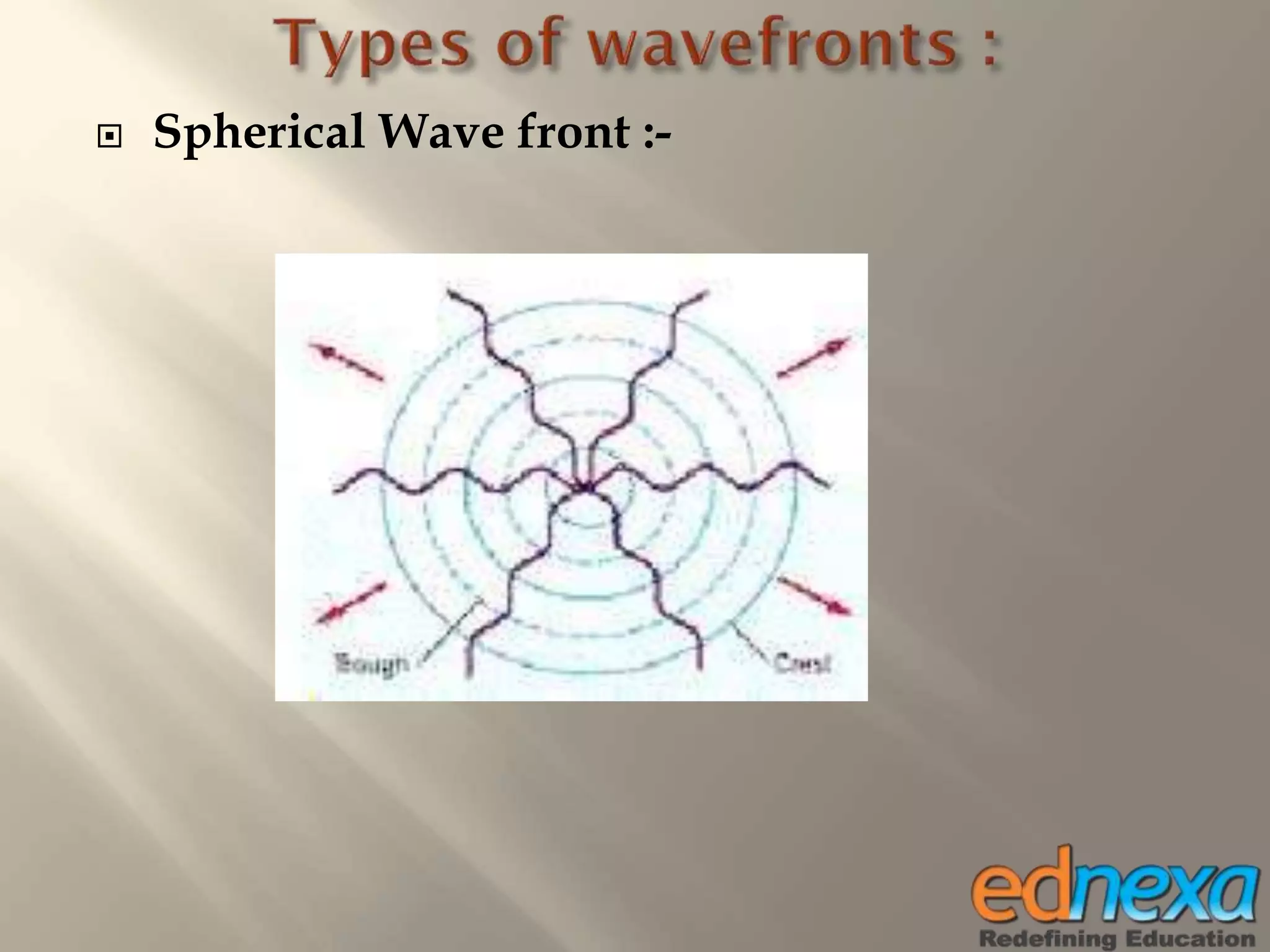
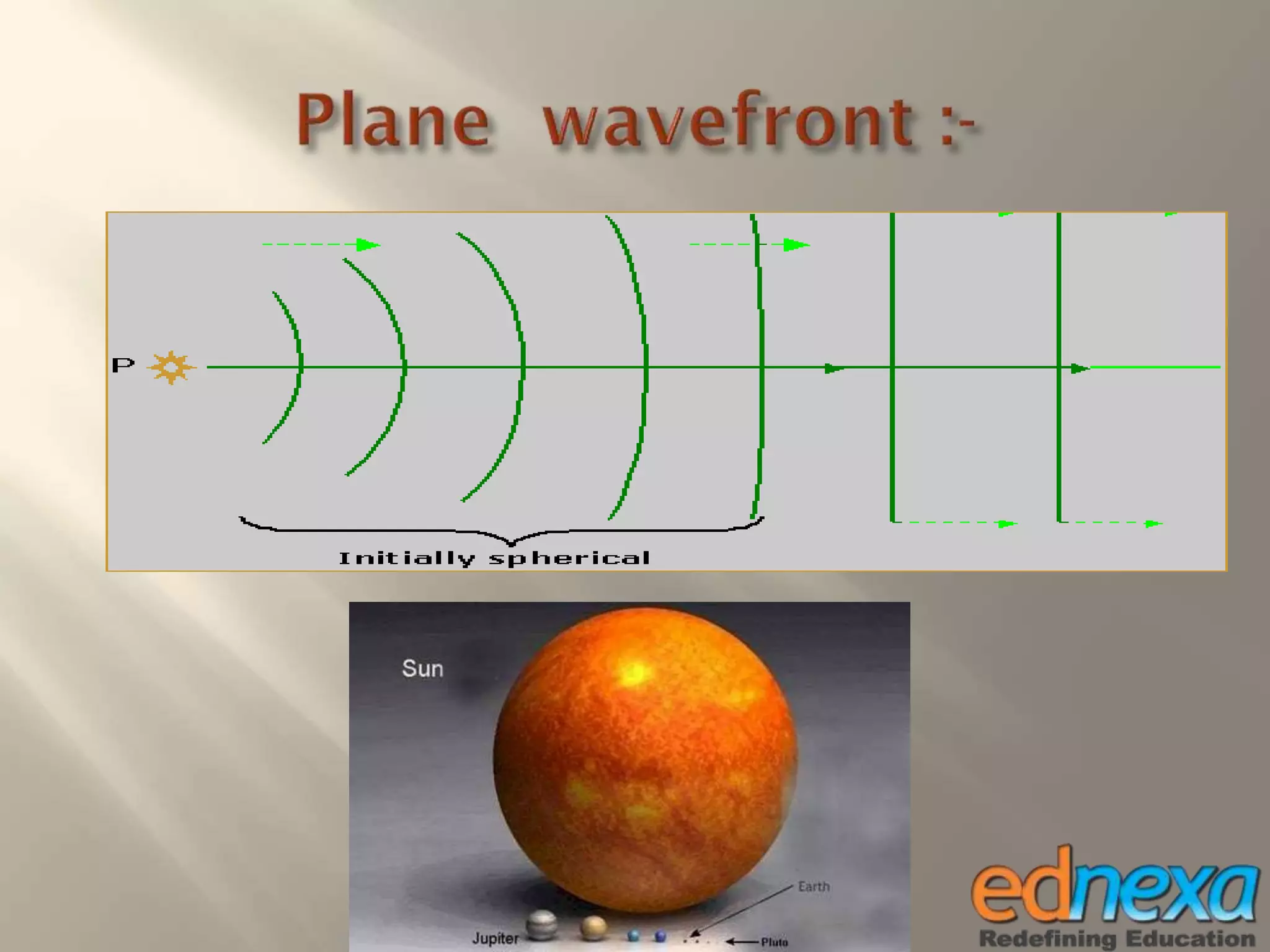
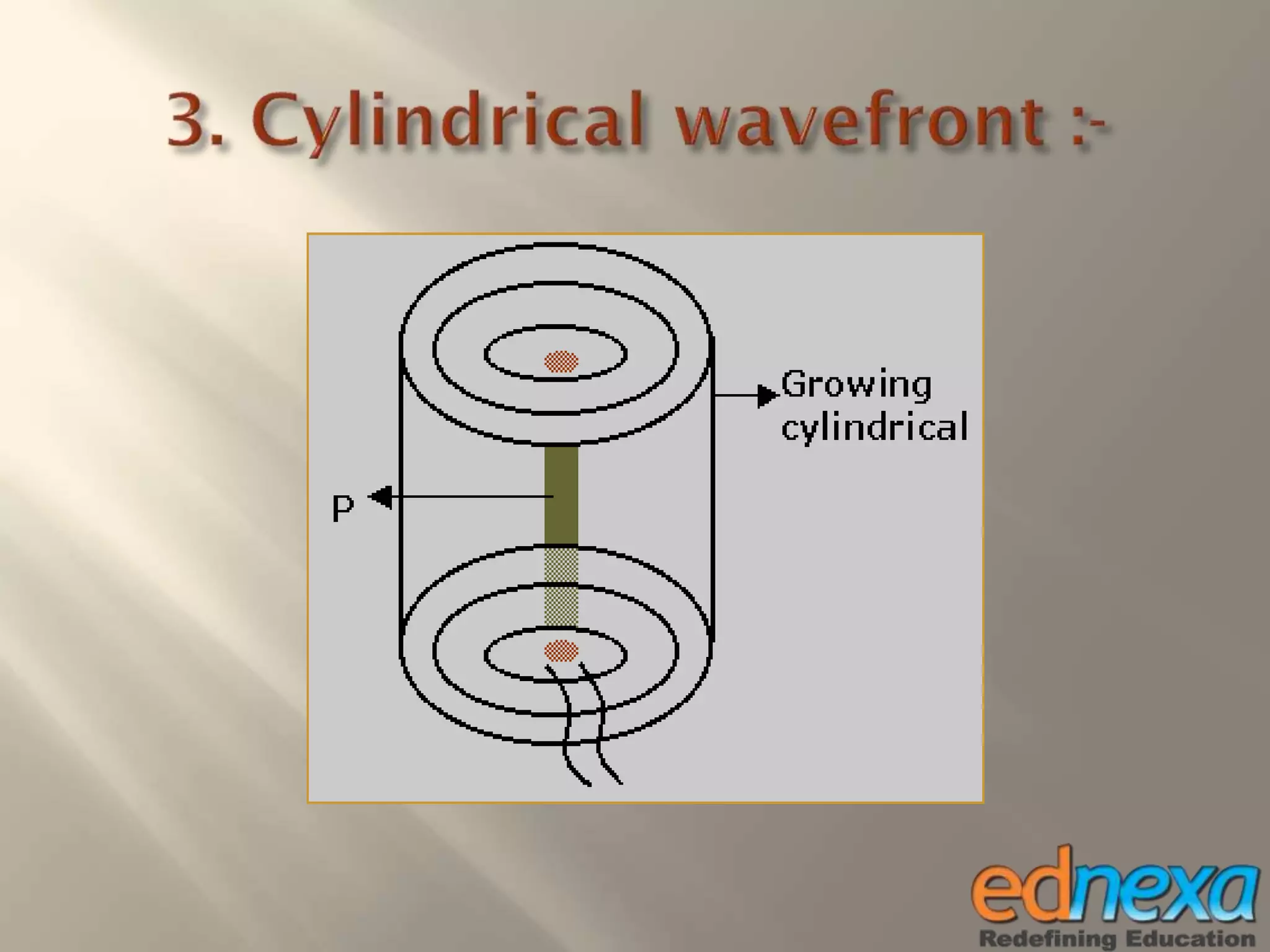
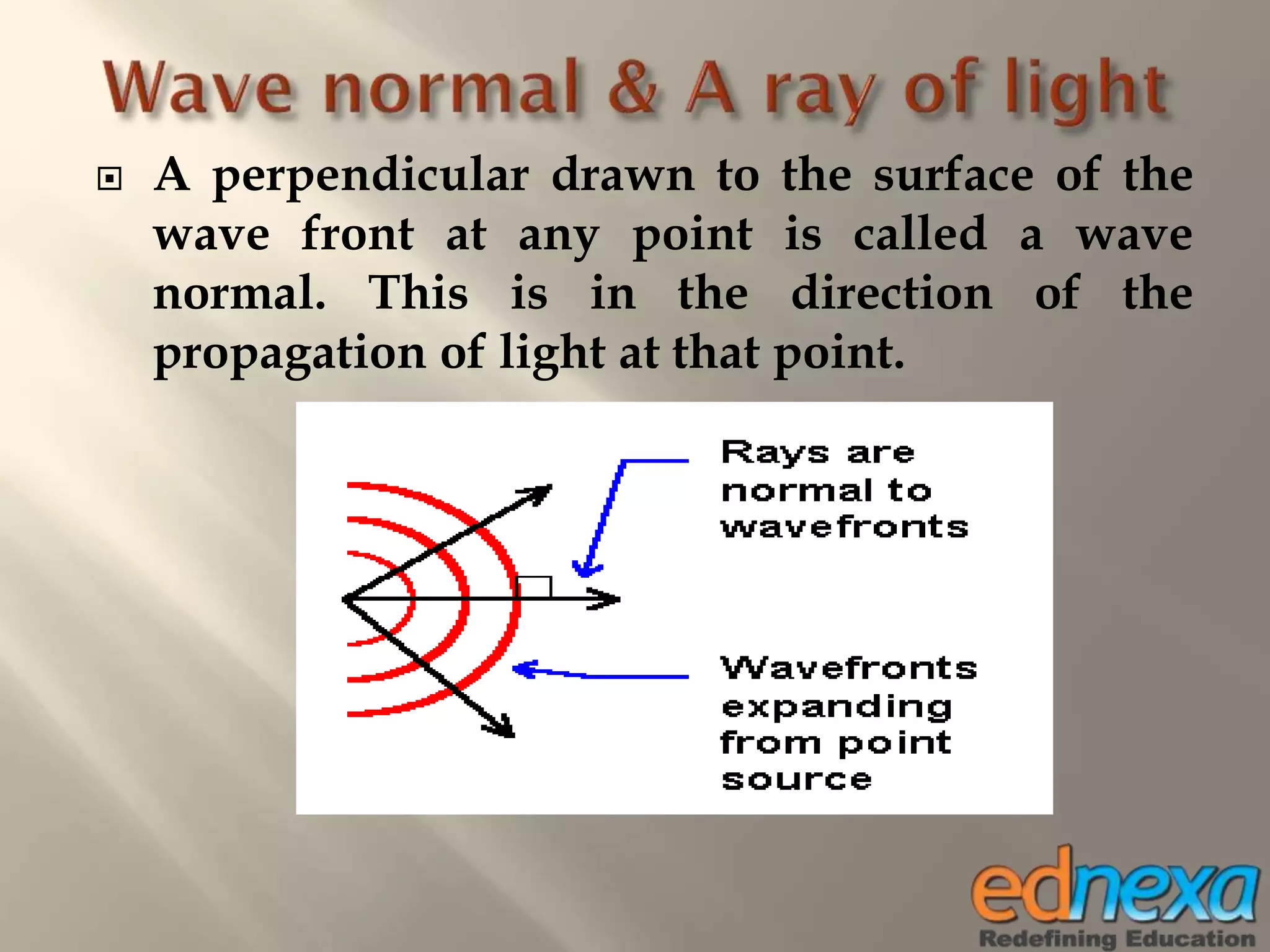
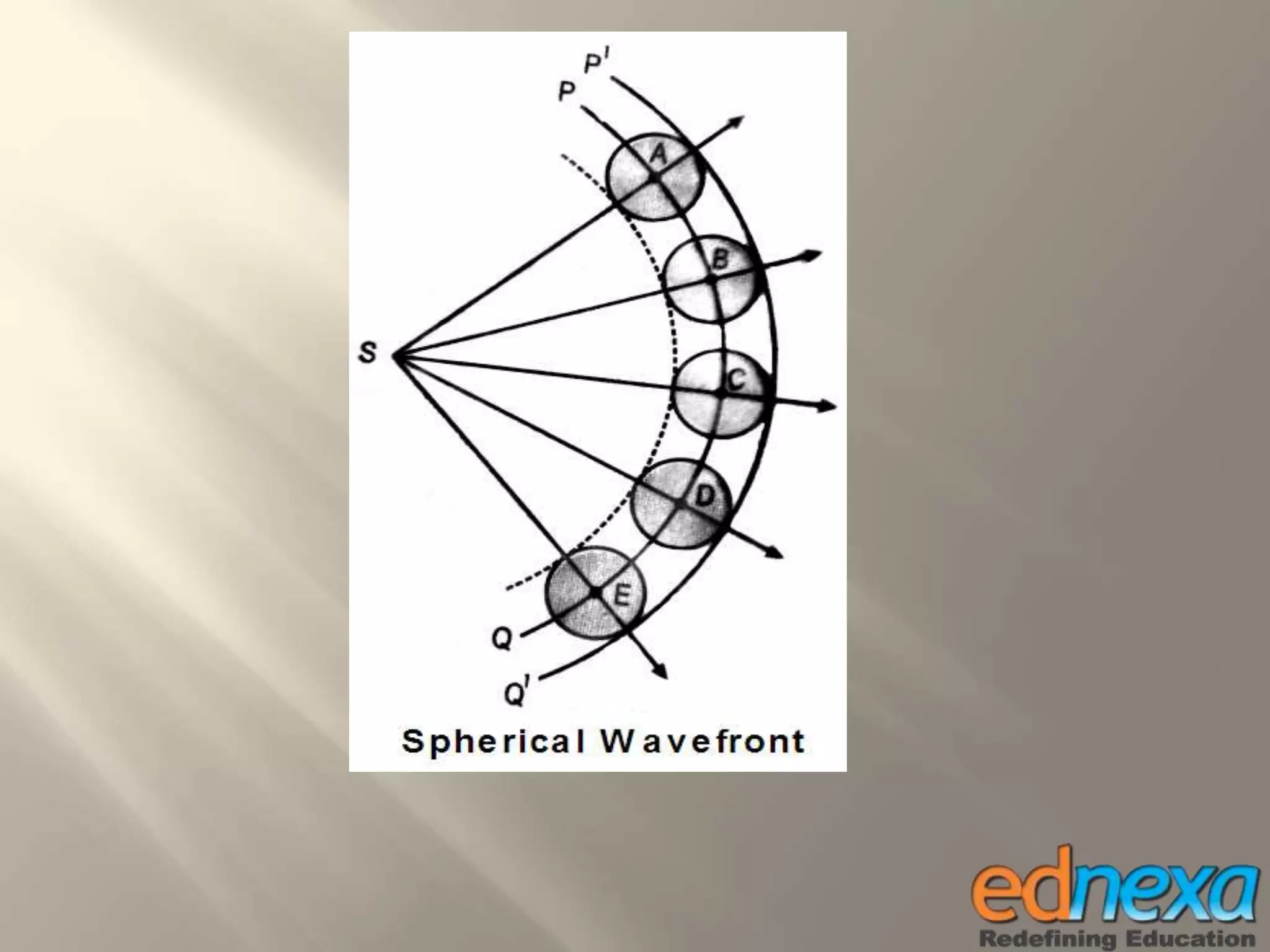
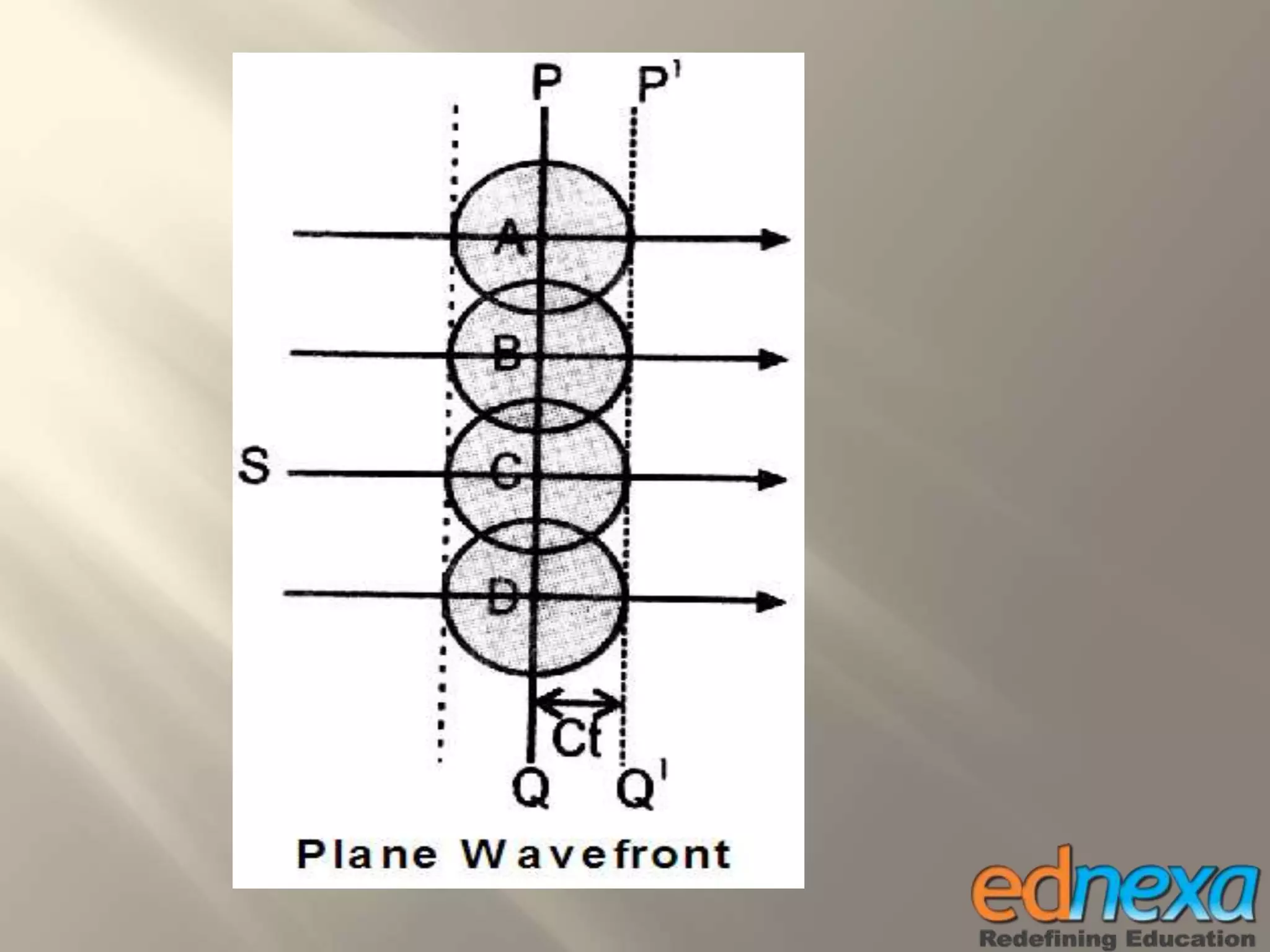
The document outlines Christiaan Huygens' wave theory of light from the 17th century. It proposes that light consists of longitudinal waves that propagate in a straight line through a hypothetical medium called the luminiferous ether. According to the theory, each point on a wavefront acts as a secondary source of waves, and the movement of the wavefront over time can be determined using Huygens' principle and construction. The wave theory was able to successfully explain several optical phenomena like reflection, refraction, and interference of light. However, it could not explain some observations like the rectilinear propagation of light and the photoelectric effect.