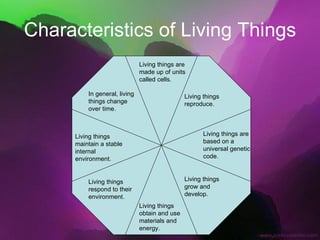
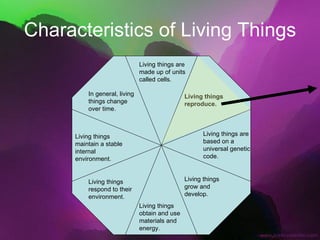
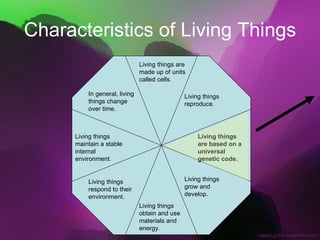
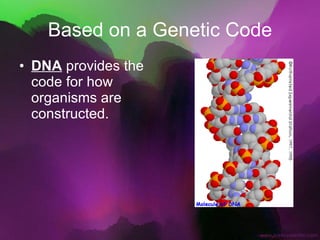
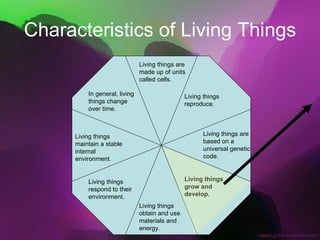
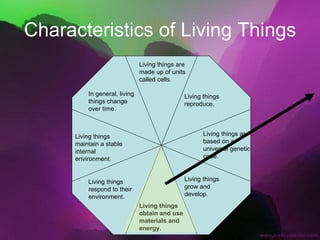
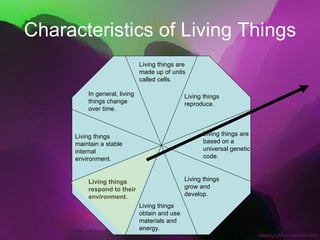
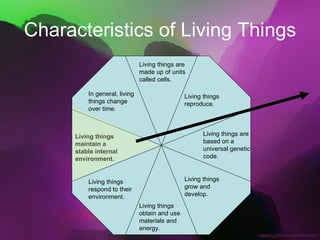
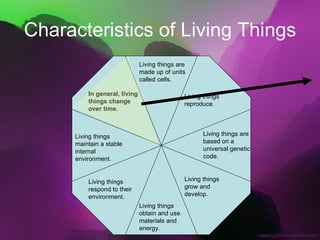
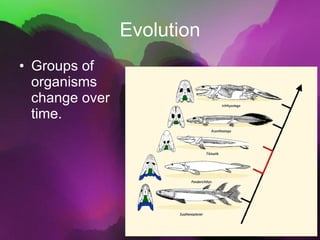
The document discusses the key characteristics of living things. It states that all living things are made of cells, can reproduce, grow and develop, obtain and use energy, respond to their environment, and maintain internal balance. It also notes that living things are based on a universal genetic code and change over time through evolution. The document provides examples and further explanations for each of these characteristics of life.