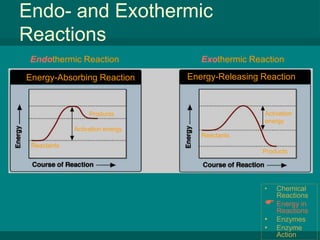
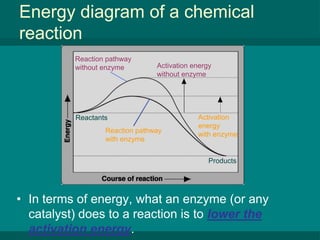
The document summarizes key concepts about chemical reactions, energy in reactions, enzymes, and enzyme action from a biology textbook chapter on chemistry of life. It defines chemical reactions as processes that transform chemicals, with reactants entering and products forming. Reactions can release or absorb energy depending on differences in bond energies between reactants and products. Enzymes are protein catalysts that lower the activation energy of reactions, speeding up rates immensely and allowing life-sustaining reactions to occur efficiently. They achieve catalysis by creating an ideal microenvironment where substrates precisely bind at active sites.