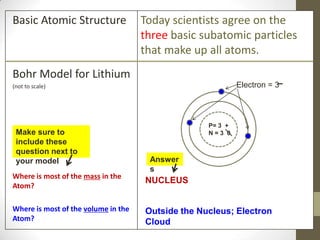
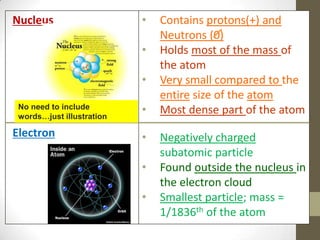
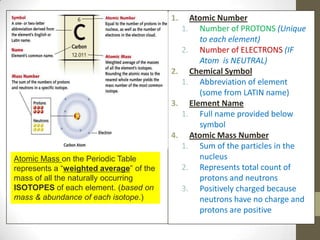
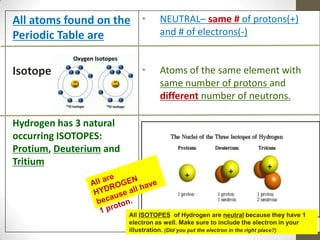
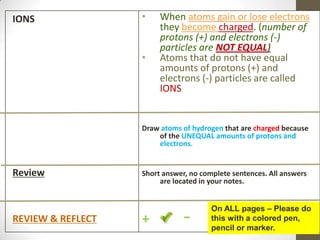
This document provides an overview of the history and development of the atomic model. It discusses early Greek philosophers like Democritus who proposed that all matter is made up of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. The document then outlines major scientists and their contributions to understanding atomic structure, including Dalton's atomic theory, Thomson's plum pudding model, Rutherford's gold foil experiment, Bohr's planetary model, and Schrodinger's wave mechanic model. It concludes by explaining current atomic structure including subatomic particles like protons, neutrons, and electrons as well as isotopes, ions, and how atomic number and mass relate to the periodic table.