Stretch reflex imu m sasi 2020
- 1. MAGDI AWAD SASI 1
- 2. The muscle spindle composition and function Gamma motor neuron The destribution of muscle tone and supraspinal control functions. Stretch reflex ,types in response to stretch Characters of stretch reflex Inverse stretch reflex MAGDI AWAD SASI 2
- 3. Muscle spindle ◦ Response to stretch Within muscle fibers as intrafusal fibrer Automonic with gamma motor neurons Golgi tendon organ ◦ Muscle tension especially during isometric Relaxation reflex - protective Joint receptors ◦ Are found in capsules and ligaments around joints MAGDI AWAD SASI 3
- 4. For skeletal muscle activity to be smoothly coordinated, proprioceptor input is necessary. Muscle spindles inform the nervous system of the length of the muscle. Golgi tendon organs inform the brain as to the amount of tension in the muscle and tendons.
- 5. The Striated Muscle ◦ Anatomy - Two types of fibers Extrafusal Fiber: these fibers do the work of the muscle. Intrafusal Fiber or Muscle Spindle: controls muscle tone and provides important sensory information. ◦ Contraction Controlled by the nervous system Muscles only shorten (i.e., only go one direction) Organized in opposition pairs. MAGDI AWAD SASI 5
- 6. A group of intrafusal fibers parallel to the surrounding extrafusal fibers (1)p:697ch55 The central part of it has no actin or myocin so it doesn't contract.(receptor) The peripheral part contract in response to type A gamma motor neuron.
- 7. MAGDI AWAD SASI 7 Extrafusal fibers are ordinary skeletal muscle cells(contractile) . Muscle spindles, composed of 3–10 small bundles of encapsulated intrafusal fibers, are dispersed throughout gross muscle. These are dynamic stretch receptors that continuously check for changes in muscle length.
- 8. 2 parts: 1- Central (receptor) 2- peripheral contractile area Types of intrafusal fibers: 1- Nuclear bag fibers (the dynamic response) 2- Nuclear chain fibers (the static response) -Nuclear chain is more abundant than the nuclear bag fibers MAGDI AWAD SASI 8
- 9. MAGDI AWAD SASI 9 Intrafusal fibers Noncontractile in their central regions (lack myofilaments) Wrapped with two types of afferent endings: primary sensory endings of type Ia fibers and secondary sensory endings of type II fibers. Contractile end regions are innervated by gamma () efferent fibers that maintain spindle sensitivity.
- 10. MAGDI AWAD SASI 10 Both nuclear bag and nuclear chain fibers possess a central, noncontractile region housing multiple nuclei, and a skeletal muscle (myofibril-containing) contractile portion at each end of the central region. The nuclear bag fibers are larger, and their multiple nuclei are clustered in the “baglike” dilated central region of the fiber. The nuclear chain fibers are smaller and consist of multiple nuclei arranged sequentially, as in a “chain” of pearls, in the central region of the fiber.
- 11. Sensory Endings in Muscles ◦ Anulospiral: wraps around muscle spindle, senses dynamic changes in muscle length. ◦ Flower spray: looks like little flowers, sense static changes in muscle length, helps determine position. MAGDI AWAD SASI 11
- 12. MAGDI AWAD SASI 12 Excited in two ways: 1. External stretch of muscle and muscle spindle 2. Internal stretch of muscle spindle: Activating the motor neurons stimulates the ends to contract, thereby stretching the spindle Stretch causes an increased rate of impulses in Ia fibers
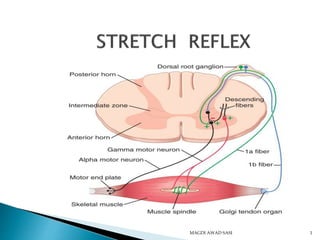
- 13. Figure 13.15 Secondary sensory endings (type II fiber) Efferent (motor) fiber to muscle spindle Primary sensory endings (type Ia fiber) Connective tissue capsule Muscle spindle Tendon Sensory fiber Golgi tendon organ Efferent (motor) fiber to extrafusal muscle fibers Extrafusal muscle fiber Intrafusal muscle fibers
- 14. Figure 13.16a, b (a) Unstretched muscle. Action potentials (APs) are generated at a constant rate in the associated sensory (la) fiber. Muscle spindle Intrafusal muscle fiber Primary sensory (la) nerve fiber Extrafusal muscle fiber Time (b) Stretched muscle. Stretching activates the muscle spindle, increasing the rate of APs. Time
- 15. MAGDI AWAD SASI 15
- 16. Muscle spindles monitor muscle length and prevent overstretching MAGDI AWAD SASI 16 Figure 13-4a Sensory neuron endings Intrafusal fibers of muscle spindle (a) Spindles are firing even when muscle is relaxed. Spinal cord Sensory neuron Alpha motor neuron Extrafusal muscle fibers at resting length Sensory neuron is tonically active. Spinal cord integrates function. Alpha motor neurons to extrafusal fibers receive tonic input from muscle spindles. Extrafusal fibers maintain a certain level of tension even at rest. 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5
- 17. MAGDI AWAD SASI 17 1-Keep CNS informed about the muscle length and the rate of velocity of change in the muscle length and provide information about position (proprioception) 2- Send either: positive and negative signals regarding the stretching of the muscles. 3- Maintain muscle length against rupture
- 18. MAGDI AWAD SASI 18 1/ Annulo-spiral (primary ending), supplies the nuclear bag fiber(mainly) and the nuclear chain fibers Type I a nerve fibers—A alpha Responsible for the rapid and dynamic response (velocity of change in the muscle length) Example: tendon jerk Very high velocity a 70 to 120 m/s
- 19. MAGDI AWAD SASI 19 2/ Flower spray (secondary ending), supplies the nuclear chain fibers only Responsible for the sustained and static response Type II nerve fibers- A beta Example: muscle tone -The brain receives inputs about the state of the skeletal muscles enabling it to coordinate the muscular movements and allow conscious awareness by sensory neurons *by sending collaterals to the brain*.
- 21. MAGDI AWAD SASI 21 Efferent: 1/ Alpha motor fiber s, supplies extrafusal muscle fibers (70%) 2/ Gamma motor fibers , supplies intrafusal muscle fibers *the peripheral contractile parts* (30)% - Gamma motor fiber has 2 types: 1- Dynamic gamma (plate ending), supplies nuclear bag (enhances the dynamic response) 2- Static gamma (trail ending), supplies nuclear chain (enhances the static response) -In general, the gamma motor fibers increase the sensitivity of the muscle spindles by contraction of the peripheral part of the intrafusal fiber
- 22. Present in the tendons. Thick myelinated Ib afferent nerve fibers –A alpha . Stimulated by passive stretch and active contraction of the muscle, slowly adapting. Tension receptors, not under nerve control. Axons from Golgi tendon organs inhibit neurons in the spinal cord that synapse with the a motor neurons that innervate the same muscle. Protects muscle from large forces. Maintains steady level of muscle force MAGDI AWAD SASI 22
- 23. MAGDI AWAD SASI 23
- 24. MAGDI AWAD SASI 24 Site: γ-MNs are thin myelinated motors neurons Represent 30% of AHCs. The axons (about 4 u) Supply the peripheral parts of intrafusal ms fibers. Types: There are 2 types of γ-MNs 1. Dynamic or d- γ-MNs→ supply nuclear bag ms fibers. 2. Static or s- γ-MNs→ supply nuclear chain ms fibers.
- 25. MAGDI AWAD SASI 25
- 26. MAGDI AWAD SASI 26 Function: Stimulation leads to stretch of the central parts of the muscle spindles ,which increase the sensitivity of the muscles to stretch and may result in reflex muscle contraction. Control : The activity is controlled by signals discharged from : 1. Several supraspinal areas – 2. The skin ---noxios stimulation 3. The skeletal muscles
- 27. MAGDI AWAD SASI 27 They adjust ms spindle sensitivity ↑ γ-MNs cause contraction of the peripheral parts of intrafusal fibers→ stretch of central parts of ms spindle → ↑es the sensitivity of the ms spindle to stretch Vice versa.
- 28. B) Load reflex (coactivation of alpha and gamma MNs)
- 29. Muscle tone is the general state of contraction of the muscles. If you have low muscle tone the muscles are flaccid (relaxed). If high muscle tone, the muscle is contracted. Muscle tone changes over time, e.g. during a step ◦ Muscle tone is low as we pick up our leg. ◦ Muscle tone is high on all leg muscles as we prepare to put it back down and it has to support our weight MAGDI AWAD SASI 29
- 30. MAGDI AWAD SASI 30 ❖ Type: monosynaptic (sensory neuron synapse with motor neuron) and deep ❖ Stimulus: Stretching of the muscles ❖ Response: Contraction of the muscles ❖ Aim of the response: to prevent tearing of the muscles by activating the extrafusal muscle fibers ❖ Receptor: Muscle spindle (located deep in the muscles): which consists of 3-12 intrafusal fibers.
- 31. Stimulus: Stretch of the muscle Afferents: Fast conducting Ia afferents Receptors: Muscle spindles (intrafusal fibers) Center: Spinal cord/Brain stem Efferents: A- alpha fibers Effector structure: Extrafusal (regular contractile) fibers of the muscle that is stretched Response: Contraction of the muscle Example: Knee jerk
- 32. Functions: 1. Maintenance of the erect posture 2. Helps both the venous and lymph flow –LL 3. The abdominal muscles prevents visceral ptosis. 4. It is an important source of heat production ,so it markedly increases on exposure to cold. MAGDI AWAD SASI 32
- 33. Distribution: Present In all skeletal muscles, especially antigravity muscles B/C they are subjected to more stretch by the force of gravity. They include: 1. Lower limb extensors 2. Upper limbs flexors 3. Back , back of the neck muscles. 4. The elevators of lower jaw 5. The anterior abdominal wall muscles. MAGDI AWAD SASI 33
- 34. Stretch reflex MAGDI AWAD SASI 34
- 35. SR is normally subjected to facilitation and inhibition by signals discharged via the descending tracts from any supraspinal centers which affect the activity of both alpha and gamma motor neurons MAGDI AWAD SASI 35
- 36. 1. The primary cortical motor area –4—alpha motor neuron 2. The neocerebellum 3. F.Pontine reticualr formation: 4. The lateral vestibular nucleus -: In medulla , activate the PontineRF. Tract---- vestibulospinal MAGDI AWAD SASI 36
- 37. Certain cortical areas –premotor 6& 4---supressor area The inhibitory (medullary)reticular formation: No intrinsic activity ,medulla It is activited by signals from other inhibitory areas It reach the spinal cord via the lateral medullary reticulospinal tract where they inhibit mainly the gamma motor neurons The red nucleus—mid brain Discharging direct I signals to the alpha motor neuron The lenticular (lentiform)nucleus of basal ganglia Inhibits the medullary RF MAGDI AWAD SASI 37
- 38. For skeletal muscles to perform normally: I. The Golgi tendon organs (proprioceptors) must constantly inform the brain as to the state of of the muscle. II. Stretch reflexes initiated by muscle spindles must maintain healthy muscle tone. MAGDI AWAD SASI 38
- 39. MAGDI AWAD SASI 39Figure 5.2
- 40. STATICDYNAMIC Maintained stretch -- gravity Sudden stretch – tendon tapping Stimulus Type II fibersType I a fibersAfferent Maintained smooth contraction Brisk contraction &rapid relaxation Response Production of muscle tone Has clinical significance Function Slowly adaptingRapidly adaptingAdaptation Slowly fatiguedRapidly fatiguedFatiguability Not enhanced by itJendrassiks maneuverenhancement the gamma-s & beta-s nerve fibers the gamma d&beta-d nerve fibers enhanced MAGDI AWAD SASI 40
- 41. It is a reflex relaxation of a muscle in response to excessive stretch. It is an inhibitory reflex . Response ---muscle relaxation It is a protective reaction against tearing of the muscle or avulsion of the tendon from its bony attachment. How? Golgi tendon organs Activity MAGDI AWAD SASI 41
- 42. MAGDI AWAD SASI 42
- 43. 1. Spinal deep reflex, servo assist, damping effect 2. It is monosynaptic 3. Reaction time is short– 19-24ms 4. Highly localized 5. No after discharge 6. Controlled by supra-spinal center 7. The contraction is jerky in dynamic type but is smooth in the static type B/C the spinal motor neurons discharge at a low frequency and alternate their activity. 8. The static type is present in all muscles –antigravity. MAGDI AWAD SASI 43
