This document provides an outline and overview of strategic management concepts related to strategy analysis and choice. It discusses:
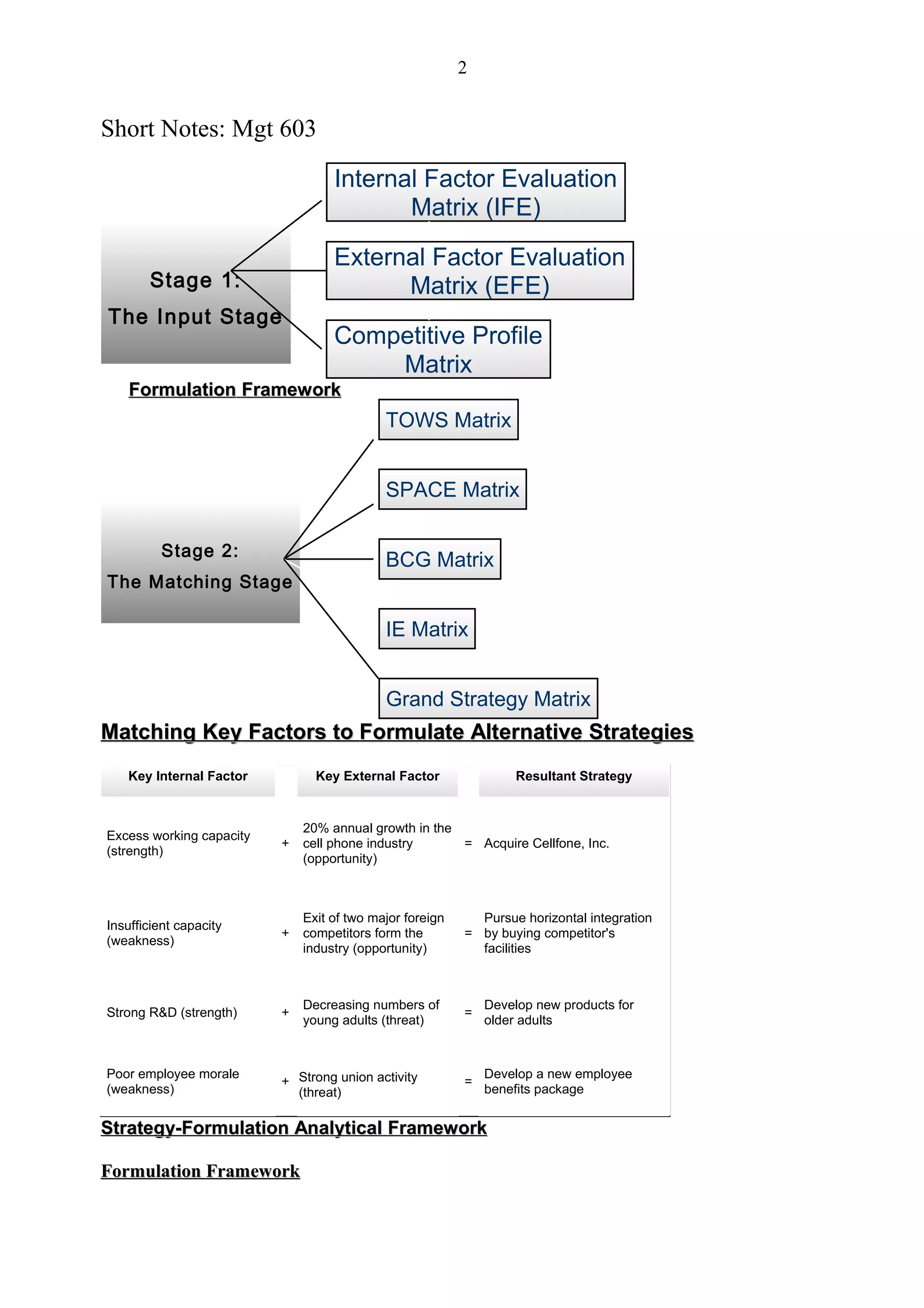
1) Three key stages in the strategy formulation framework - the input, matching, and decision stages. Various analytical tools are used at each stage like IFE, EFE, TOWS matrices.
2) The TOWS matrix as a tool to match internal strengths and weaknesses to external opportunities and threats to generate alternative strategies. Four types of strategies - SO, WO, ST, WT - can be developed.
3) The SPACE matrix, another strategic planning tool that evaluates strategic position based on internal financial strength and competitive advantage and external environmental stability and industry strength to determine appropriate strategies.


![4
Short Notes: Mgt 603
– List the firm’s key internal weaknesses
TOWS Matrix
Developing the TOWS Matrix
• Match internal strengths with external opportunities and record the resultant SO Strategies
• Match internal weaknesses with external opportunities and record the resultant WO
Strategies
• Match internal strengths with external threats and record the resultant ST Strategies
• Match internal weaknesses with external threats and record the resultant WT Strategies
Leave Blank Strengths-S Weaknesses-W
List Strengths List Weaknesses
Opportunities-O SO Strategies WO Strategies
List Opportunities Use strengths to take Overcome weaknesses
advantage of opportunities by taking advantage of
opportunities
Threats-T ST Strategies WT Strategies
List Threats Use strengths to avoid Minimize weaknesses
threats and avoid threats
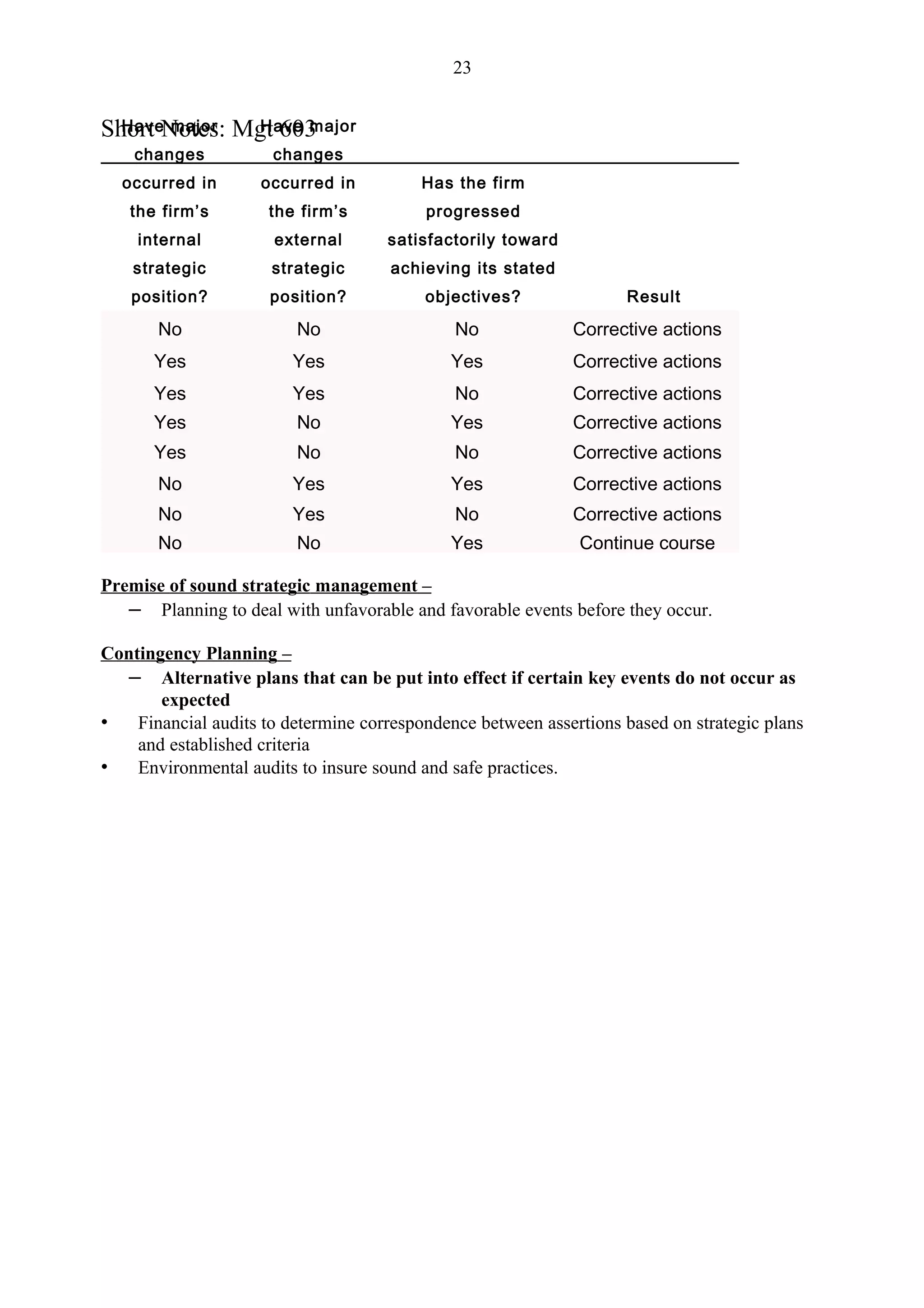
Lecture No, 25-26
Formulation Framework
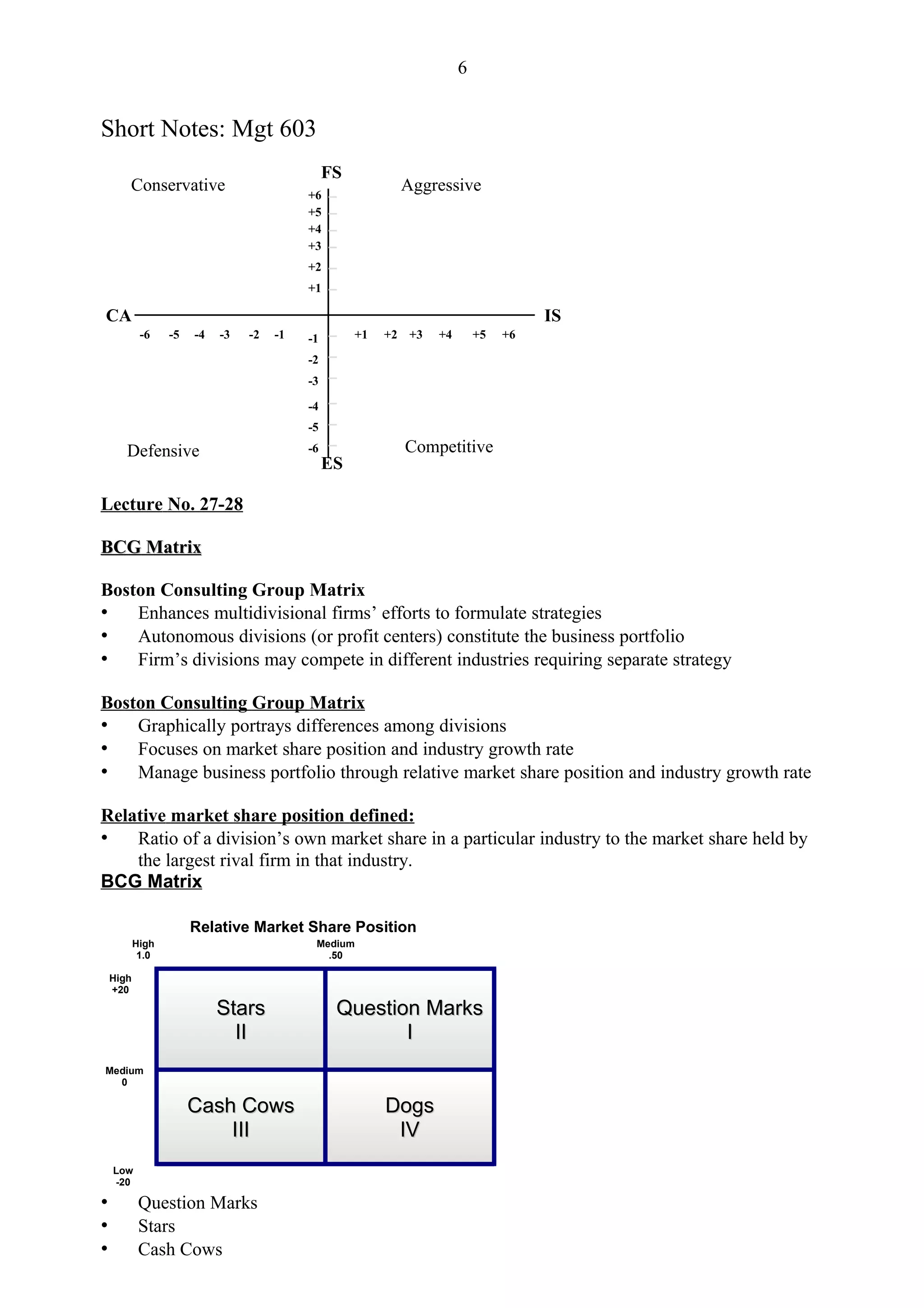
SPACE Matrix
Strategic Position and Action Evaluation Matrix
Four quadrant framework
Determines appropriate strategies
Aggressive
Conservative
Defensive
Competitive
Two Internal Dimensions
Financial Strength [FS]
Competitive Advantage [CA]
Two External Dimensions
Environmental Stability [ES]
Industry Strength [IS]
Overall Strategic position determined by:
– Financial Strength [FS]
– Competitive Advantage [CA]
– Environmental Stability [ES]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mgt603shortnotes-120911144945-phpapp01/75/Strategic-short-notes-4-2048.jpg)
![5
Short Notes: Mgt 603
– Industry Strength [IS]
Developing the SPACE Matrix:
• EFE Matrix
• IFE Matrix
• Financial Strength
• Competitive Advantage
• Environmental Stability
• Industry Strength
• Select variables to define FS, CA, ES, & IS
• Assign numerical ranking from +1 (worst) to +6 (best) for FS and IS; Assign numerical
ranking from –1 (best) to –6 (worst) for ES and CA.
• Compute average score for FS, CA, ES, & IS
• Plot the average scores on the Matrix
• Add the two scores on the x-axis and plot point on X. Add the scores on the y-axis and plot
Y. Plot the intersection of the new xy point.
• Draw a directional vector from origin through the new intersection point.
• SPACE Factors
Internal Strategic Position External Strategic Position
Financial Strength (FS) Environmental Stability (ES)
Return on investment Technological changes
Leverage Rate of inflation
Liquidity Demand variability
Working capital Price range of competing products
Cash flow Barriers to entry
Ease of exit from market Competitive pressure
Risk involved in business Price elasticity of demand
Internal Strategic Position External Strategic Position
Competitive Advantage CA Industry Strength (IS)
Market share Growth potential
Product quality Profit potential
Product life cycle Financial stability
Customer loyalty Technological know-how
Competition’s capacity utilization Resource utilization
Technological know-how Capital intensify
Control over suppliers & distributors Ease of entry into market
Productivity, capacity utilization
SPACE Matrix](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mgt603shortnotes-120911144945-phpapp01/75/Strategic-short-notes-5-2048.jpg)