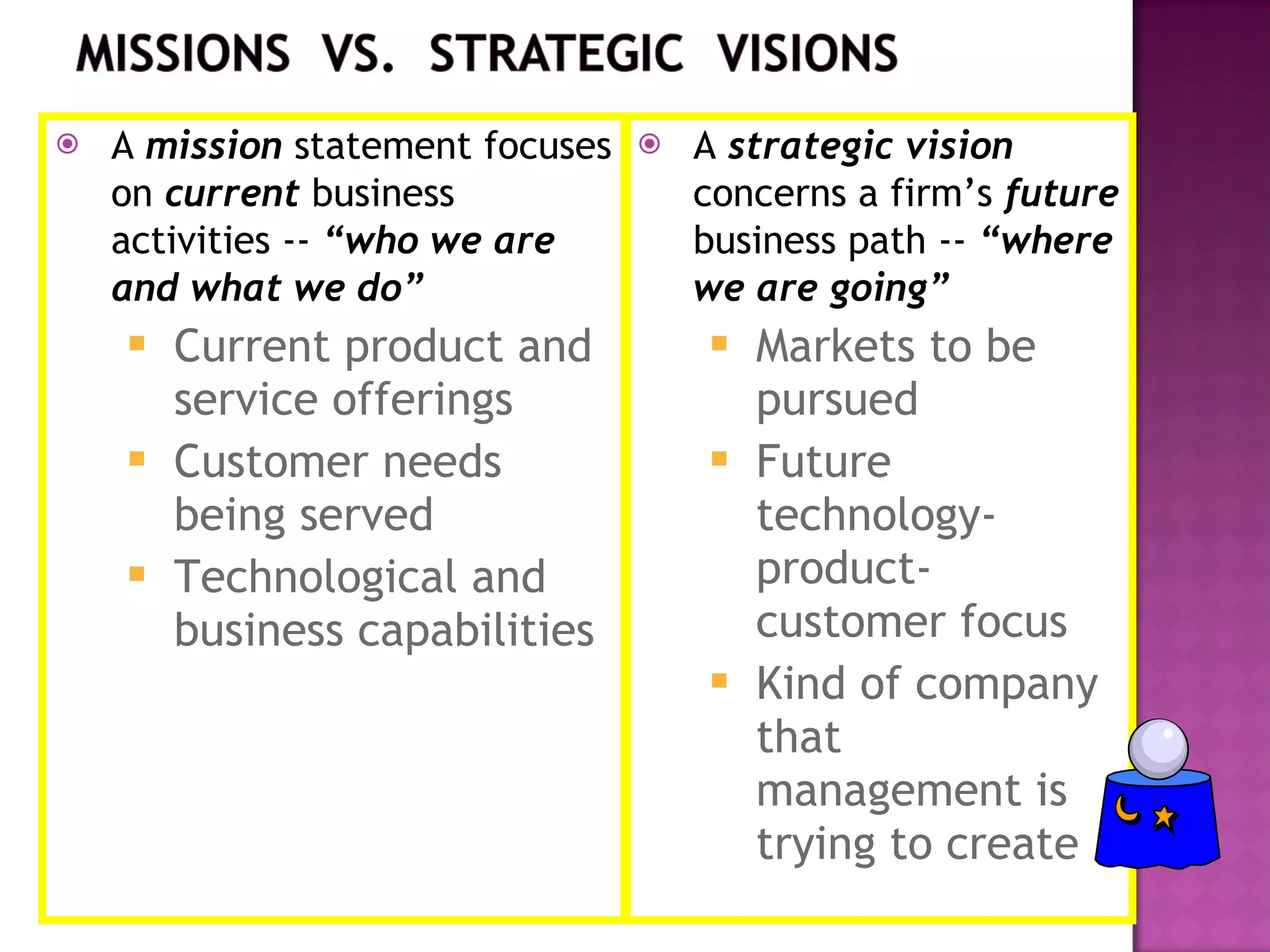
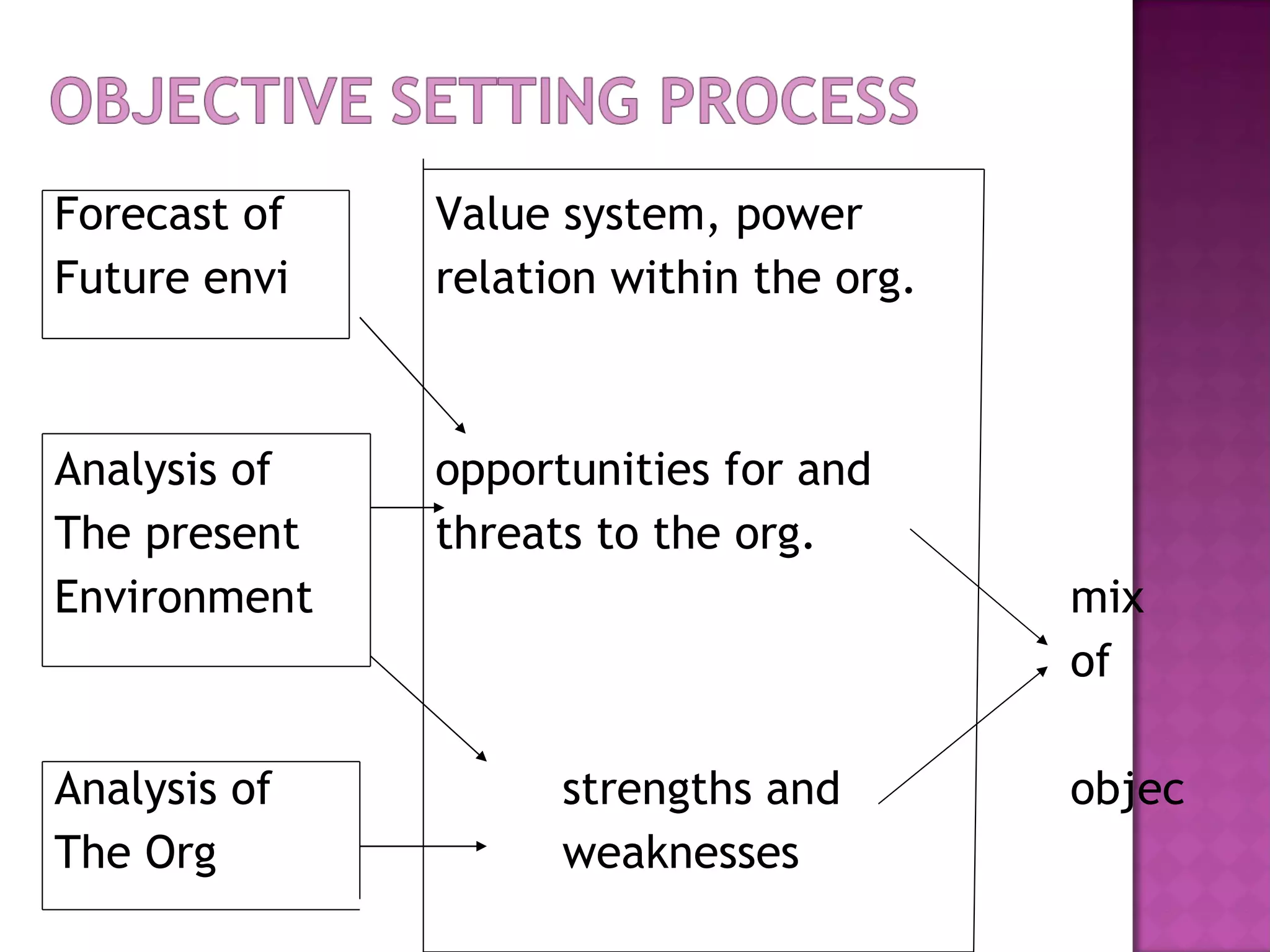
The document discusses the key concepts of vision, mission, goals and strategies for organizations. It provides definitions and explanations for each concept: A vision describes an organization's aspirations and desired future state without specifying how to achieve it. A mission statement expresses the overriding purpose and reason for an organization's existence. Goals are qualitative targets an organization aims to achieve, and should be consistent, feasible, understandable and agreed upon. Objectives are specific, measurable targets with deadlines that help achieve goals and missions. Strategies are the plans and approaches used to pursue objectives and achieve the vision.