The document outlines several strategic planning and analysis tools including:
1. Developing alternative strategies and evaluating their advantages, disadvantages, and costs/benefits.
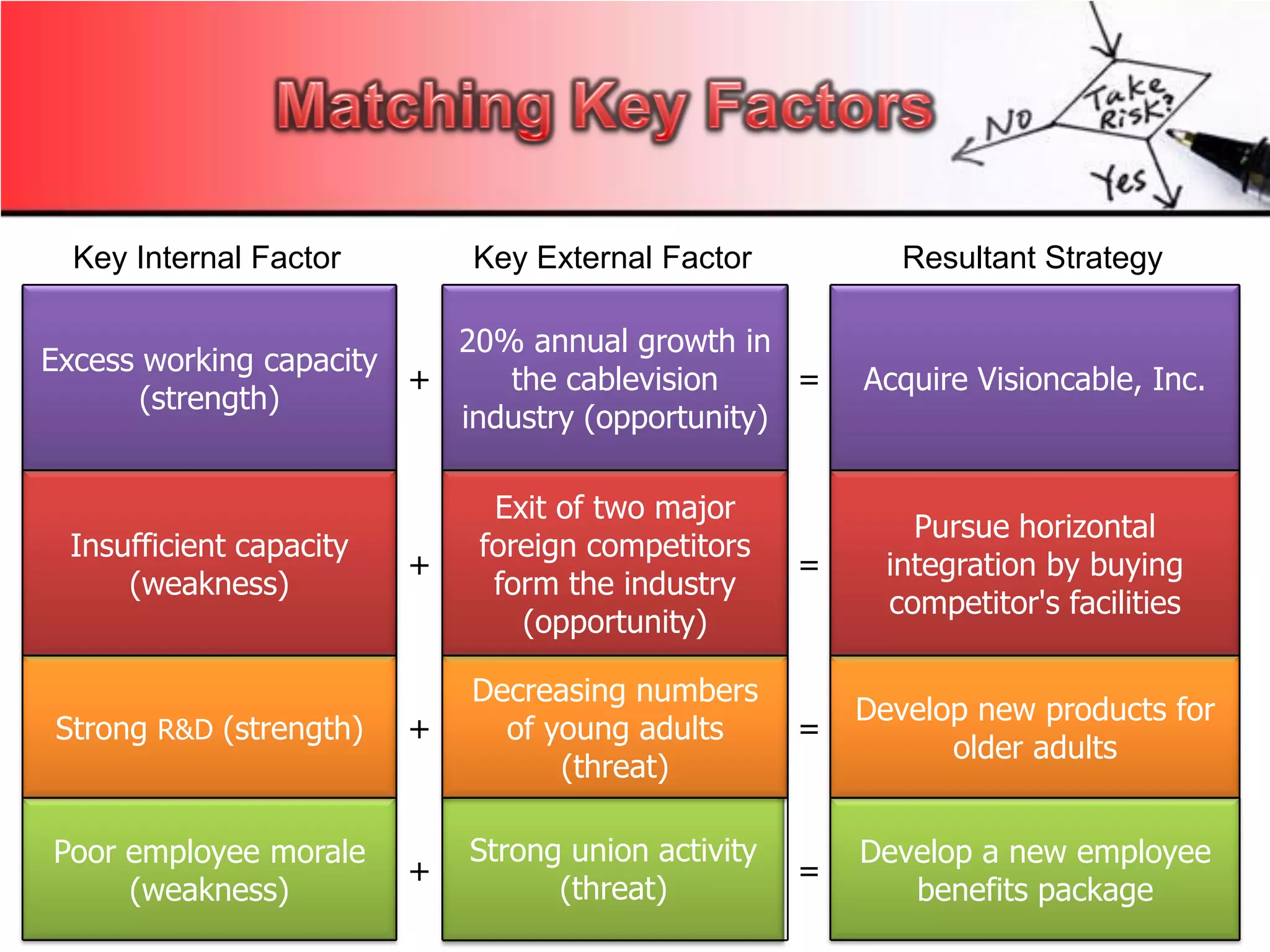
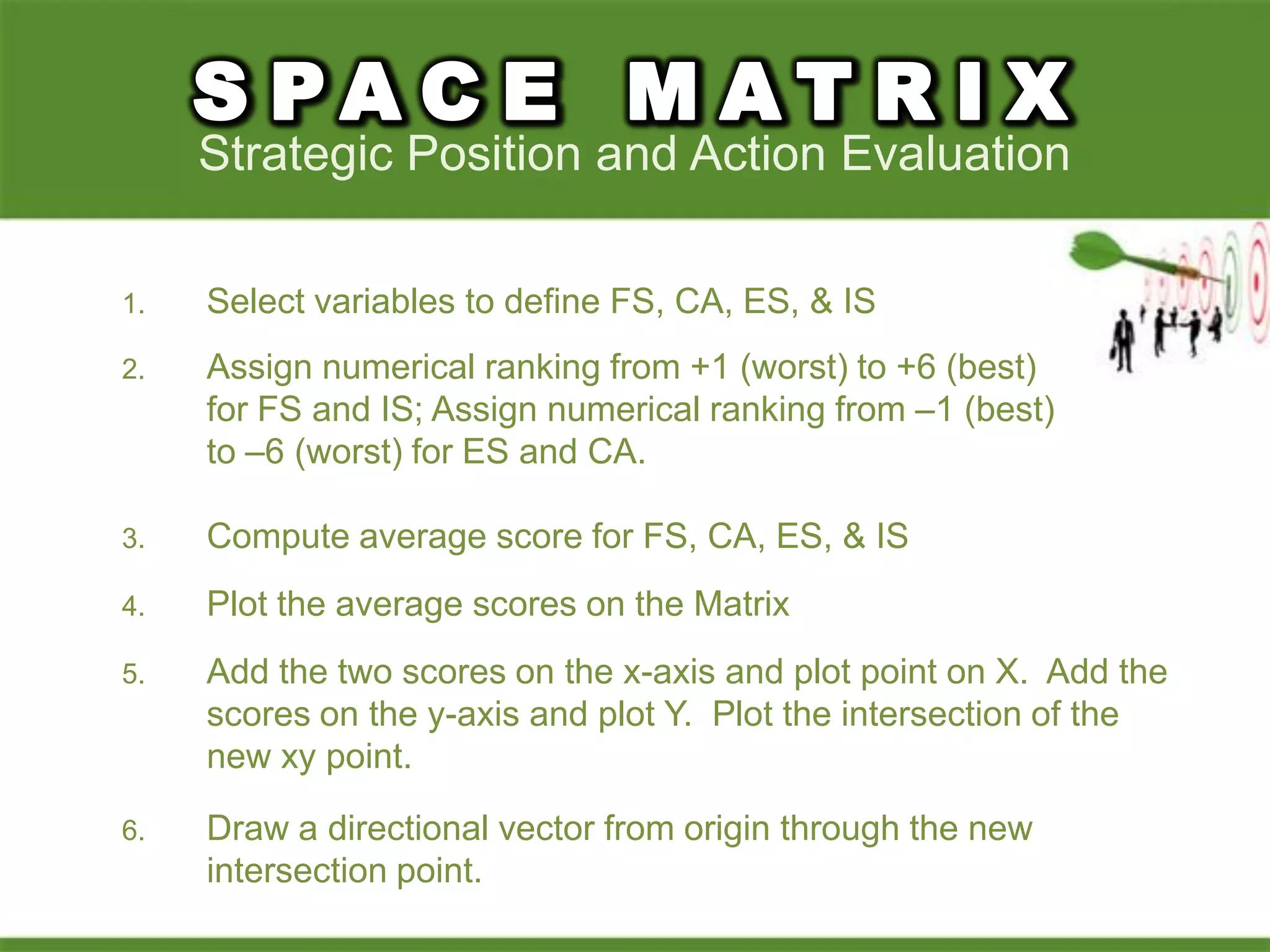
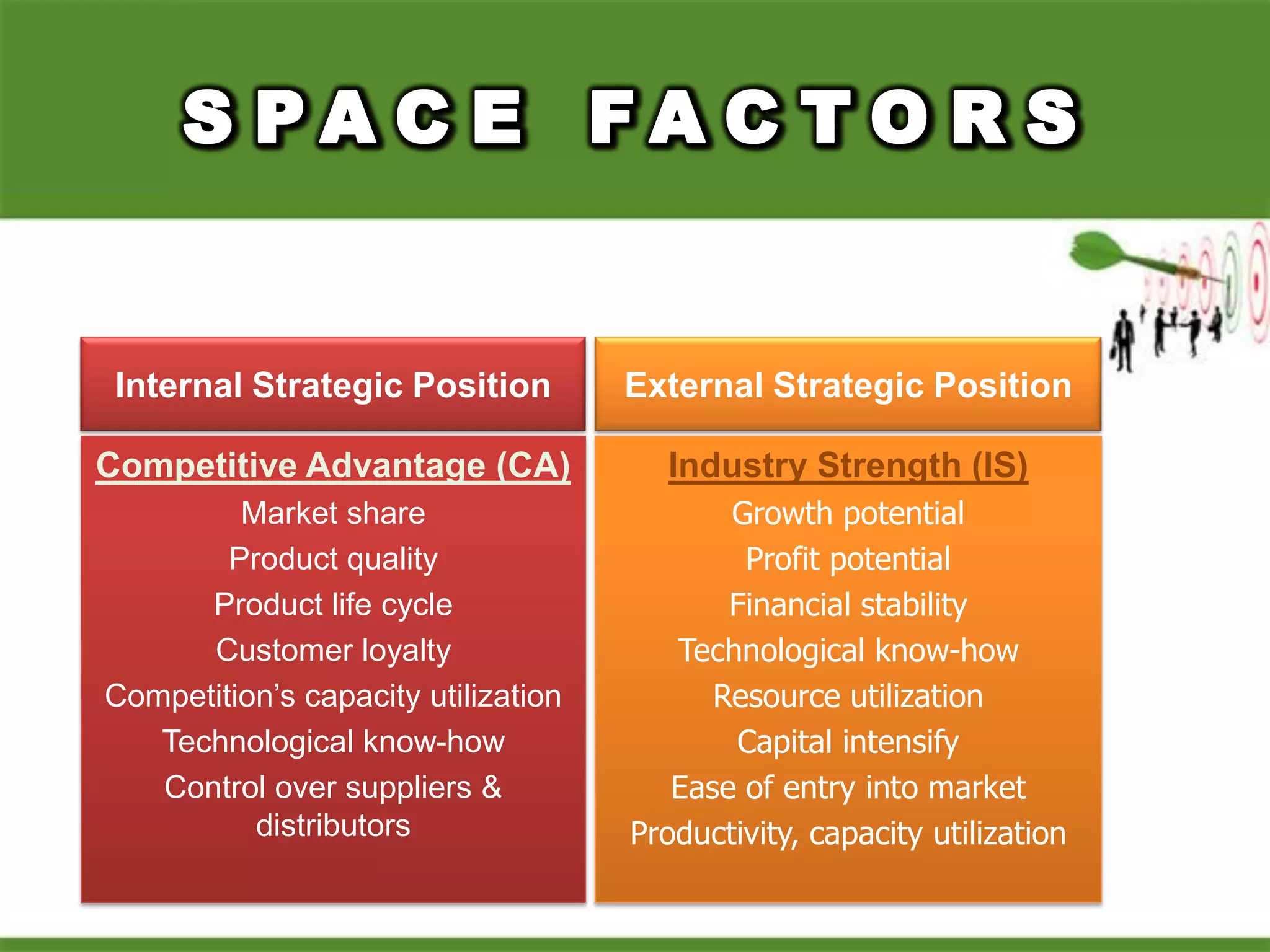
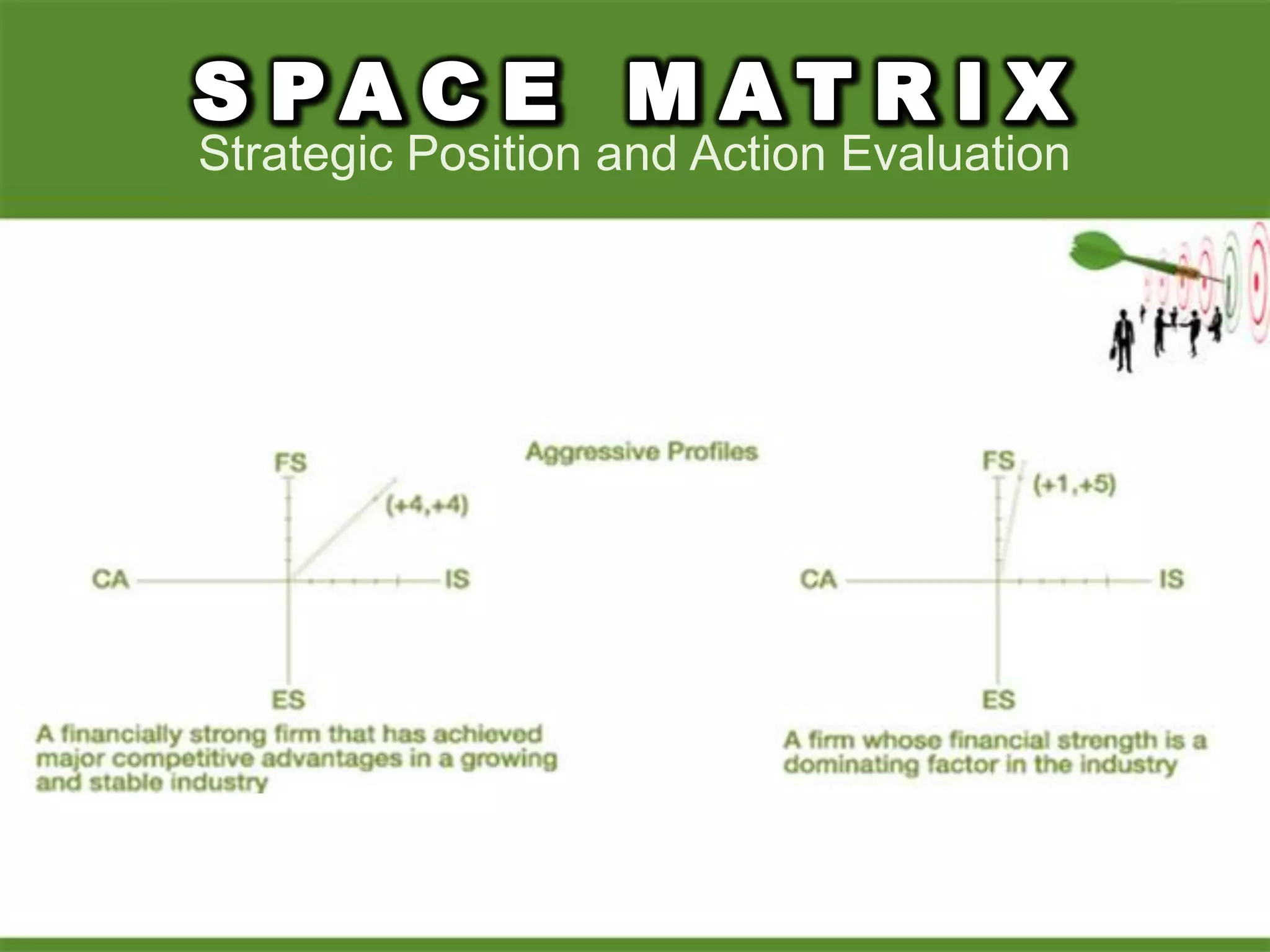
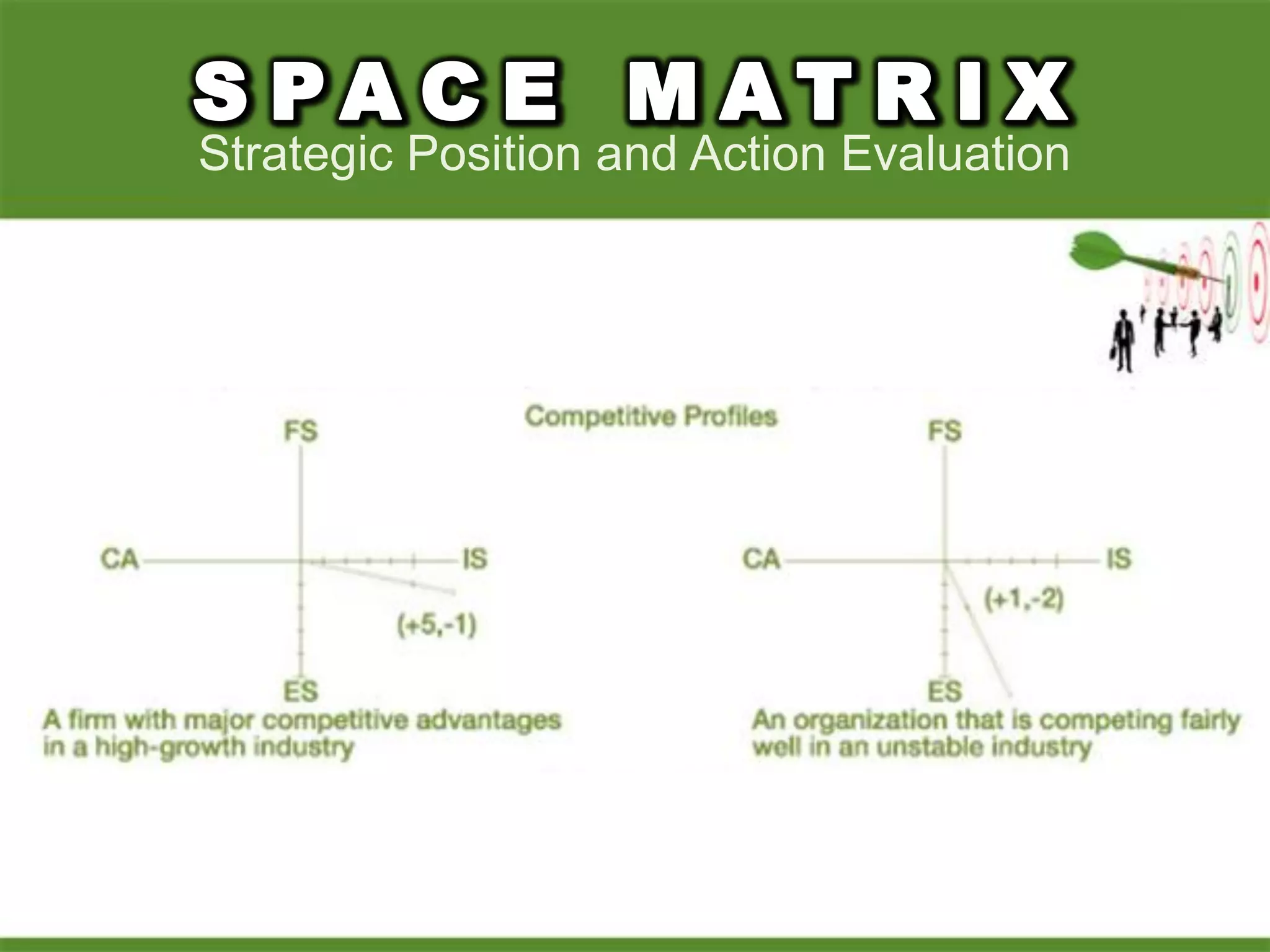
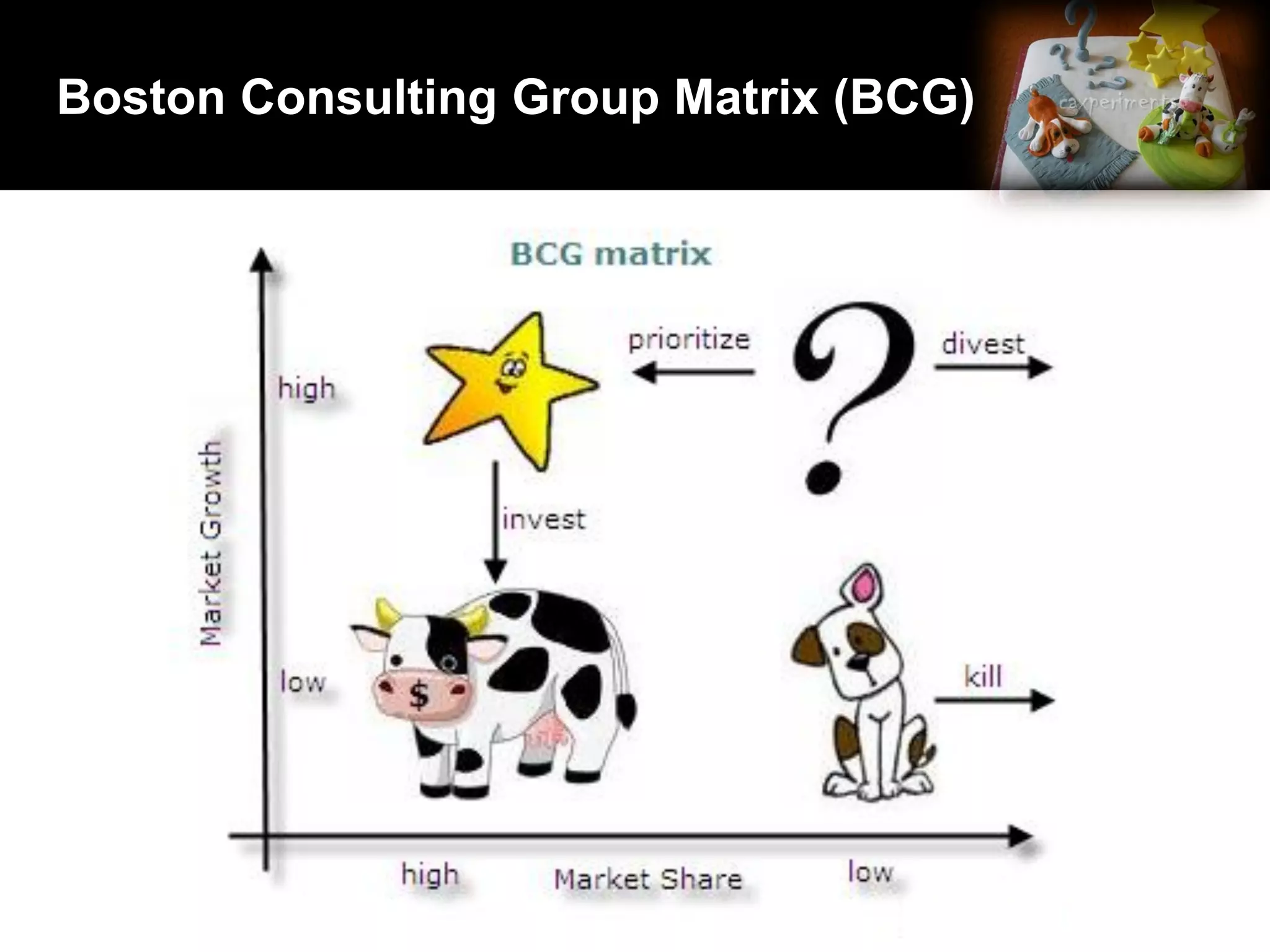
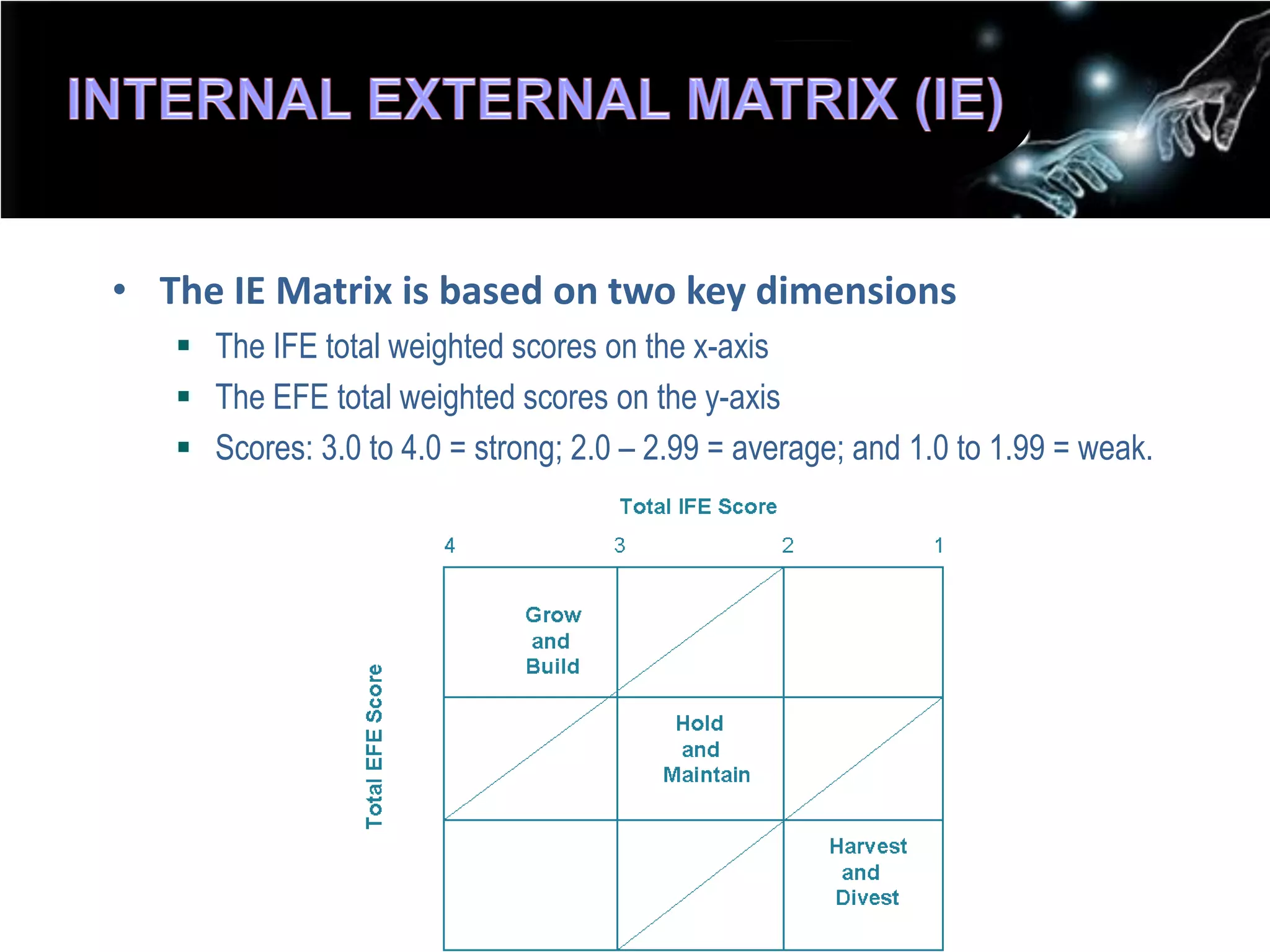
2. Using matrices like TOWS, SPACE, BCG, and IE to match internal strengths/weaknesses with external opportunities/threats and determine appropriate strategies.
3. Evaluating strategies using the Grand Strategy Matrix based on competitive position and market growth to identify strategies like market penetration, product development, divestment.