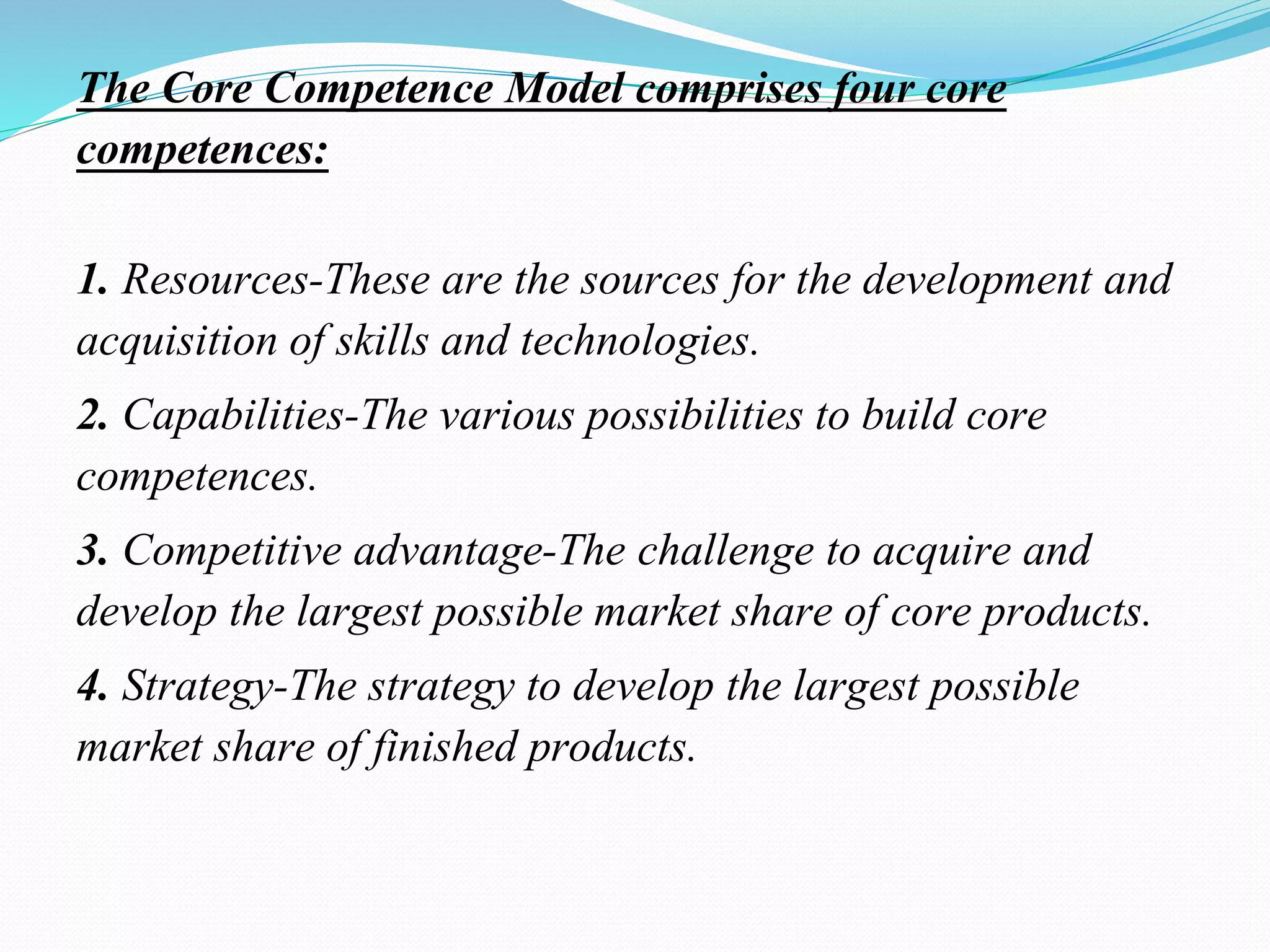
Core competencies are a firm's unique skills and abilities that distinguish it in the marketplace. They fulfill three criteria: provide access to markets, contribute significantly to customer benefits, and are difficult for competitors to imitate. The document discusses how core competencies facilitate strategy, innovation, and competitive advantage. It provides examples of companies like Apple, 3M, and Starbucks that have differentiated themselves through core competencies. The core competence model outlines how resources, capabilities, competitive advantage, and strategy are related. Management must identify and build upon a company's core competencies to develop successful long-term strategies.