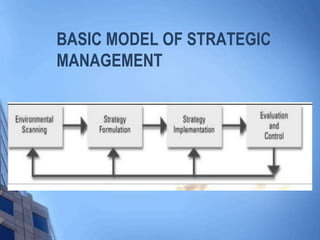
This document provides an overview of strategic management. It discusses key concepts like business policy, the nature and importance of business policy, limitations of business policy, and the process of formulating business policy. It also describes strategic management in terms of its beginning with a mission statement, preparation of a business portfolio, and periodic re-evaluation. The basic model of strategic management involves environmental scanning, strategy formulation and implementation, evaluation and control, and feedback. Vision, mission, objectives, strategic decision making, global strategic management, the impacts and barriers of globalization are also summarized.