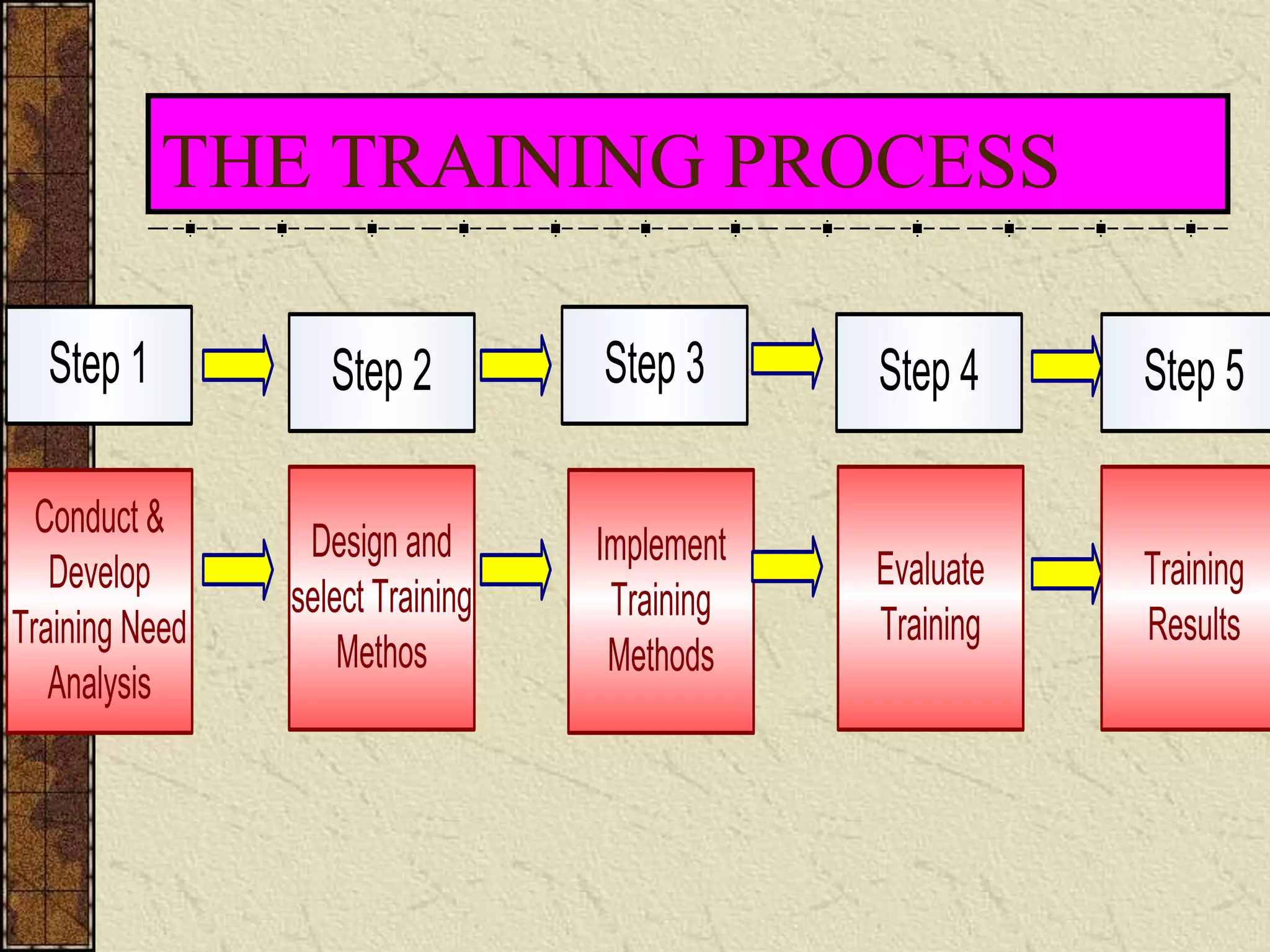
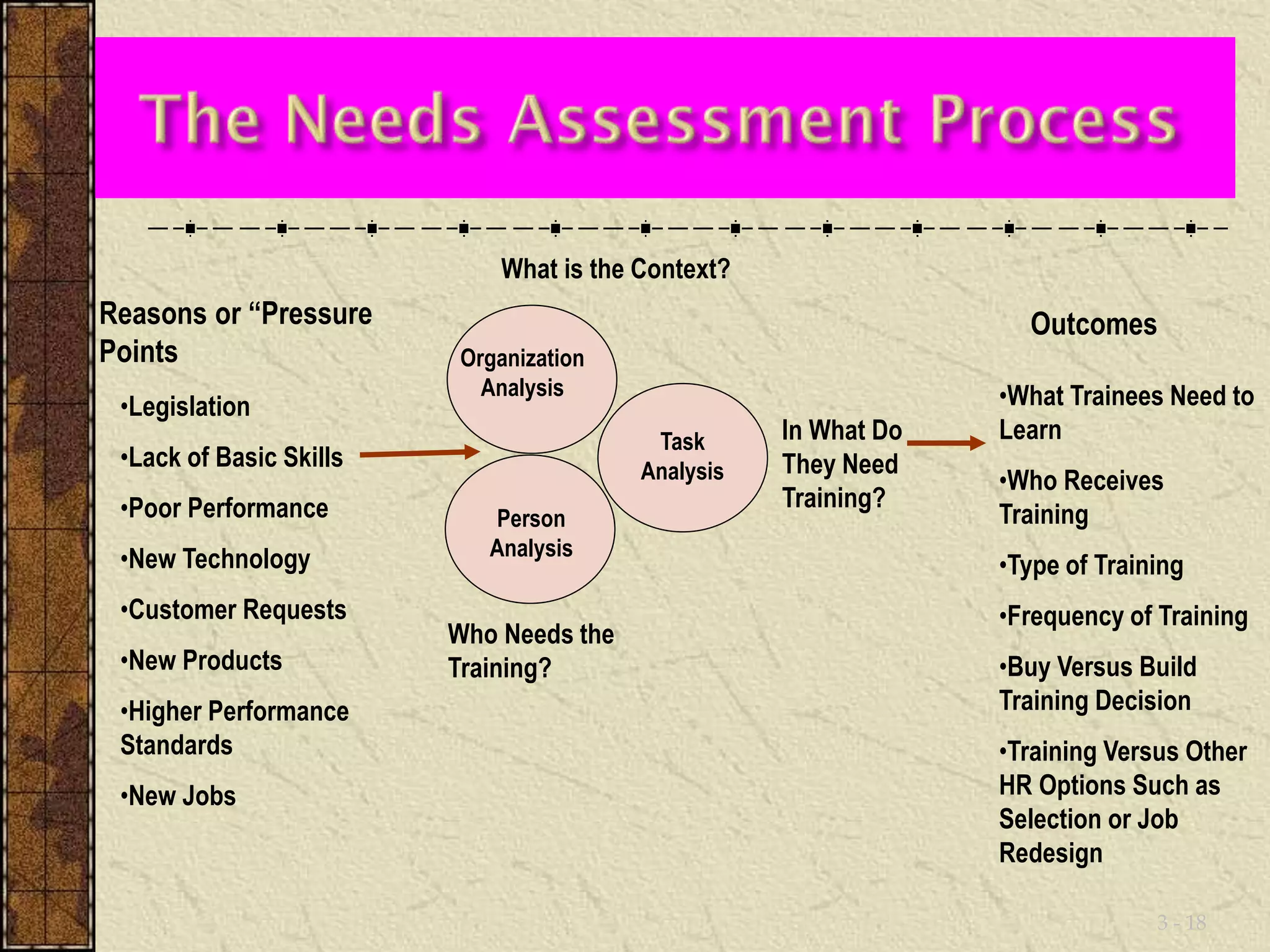
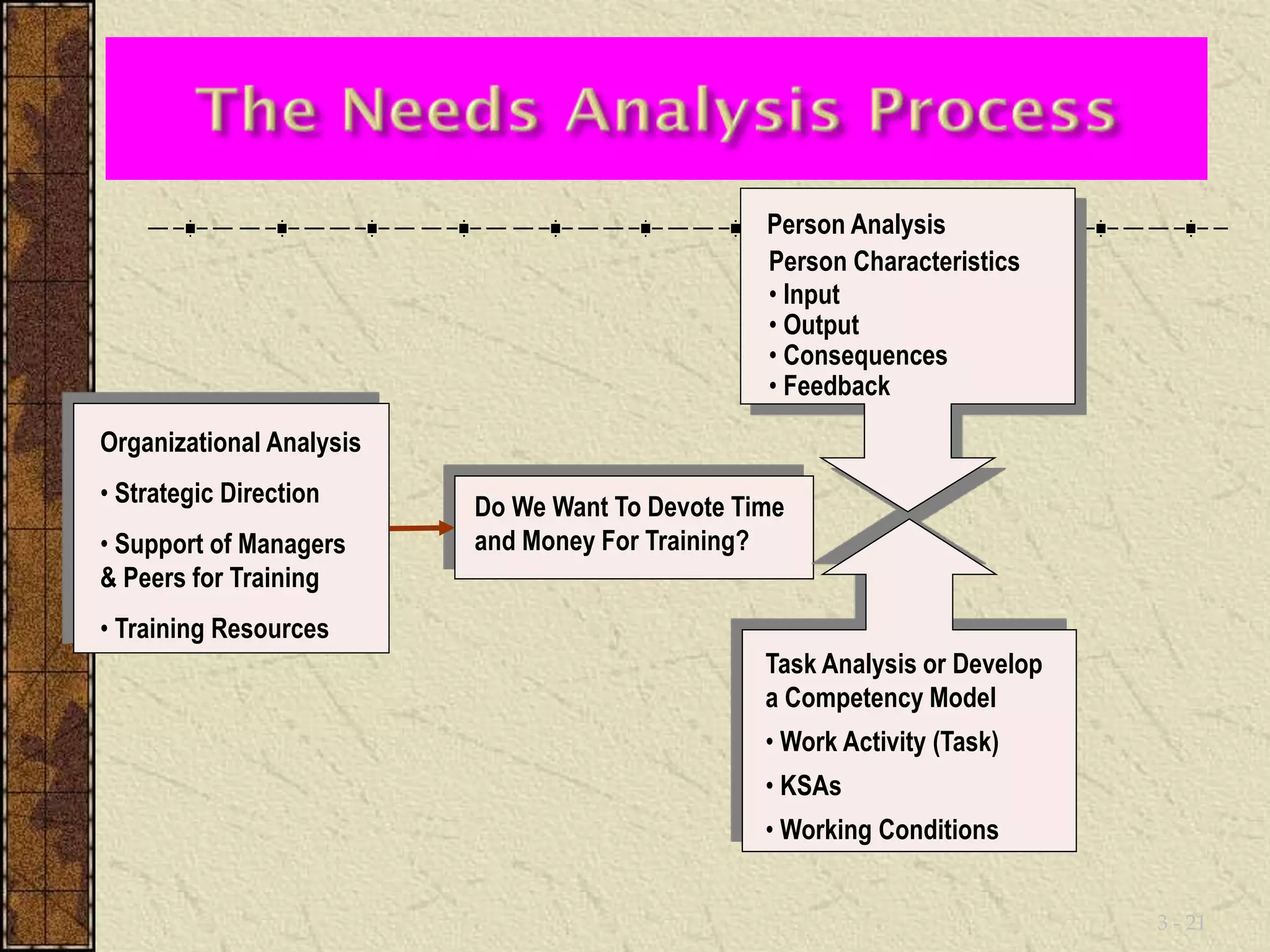
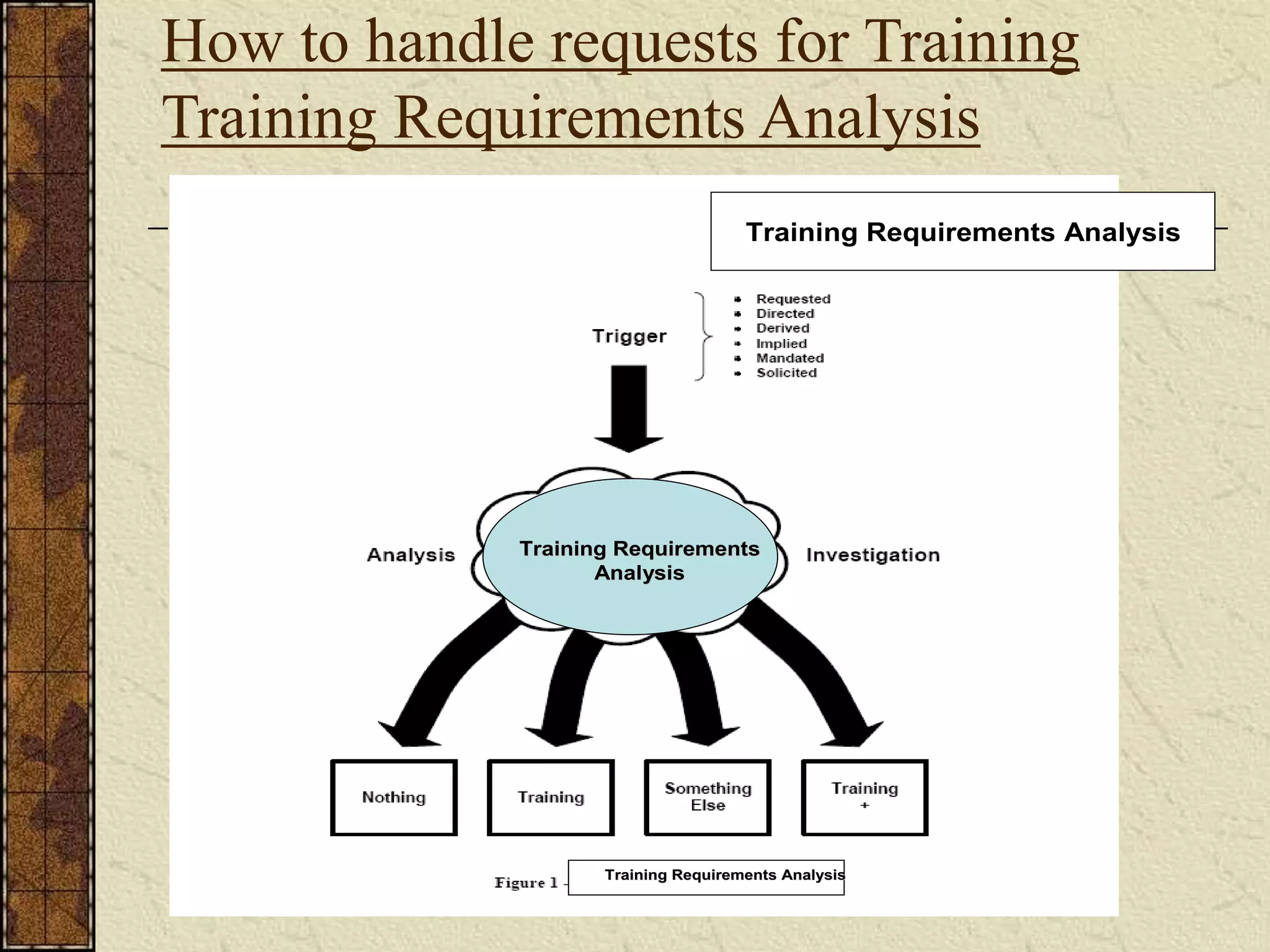
This document discusses training and development. It defines training as seeking to improve an individual's ability to perform their job by changing their skills, attitudes, and knowledge. Development focuses more on long-term personal growth and career advancement. The training process involves analyzing needs, setting objectives, designing training methods, implementing training, and evaluating results. Determining training needs requires analyzing the organization, tasks, and individuals to identify performance gaps that training could address.