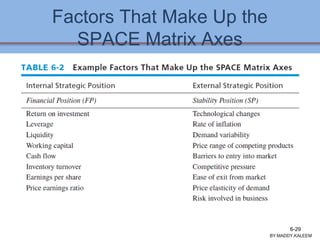
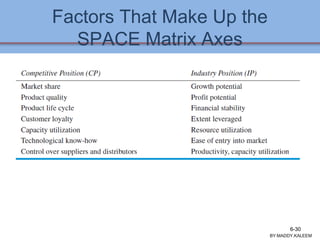
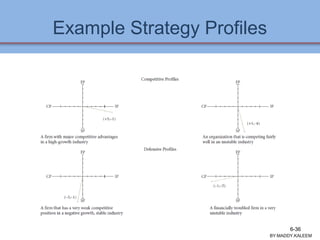
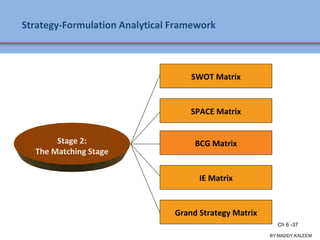
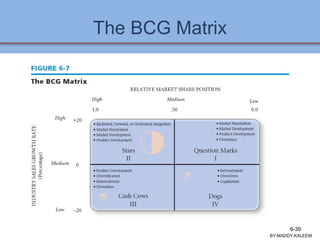
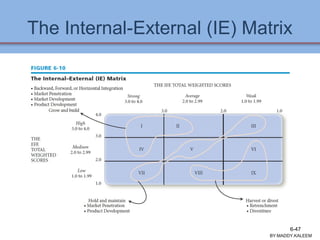
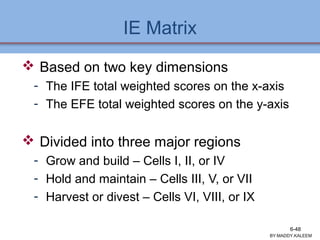
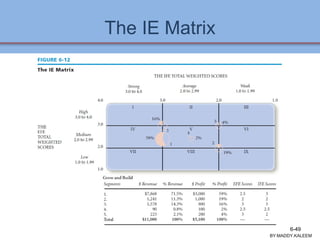
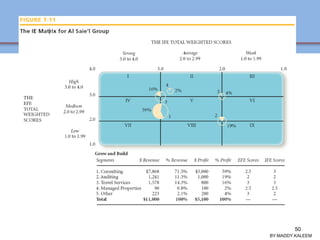
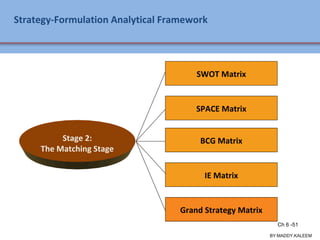
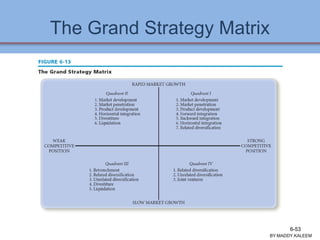
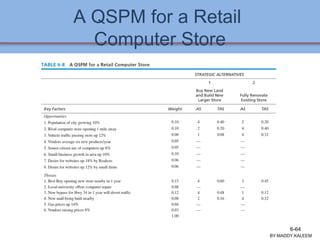
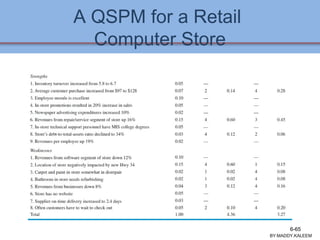
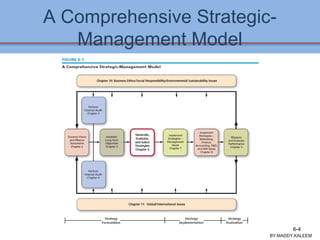
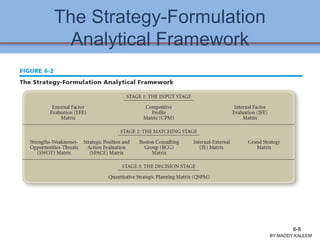
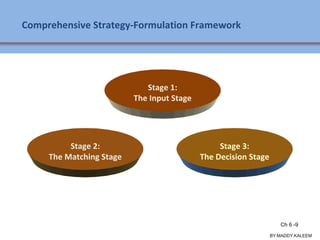
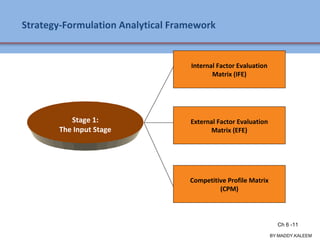
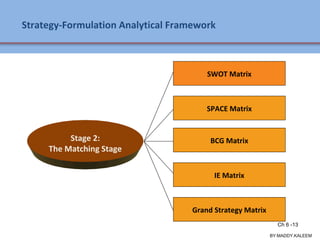
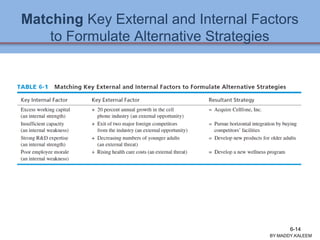
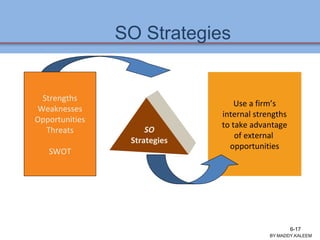
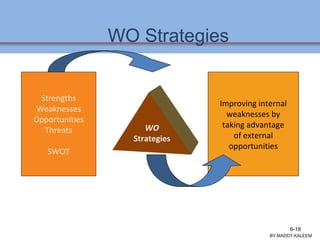
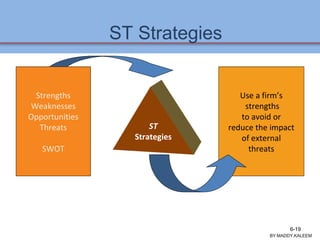
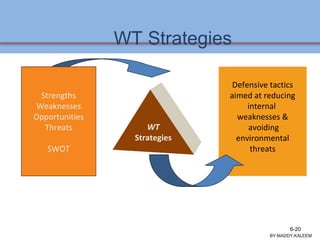
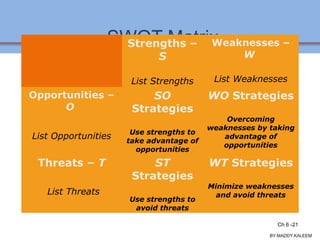
The document discusses strategic analysis and choice, providing a three-stage framework for choosing among alternative strategies. It describes various analytical tools that can be used in each stage: the input stage uses SWOT, IFE, and CPM matrices; the matching stage uses SWOT, SPACE, BCG, IE, and grand strategy matrices; and the decision stage uses the QSPM matrix. The tools help generate alternative strategies, evaluate them objectively, and select the most attractive strategies to pursue.












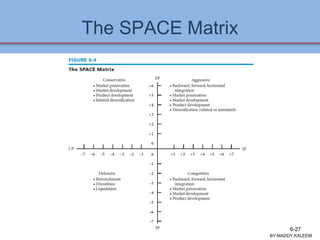
![The Strategic Position and Action
Evaluation (SPACE) Matrix
Two internal dimensions (financial
position [FP] and competitive position
[CP])
Two external dimensions (stability
position [SP] and industry position [IP])
Most important determinants of an
organization’s overall strategic position
BY:MADDY.KALEEM
6-28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter06-strategyanalysisandchoice-180718193109/85/Strategic-Management-Concepts-Cases-Chapter-06-28-320.jpg)