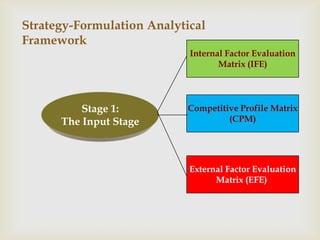
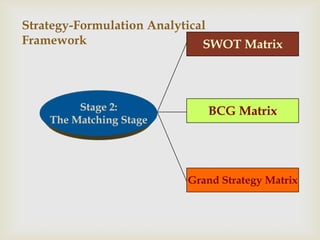
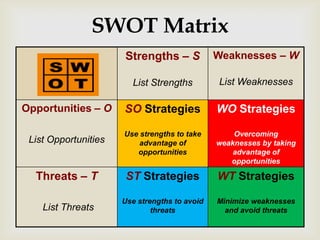
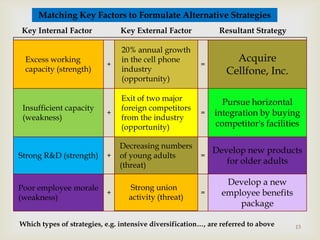
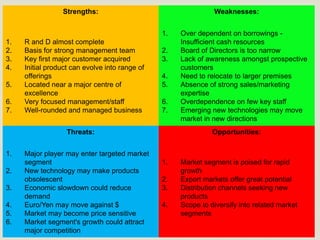
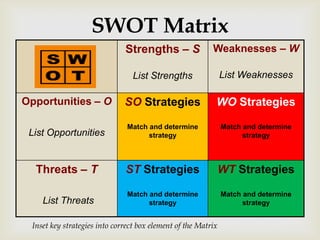
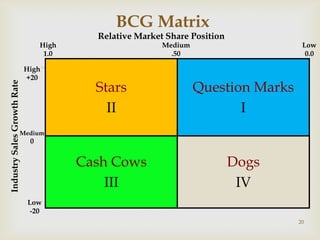
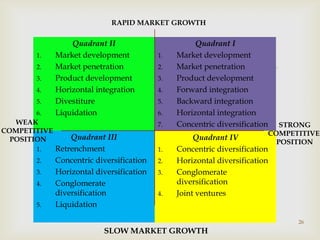
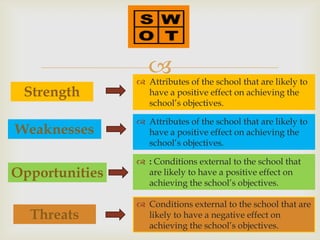
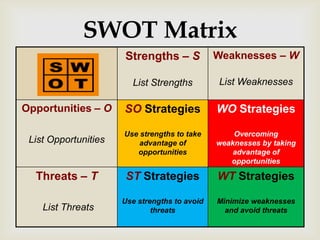
This document discusses strategic analysis and choice frameworks. It introduces concepts to help strategists generate alternatives, evaluate them, and choose a course of action. It describes the nature of strategy analysis and choice, including establishing objectives, generating alternatives, and selecting strategies. Analytical frameworks covered include the internal-external factor matrices, SWOT analysis, BCG matrix, and matching key internal and external factors to formulate alternative strategies. Limitations of the SWOT matrix are also noted. The overall purpose is to provide strategists with tools and concepts to aid in strategic decision making.