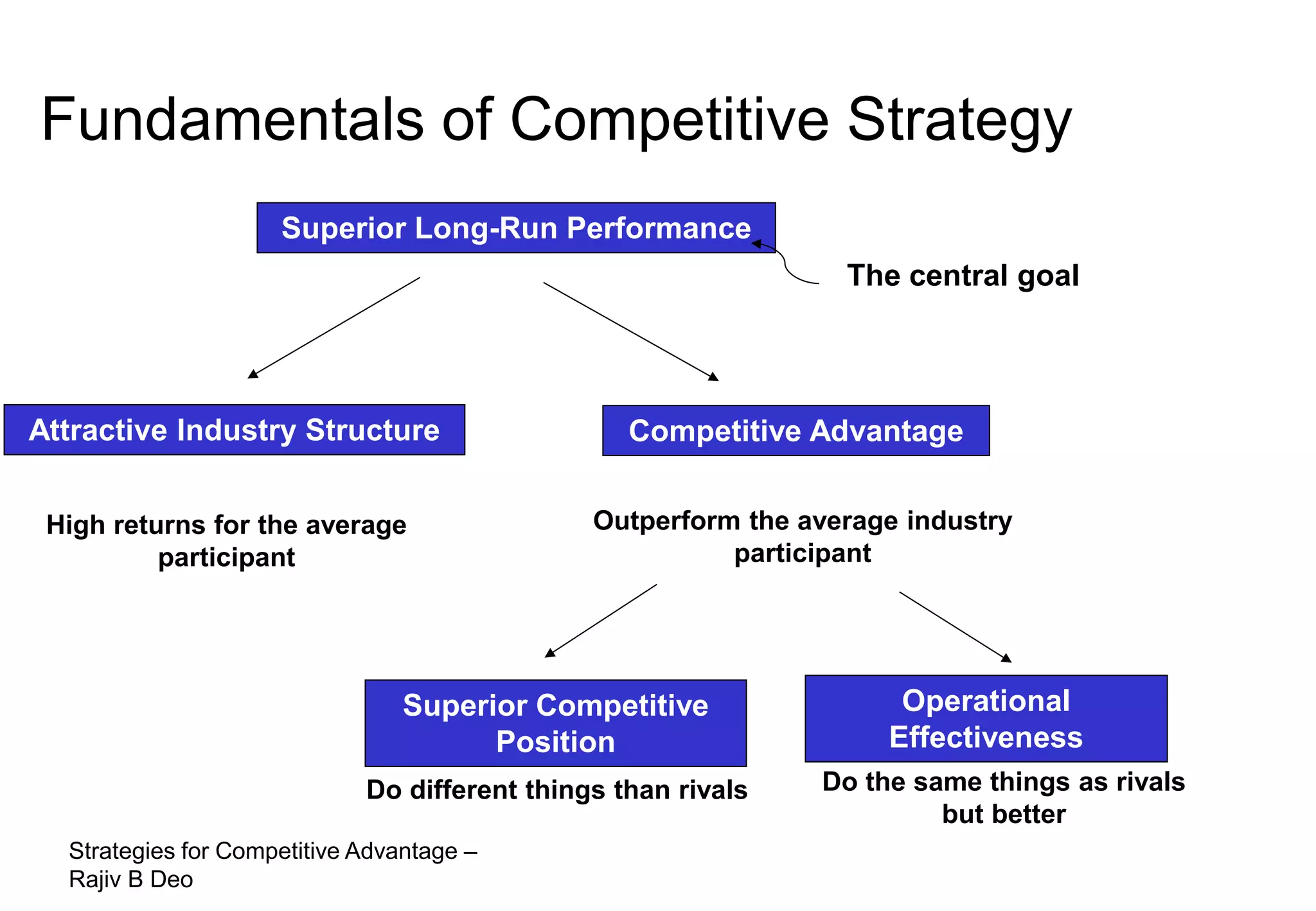
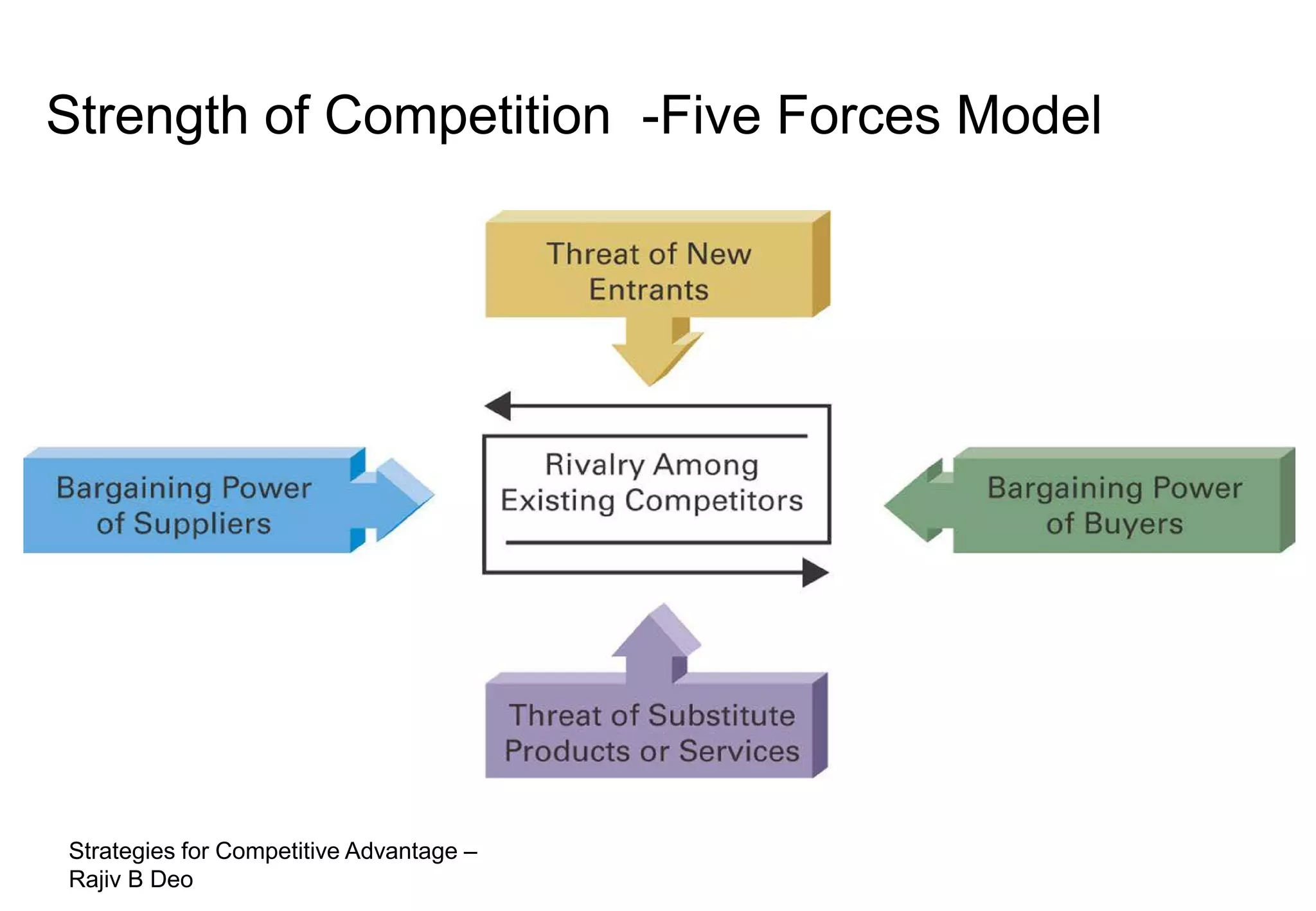
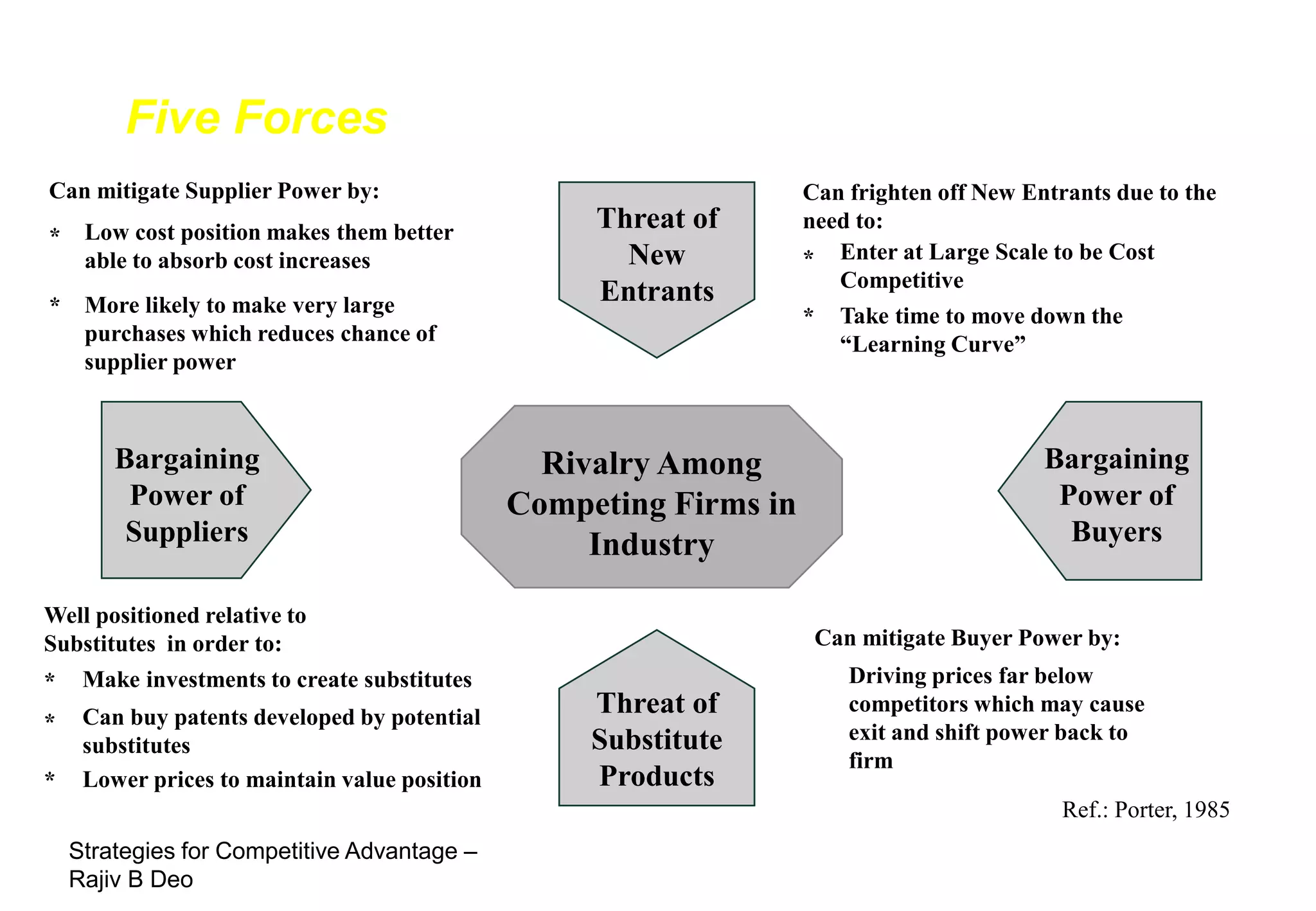
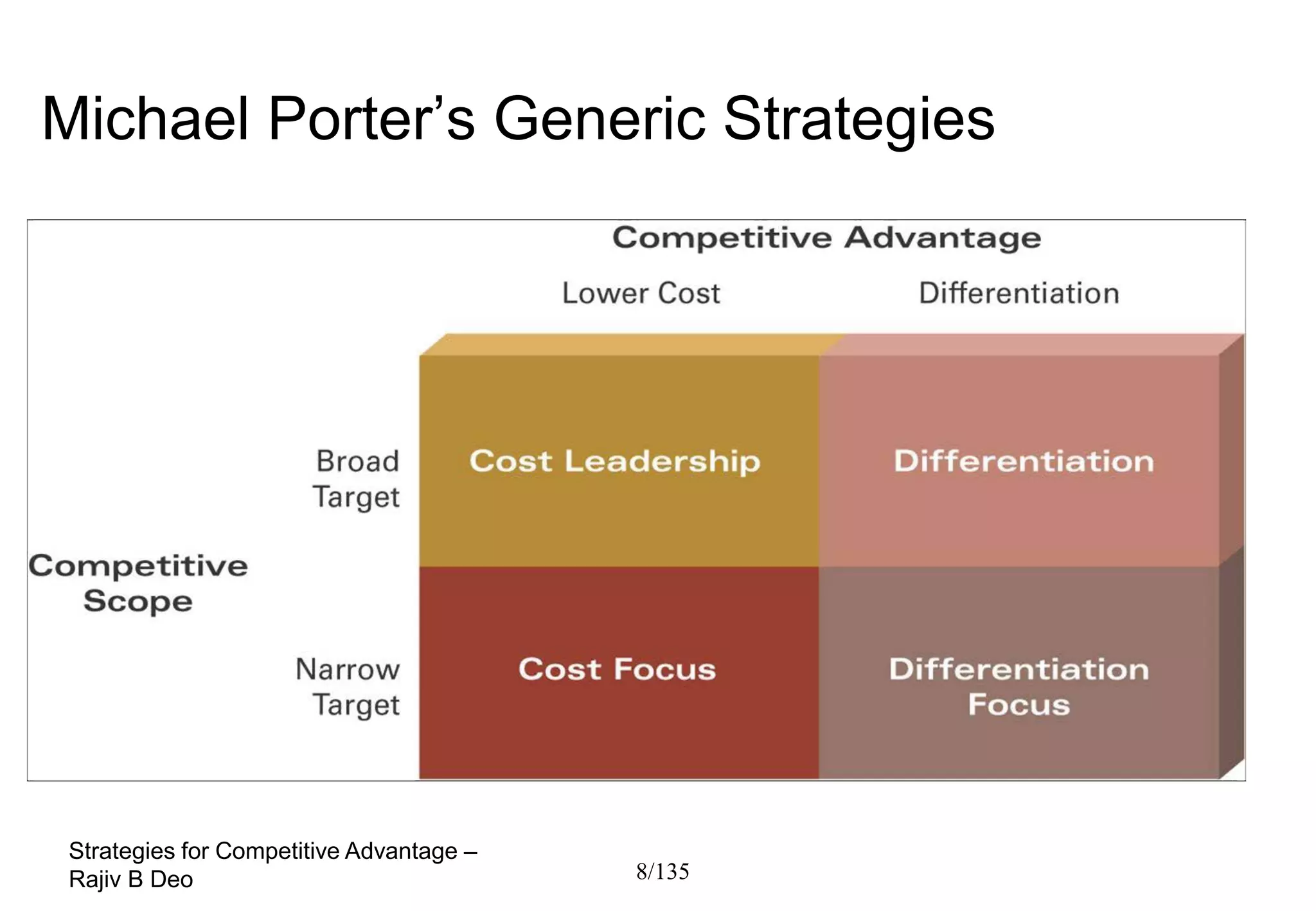
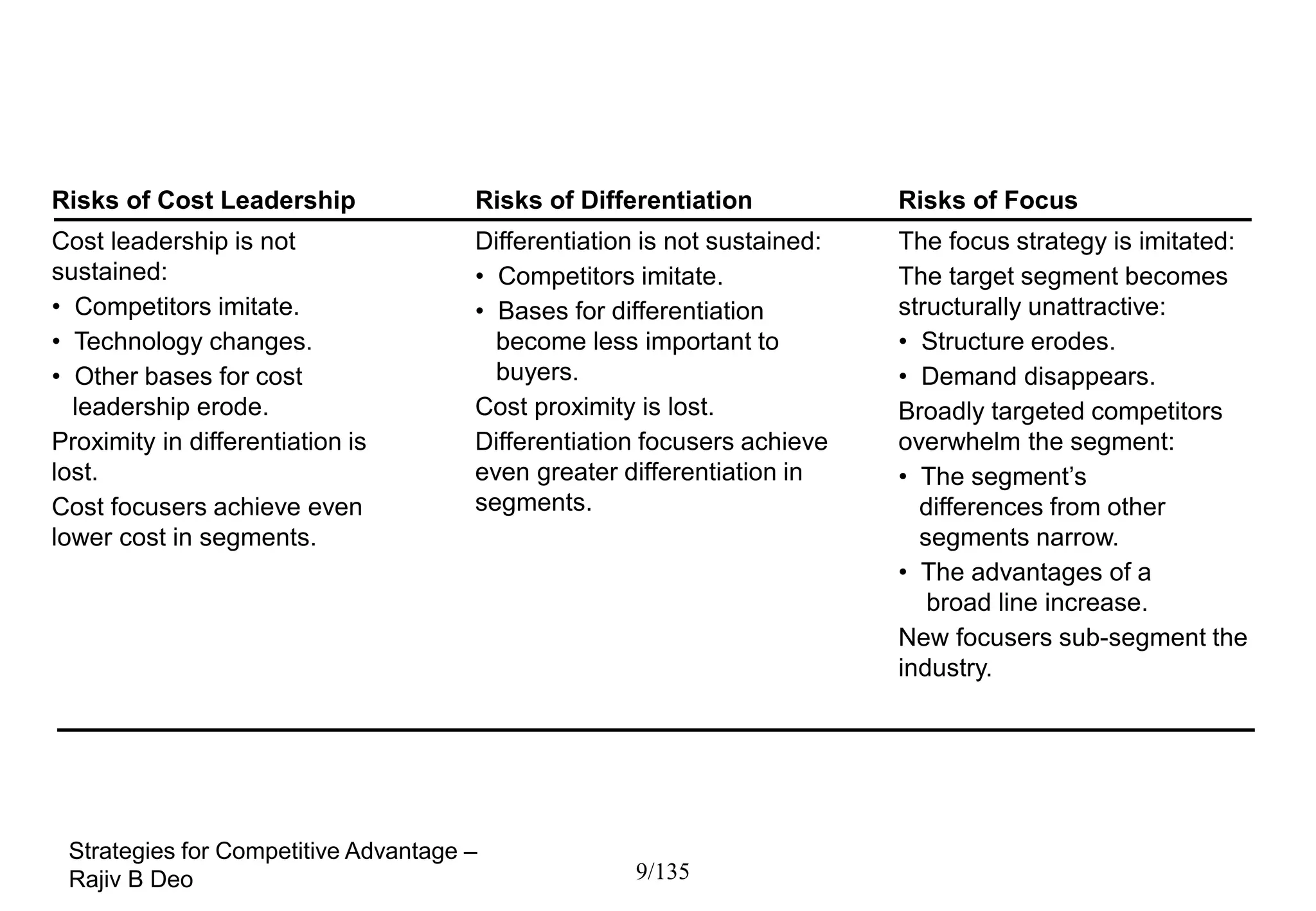
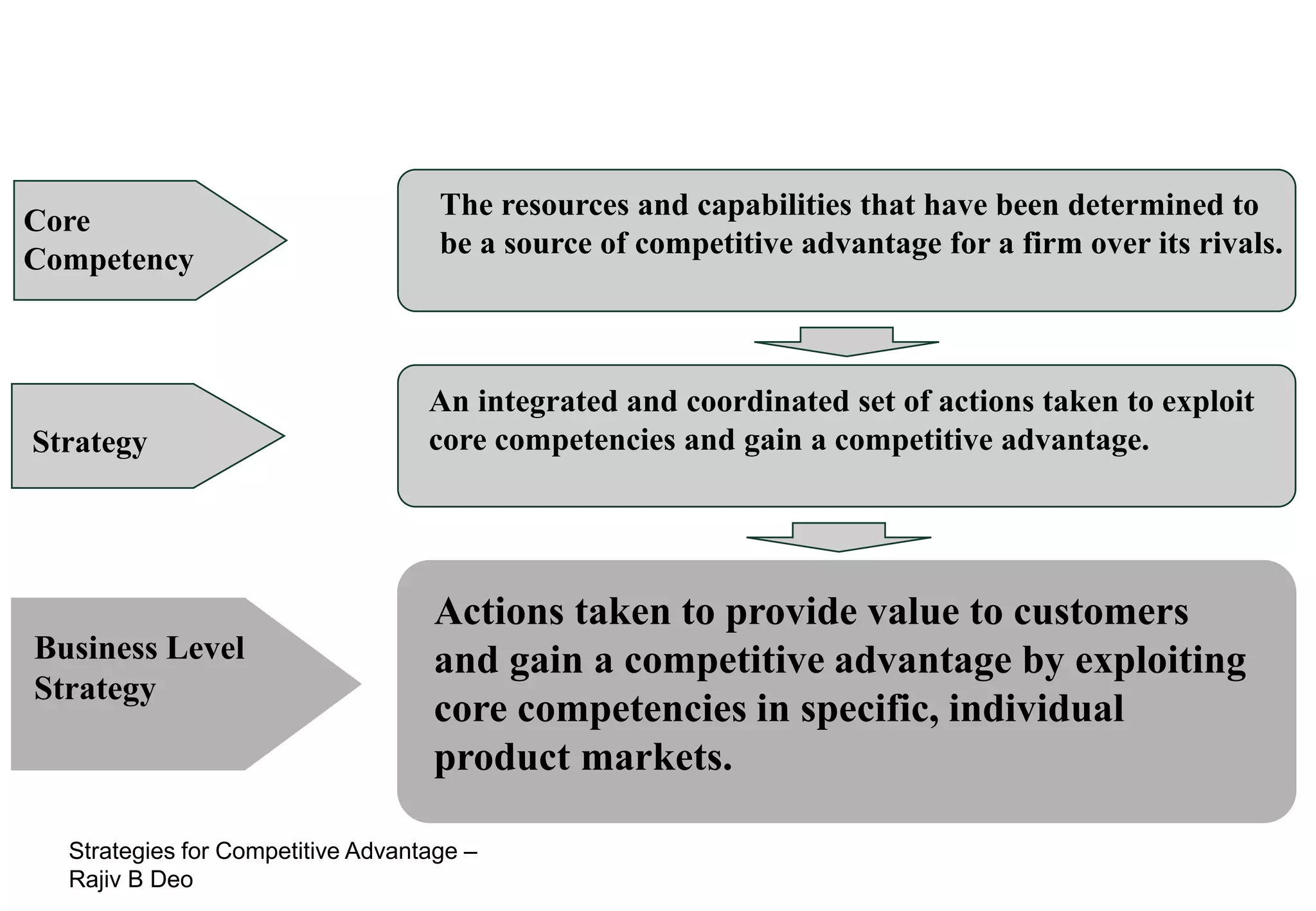
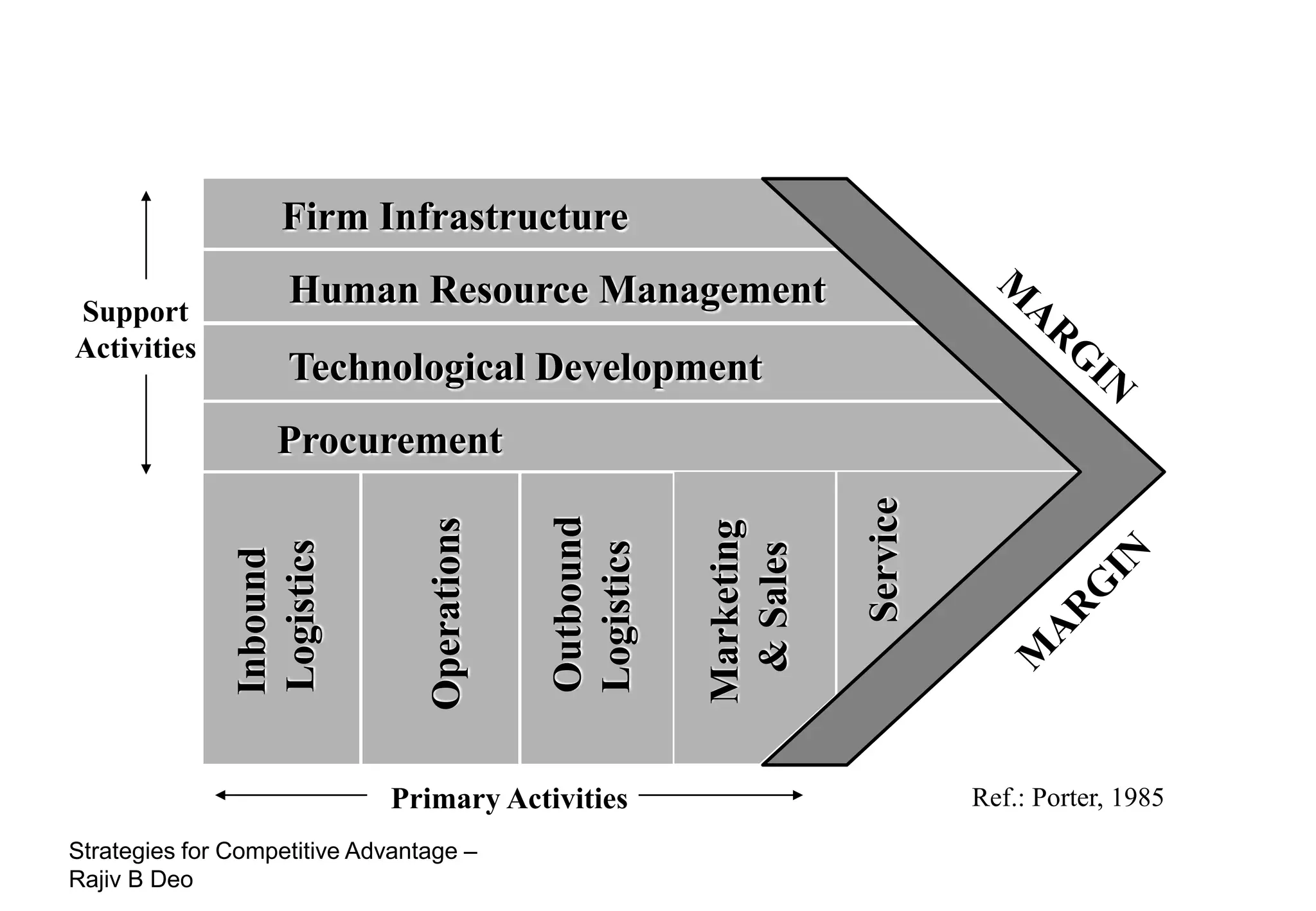
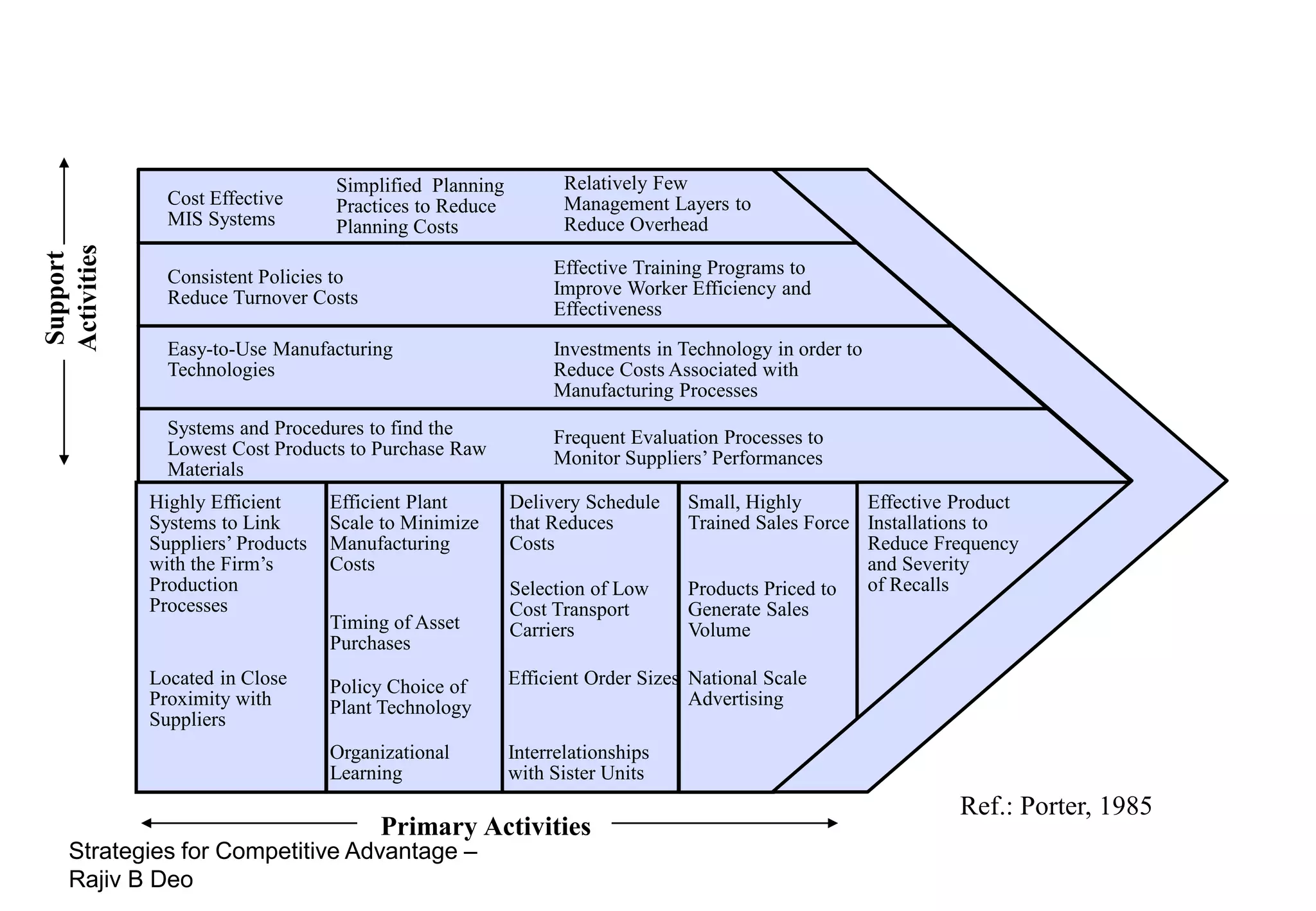
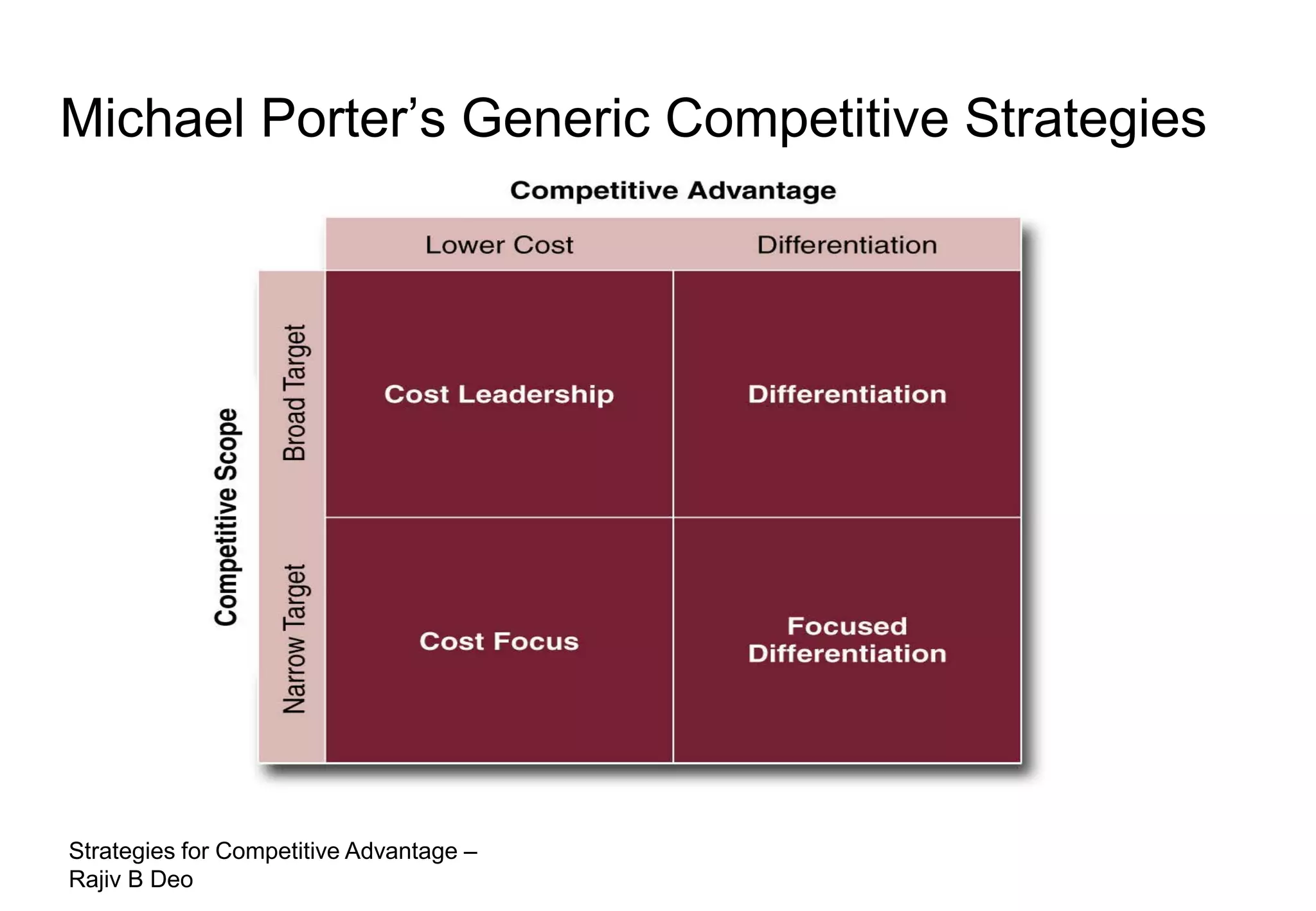
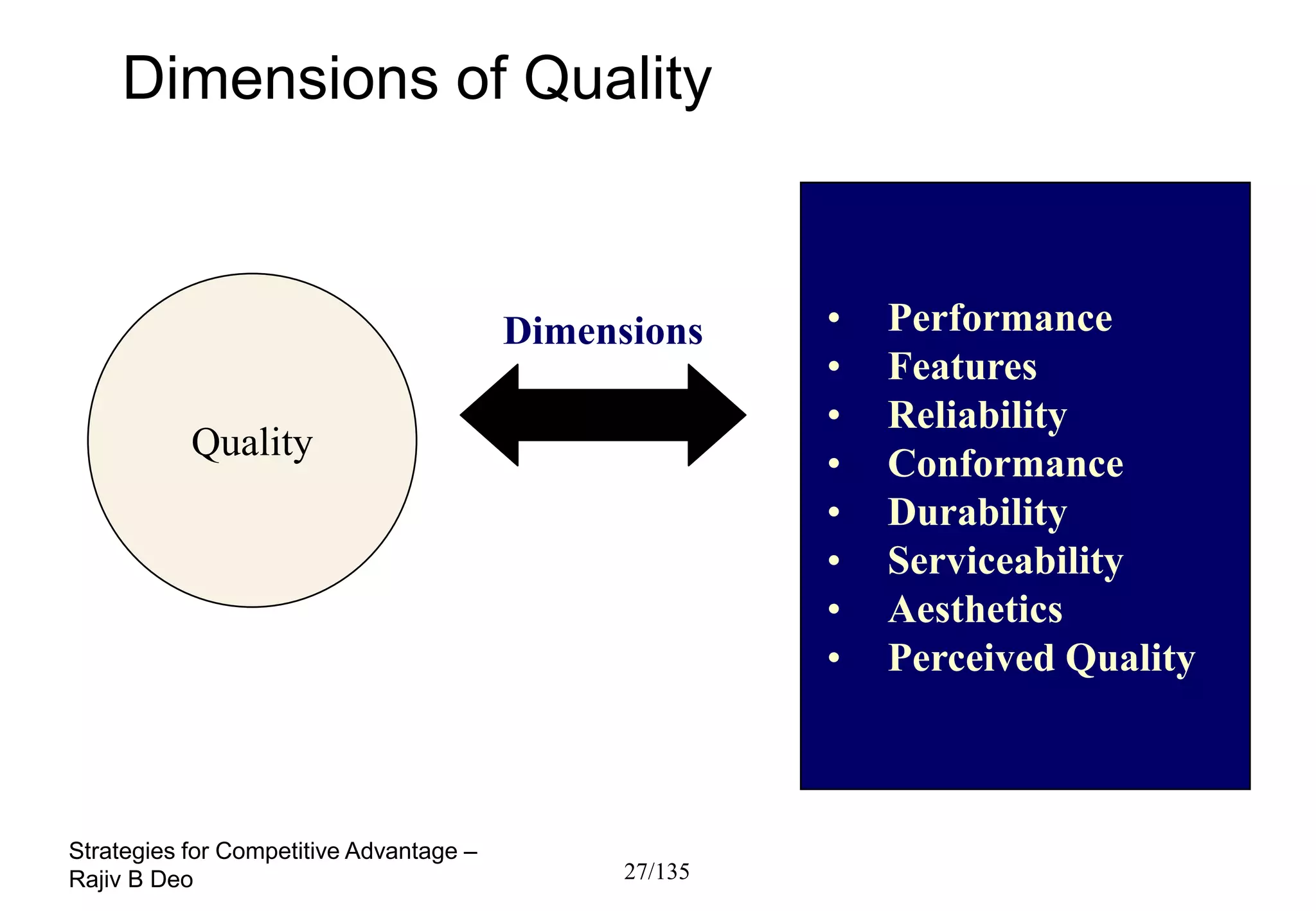
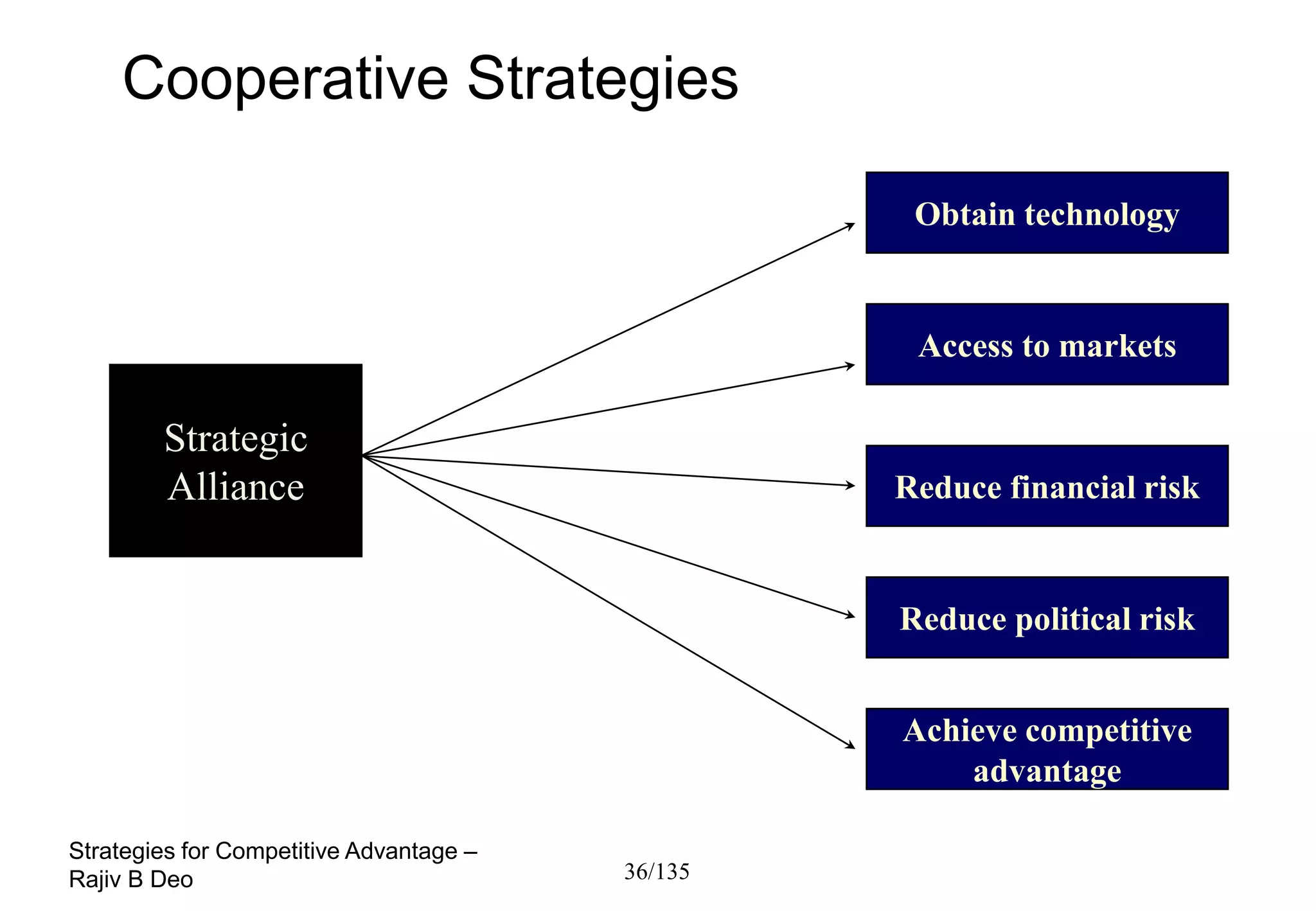
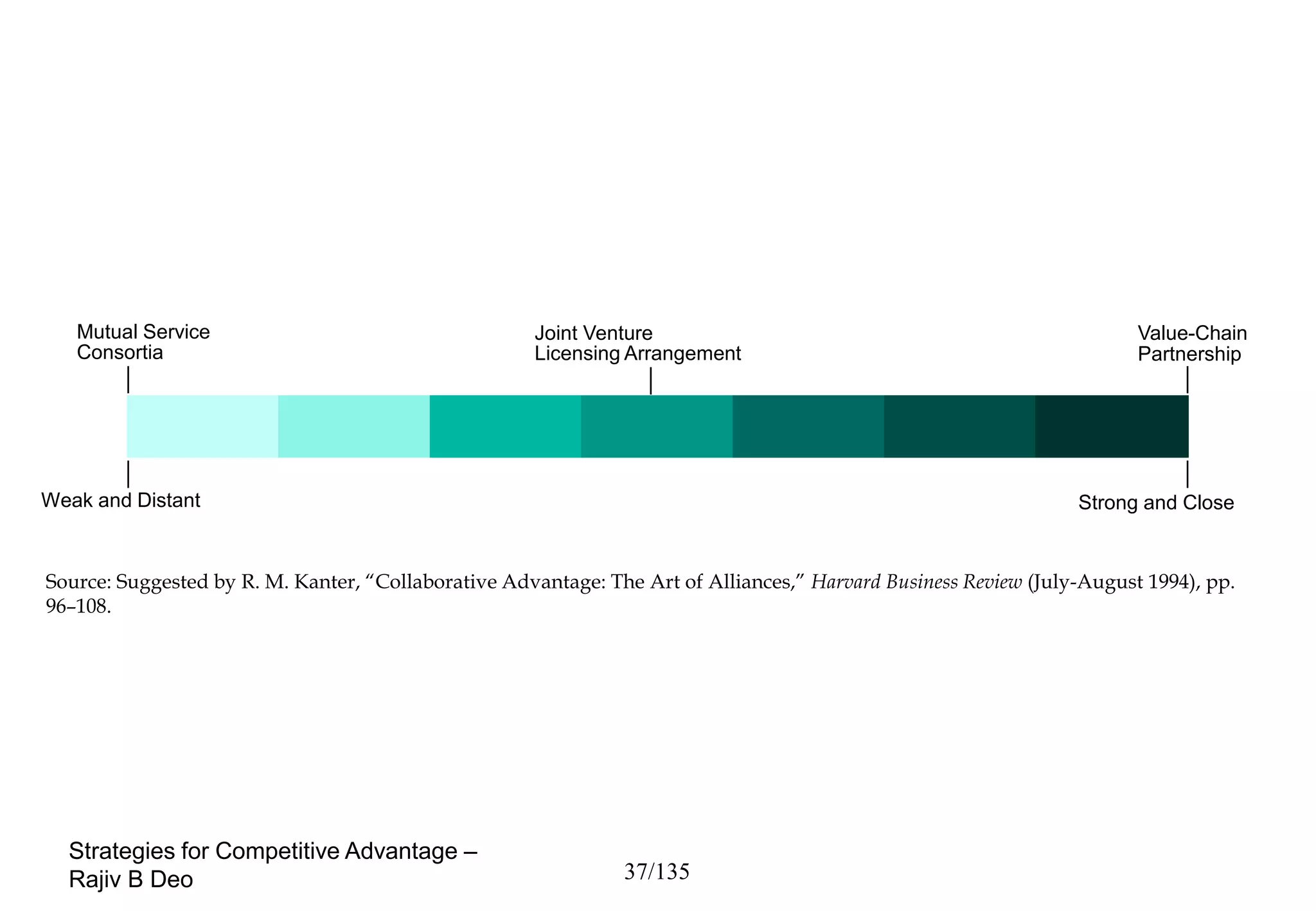
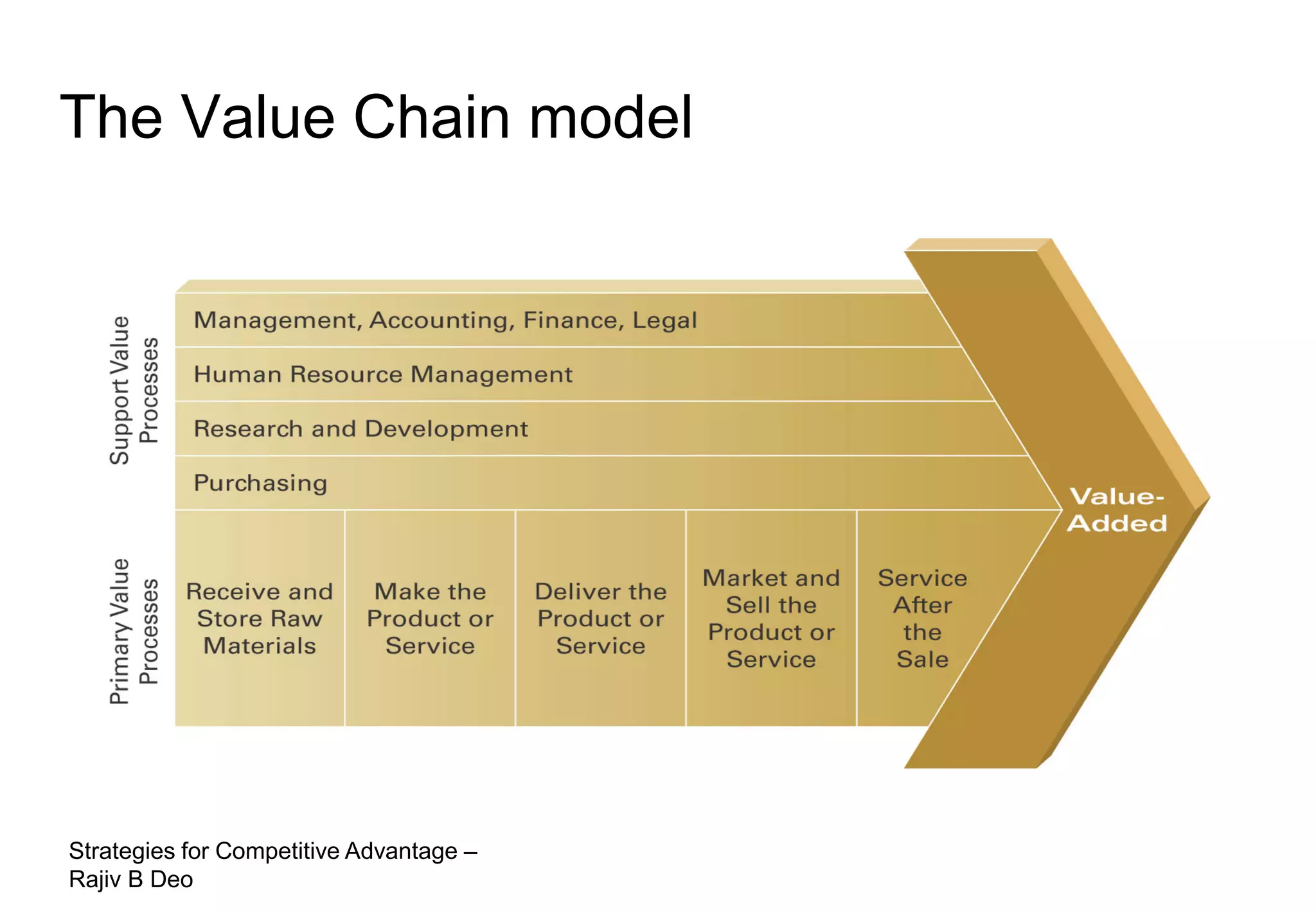
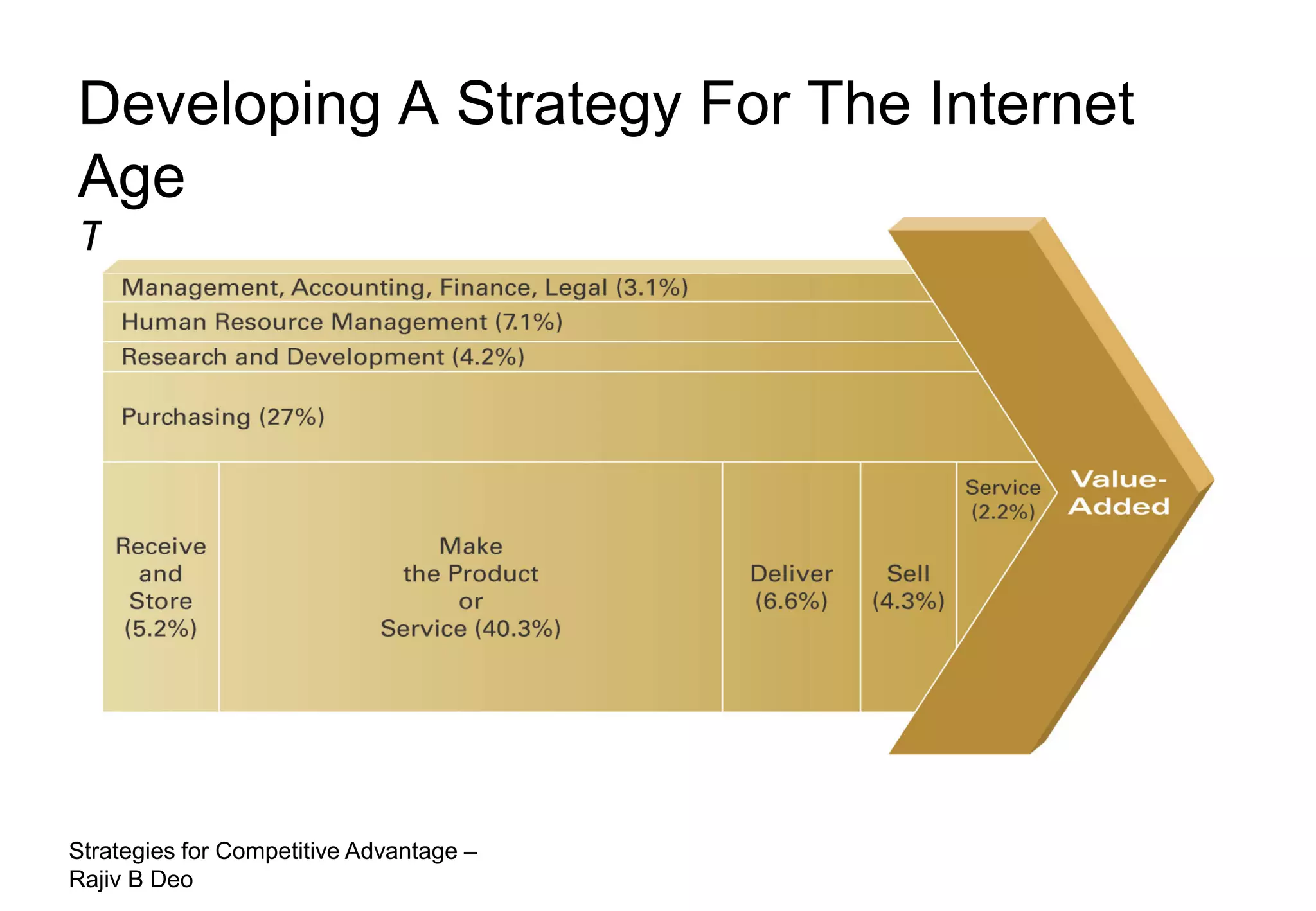
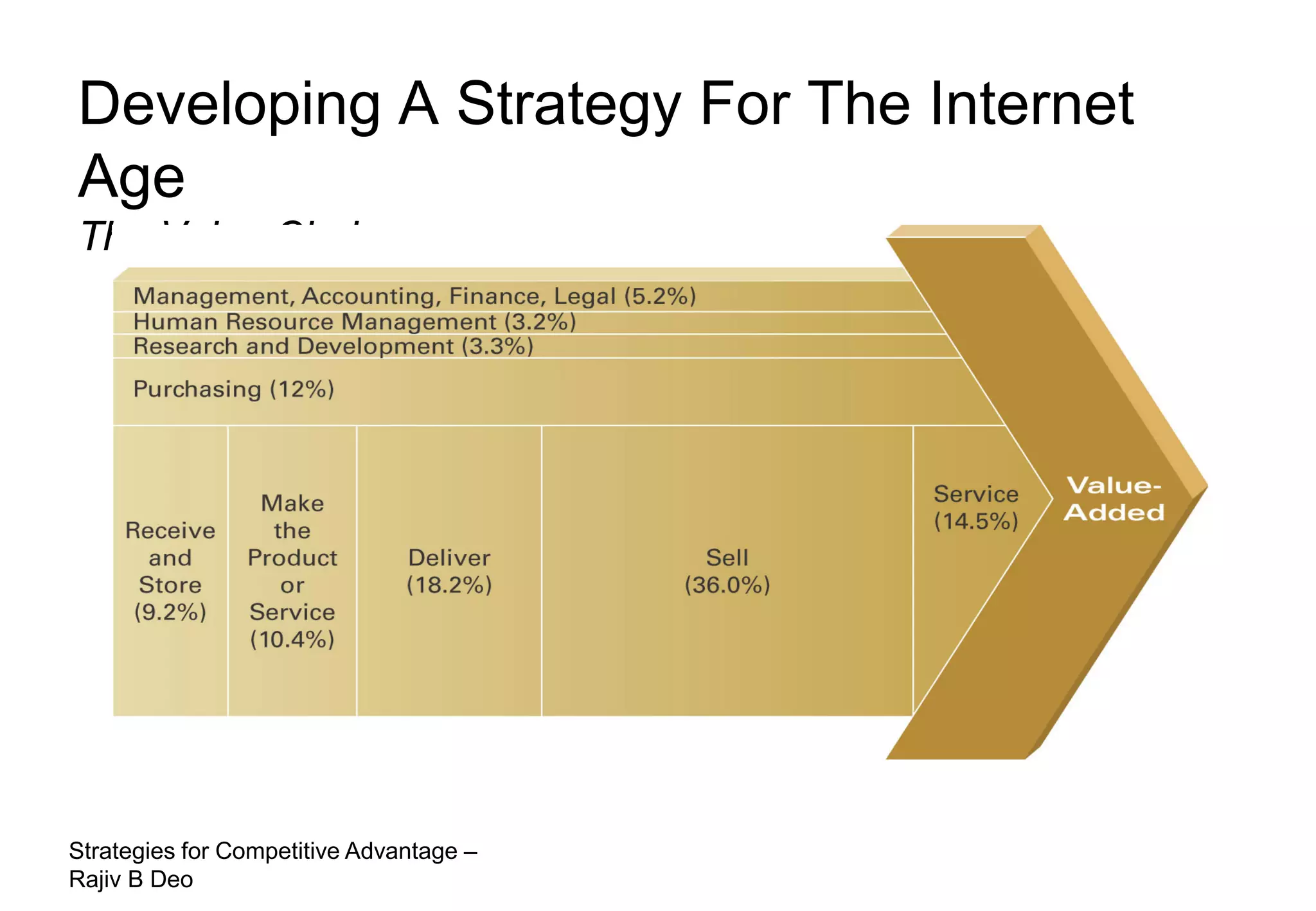
The document discusses strategies for achieving competitive advantage. It introduces Porter's value chain model which views a firm as a collection of primary and support activities that add value. The value chain can be used to identify processes that add or reduce value for customers. Developing strategies may involve planning better ways to meet customer demands, identifying value-adding processes, and looking beyond the firm's boundaries to its supply chain. Maintaining a competitive advantage requires being efficient, aware of competition, innovating technology, and recognizing that advantages are temporary.