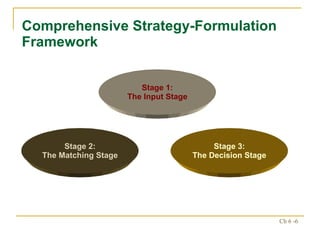
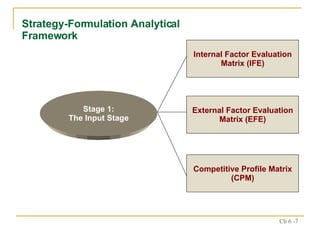
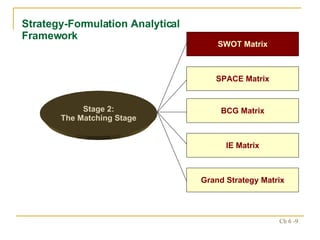
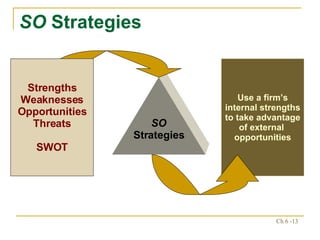
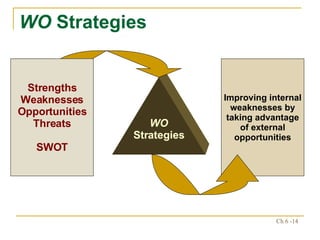
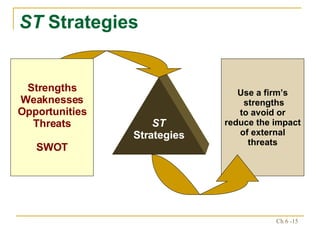
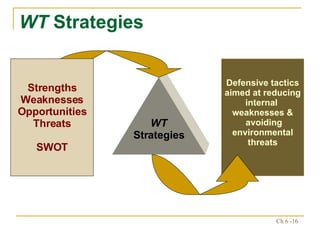
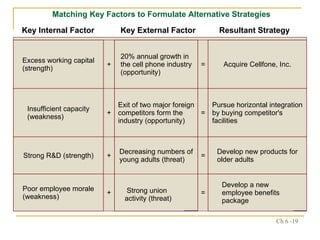
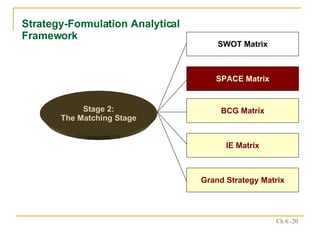
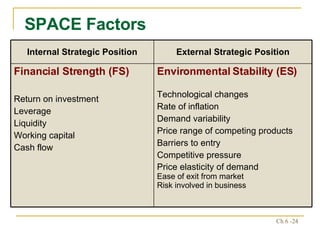
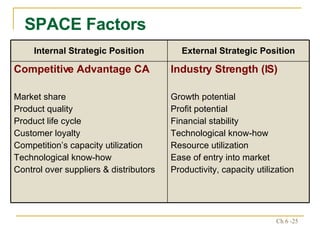
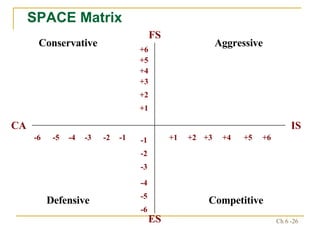
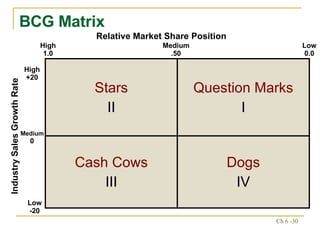
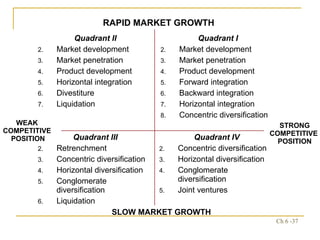
The document discusses various frameworks and models for strategic analysis and choice, including the SWOT analysis, SPACE matrix, BCG matrix, IE matrix, and grand strategy matrix. It explains that strategic analysis involves generating alternative strategies by considering internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats. The models help match internal resources with external factors to develop alternative strategies and ultimately select the best strategies to pursue the organization's objectives and mission.