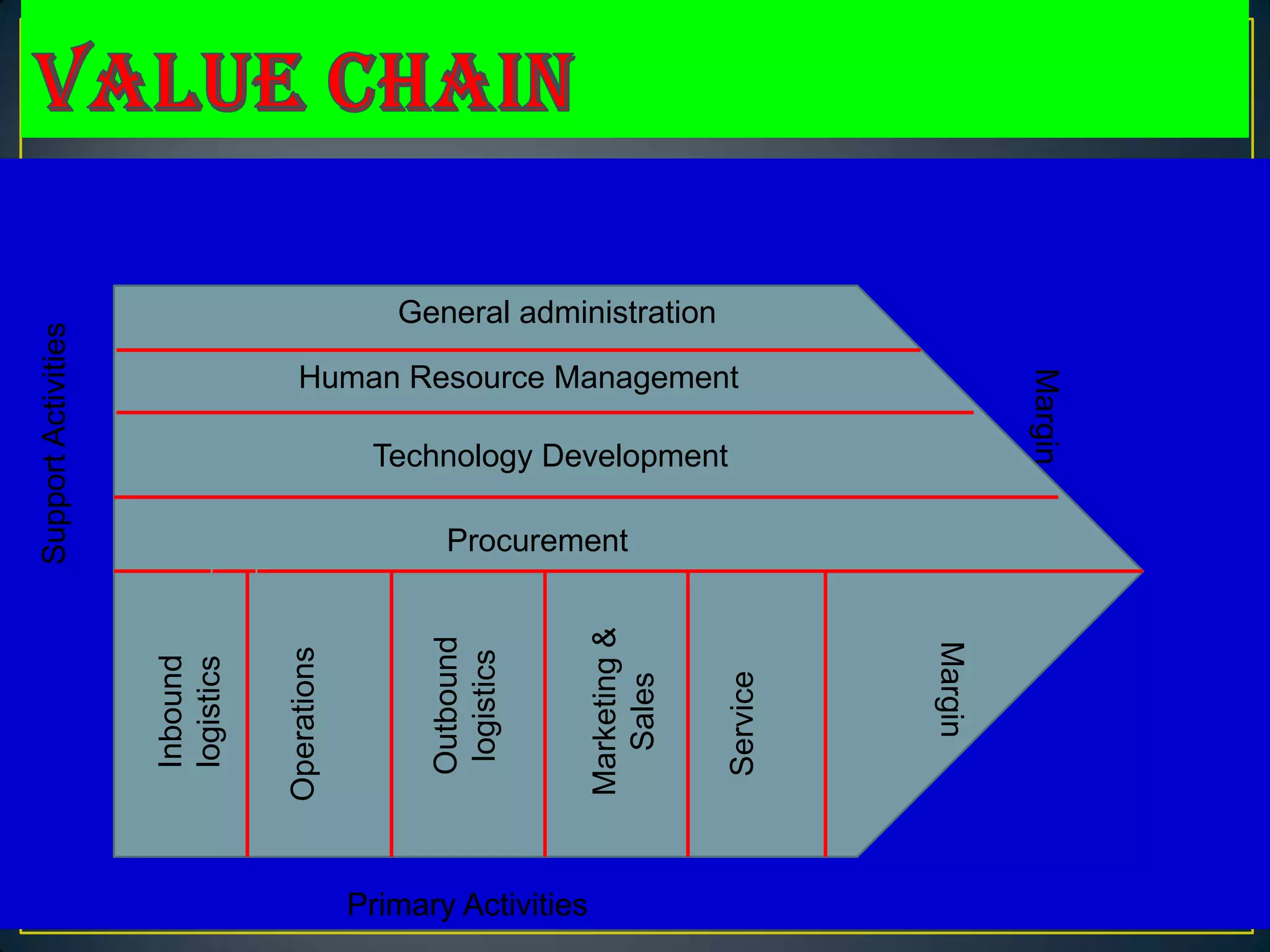
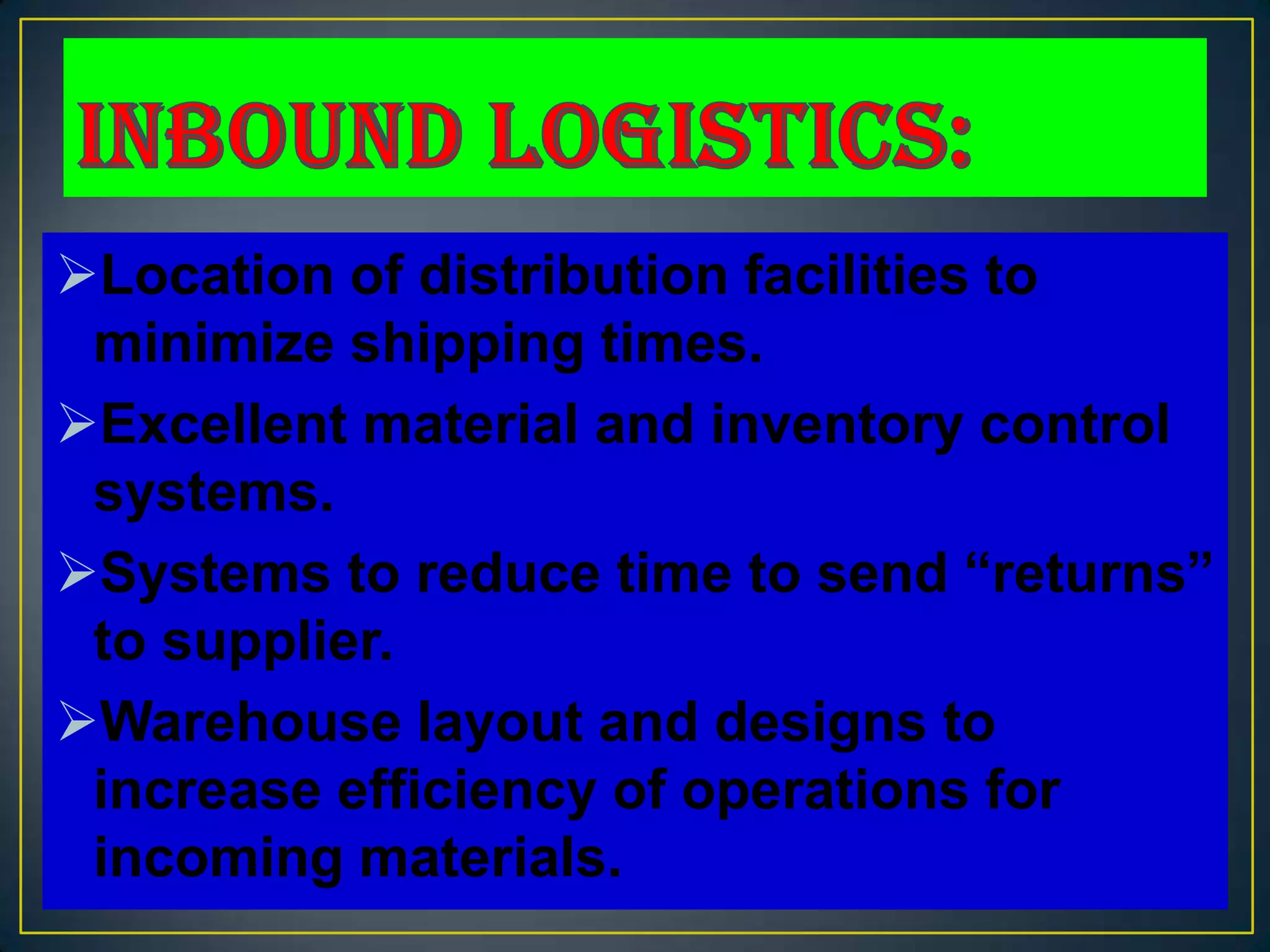
The document discusses assessing a firm's internal environment, including conducting SWOT and value chain analyses to evaluate strengths, weaknesses, and competitive advantages. It describes the primary and support activities in a value chain, such as inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, service, technology development, and general administration. The document also covers assessing a firm's tangible, intangible, and organizational resources based on whether they are valuable, rare, difficult to imitate or substitute. Financial ratio analysis and stakeholder interests are mentioned as additional factors for internal assessment.