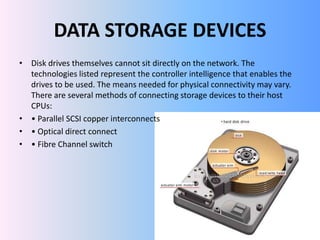
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Storage Area Networks (SAN), detailing their advantages, disadvantages, and components, as well as RAID technology. SANs enhance performance and capacity for data storage but can be expensive and have limited vendor interoperability. The document also outlines hardware and software requirements for SAN and includes installation guidelines for ESXi and vSphere clients.