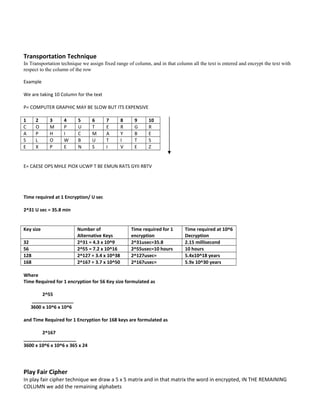
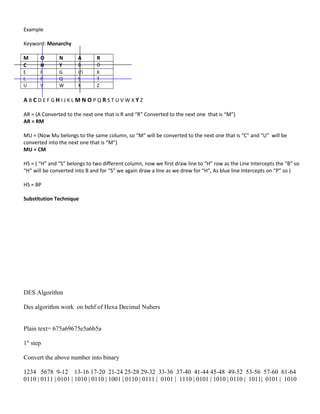
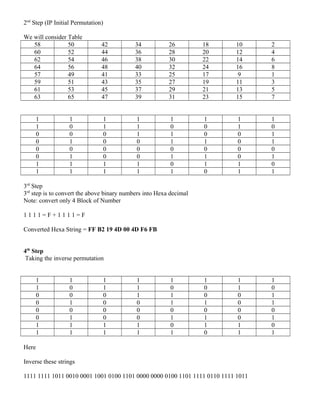
The document discusses fundamental concepts of information security, including security mechanisms, services, and attacks, with examples of encryption techniques such as the Caesar cipher, Playfair cipher, and DES algorithm. It explains the mathematical equations used for encoding and decrypting messages, highlighting the time complexity associated with different key sizes for encryption. The document provides examples and methodologies for these cryptographic techniques and their applications.