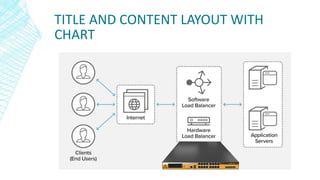
Cloud load balancing distributes workloads and network traffic across computing resources in a cloud environment to improve performance and availability. It routes incoming traffic to multiple servers or other resources while balancing the load. Load balancing in the cloud is typically software-based and offers benefits like scalability, reliability, reduced costs, and flexibility compared to traditional hardware-based load balancing. Common cloud providers like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure offer multiple load balancing options that vary based on needs and network layers.