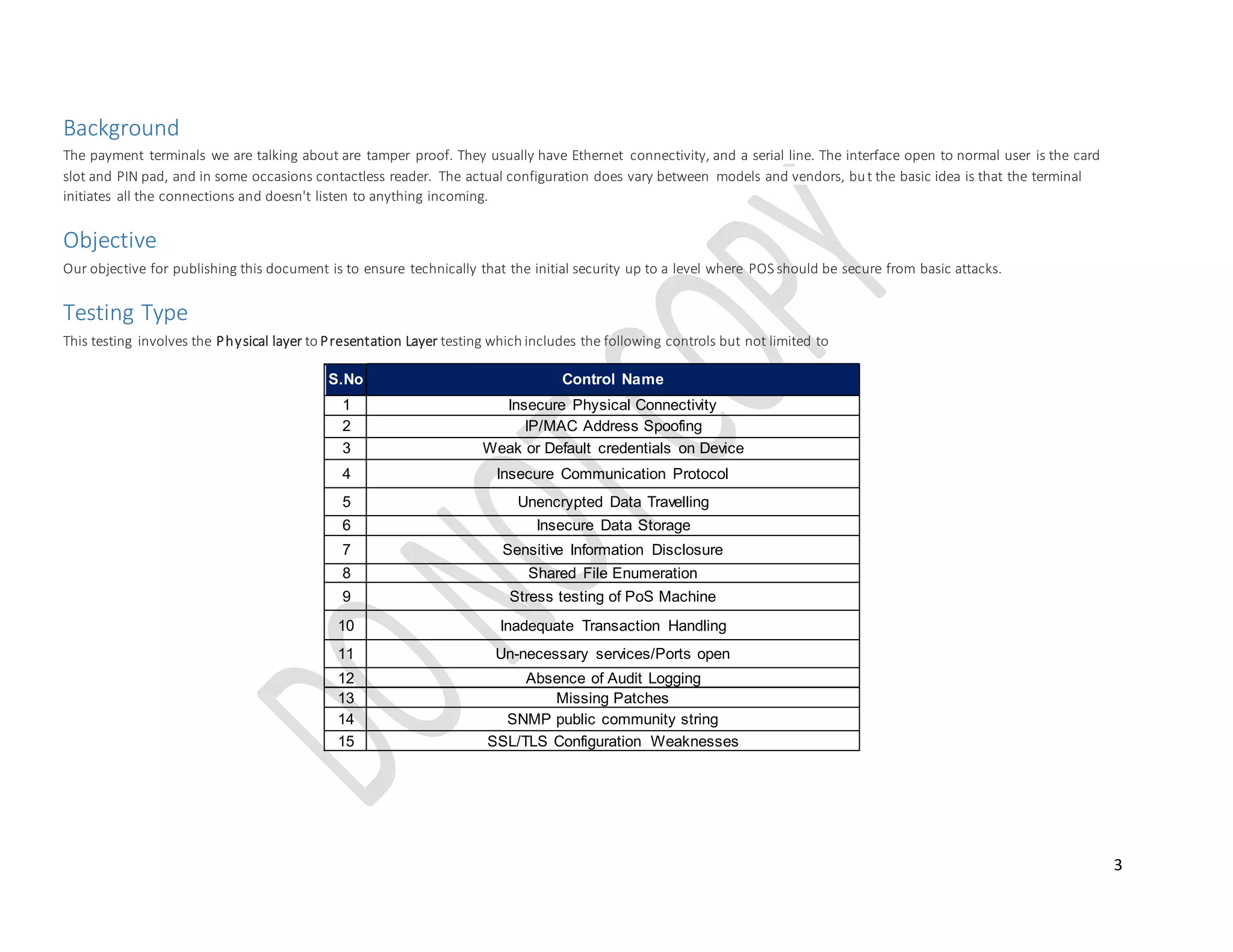
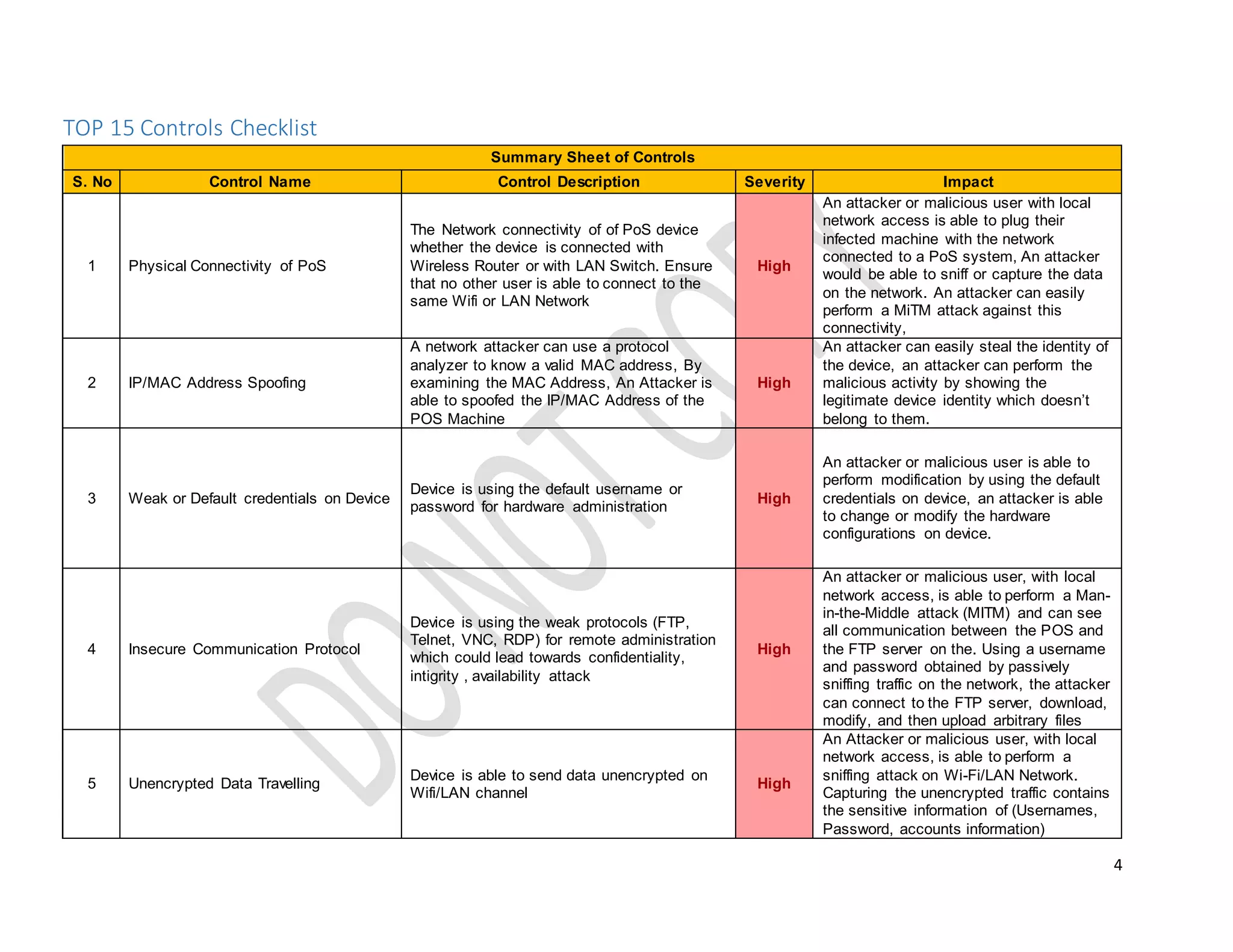
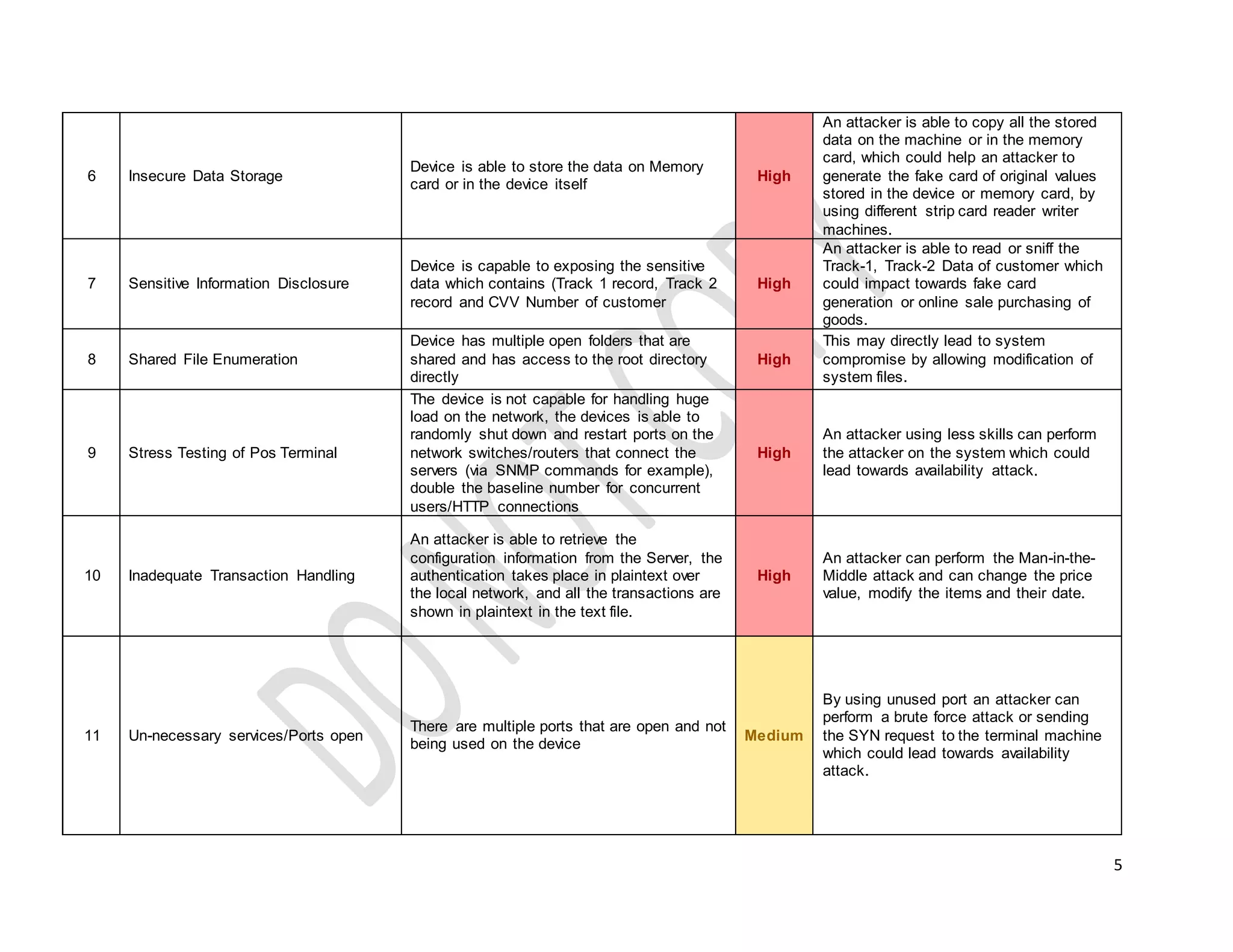
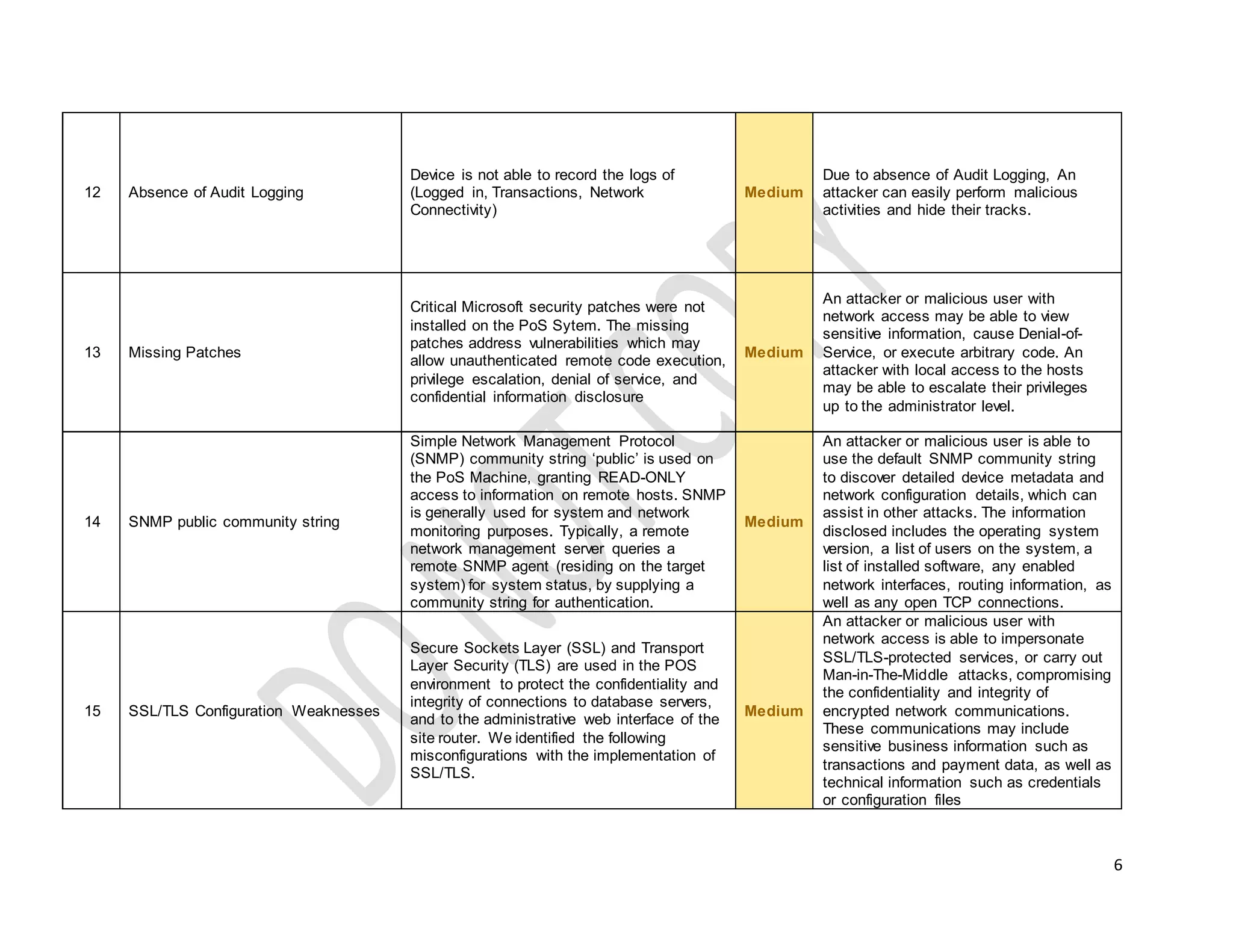
This document provides technical guidelines on how to secure a point-of-sale (POS) system from hackers. It outlines 15 common controls that should be checked, including securing physical connectivity, changing default credentials, encrypting data transmission, patching systems, and properly configuring SSL/TLS. A checklist is also included for assessing POS systems and identifying vulnerabilities, risks, impacts, and recommendations for remediation. The objective is to ensure POS systems are secure from basic attacks by targeting the physical through presentation layers.