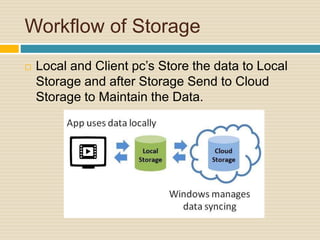
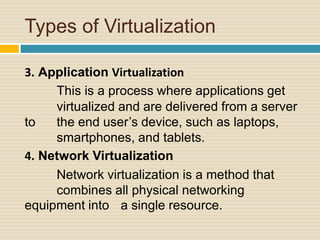
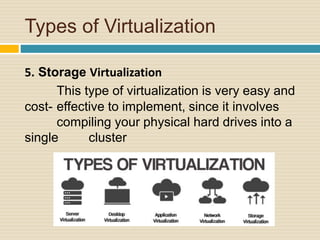
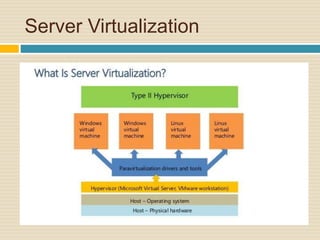
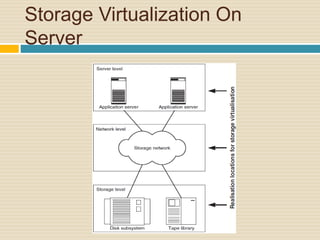
This document discusses storage virtualization on servers. It begins by defining storage and virtualization, explaining that virtualization allows system resources like storage to be divided into virtual resources. It then discusses server virtualization specifically and how storage can be virtualized on individual servers through volume managers that abstract physical disks into logical volumes. The benefits of storage virtualization on servers are efficient use of resources and integration of multiple storage systems, though it requires software on each server.