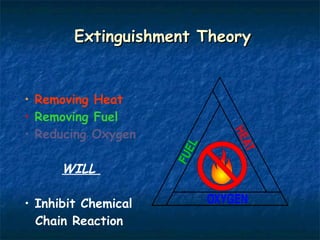
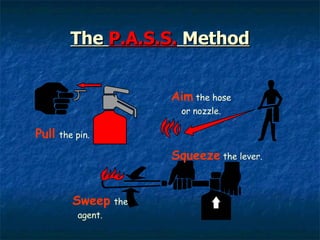
This document provides an overview of fire safety training presented by Environmental Safety Services at Georgia Southern University. It discusses how fires start, what constitutes a fire, fire classification, emergency procedures, and the use of portable fire extinguishers. The training aims to educate attendees on fire prevention, emergency response, and safe fire extinguisher operation.