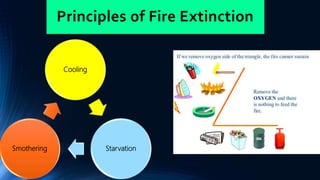
Fire safety involves understanding fire, its causes, and how to prevent and respond to fires. The fire tetrahedron shows that a fire requires heat, fuel, oxygen and a chain reaction. Common fire causes include electrical faults, smoking, welding sparks, and arson. Fuels include building materials, stored products, liquids and gases. Oxygen comes from the air. Those at highest risk include lone workers, isolated workers, new/unfamiliar people, non-native language speakers, young/pregnant/disabled people, and those near the building.
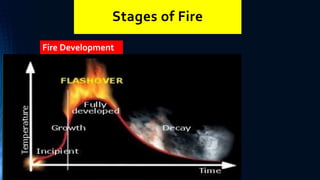
Fires spread via conduction, convection and radiation. There are different fire classifications based on the fuel type. General fire precautions center around escape routes, equipment, alarms,