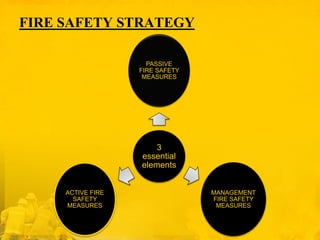
This document outlines fire safety management strategies. It discusses three essential elements: passive fire safety measures that are built into the structure, active measures like alarms and sprinklers, and management measures to prevent fires and ensure staff training. Emergency procedures, inspections, equipment maintenance, staff training, and record keeping are key parts of an effective fire safety program. Advance planning should also be done to minimize damage from any fires that do occur.