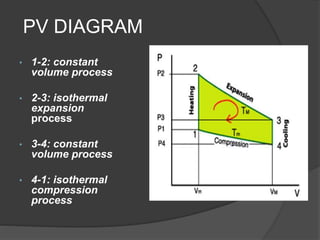
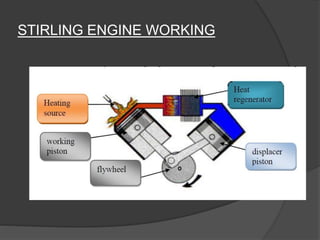
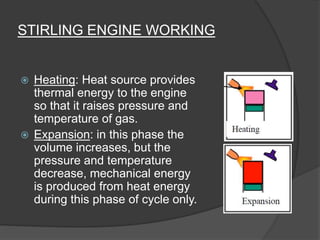
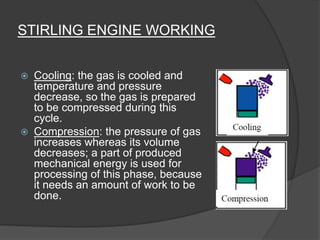
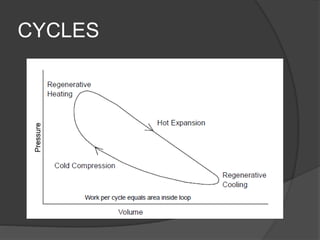
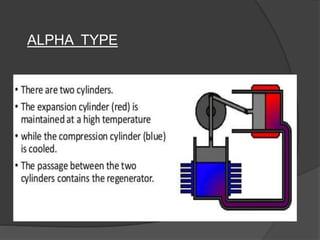
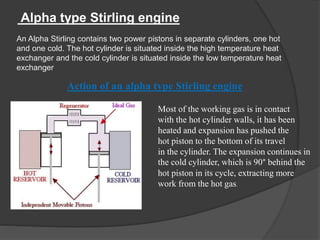
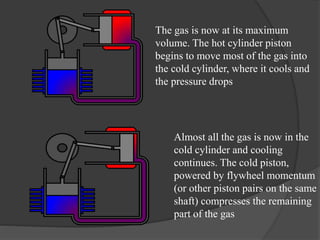
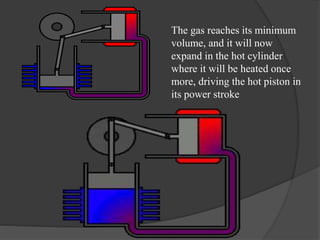
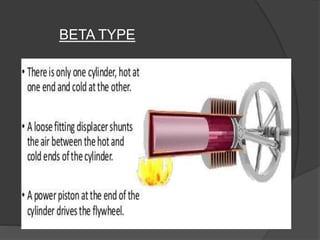
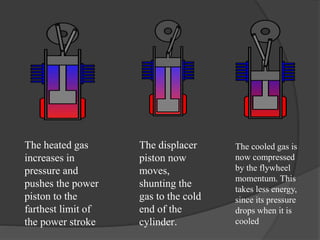
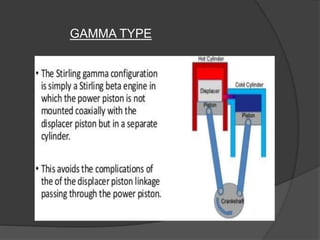
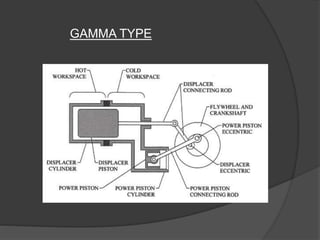
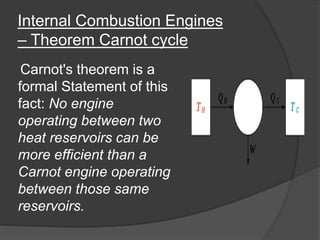
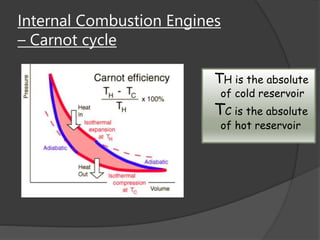
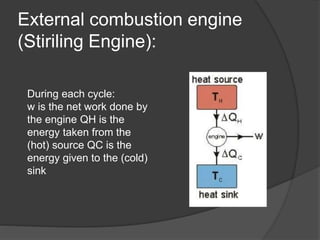
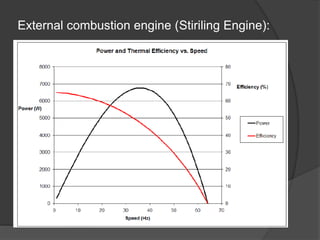
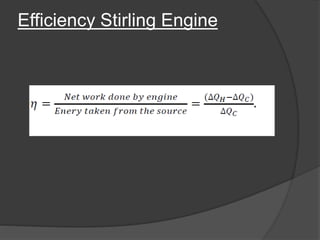
The document discusses Stirling engines, including their history, types (Alpha, Beta, Gamma), efficiency comparison to internal combustion engines, key components, and advantages/disadvantages. Stirling engines operate using cyclic compression and expansion of a gas between hot and cold temperatures to convert heat into mechanical work. They were invented in the 1800s as a safer alternative to steam engines and can achieve higher efficiencies than internal combustion engines. The main types differ in their piston arrangements, and key components include the working gas, heat exchangers, displacer, regenerator, and expansion/compression mechanisms. Advantages include quiet operation and ability to use various heat sources, while disadvantages include higher costs and lack of power flexibility.