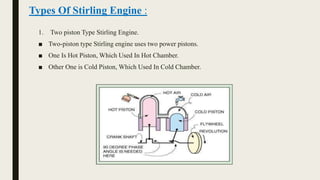
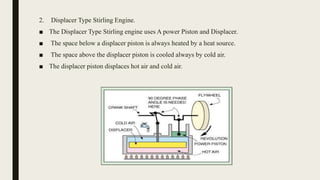
The document discusses the Stirling engine, an external combustion engine that uses the expansion and contraction of gases to produce useful work. It describes the Stirling engine's inventor, Robert Stirling, and provides details on its history, types, parts, cycle of operation, advantages over internal combustion engines in being pollution-less, and applications. The conclusion reiterates that the Stirling engine uses heat from an external source to expand and contract trapped gases for power production without combustion or exhaust, making it a pollution-less alternative.