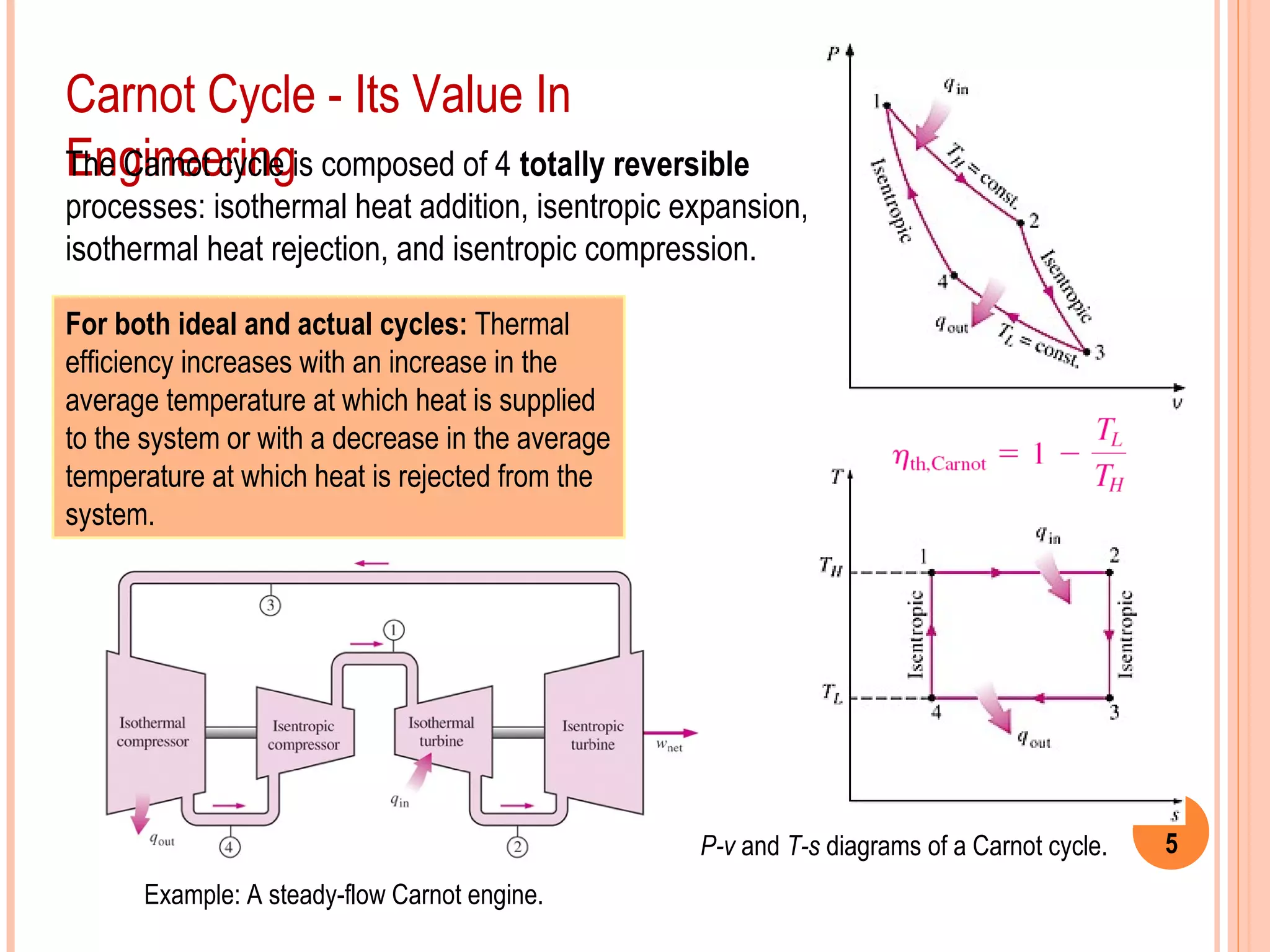
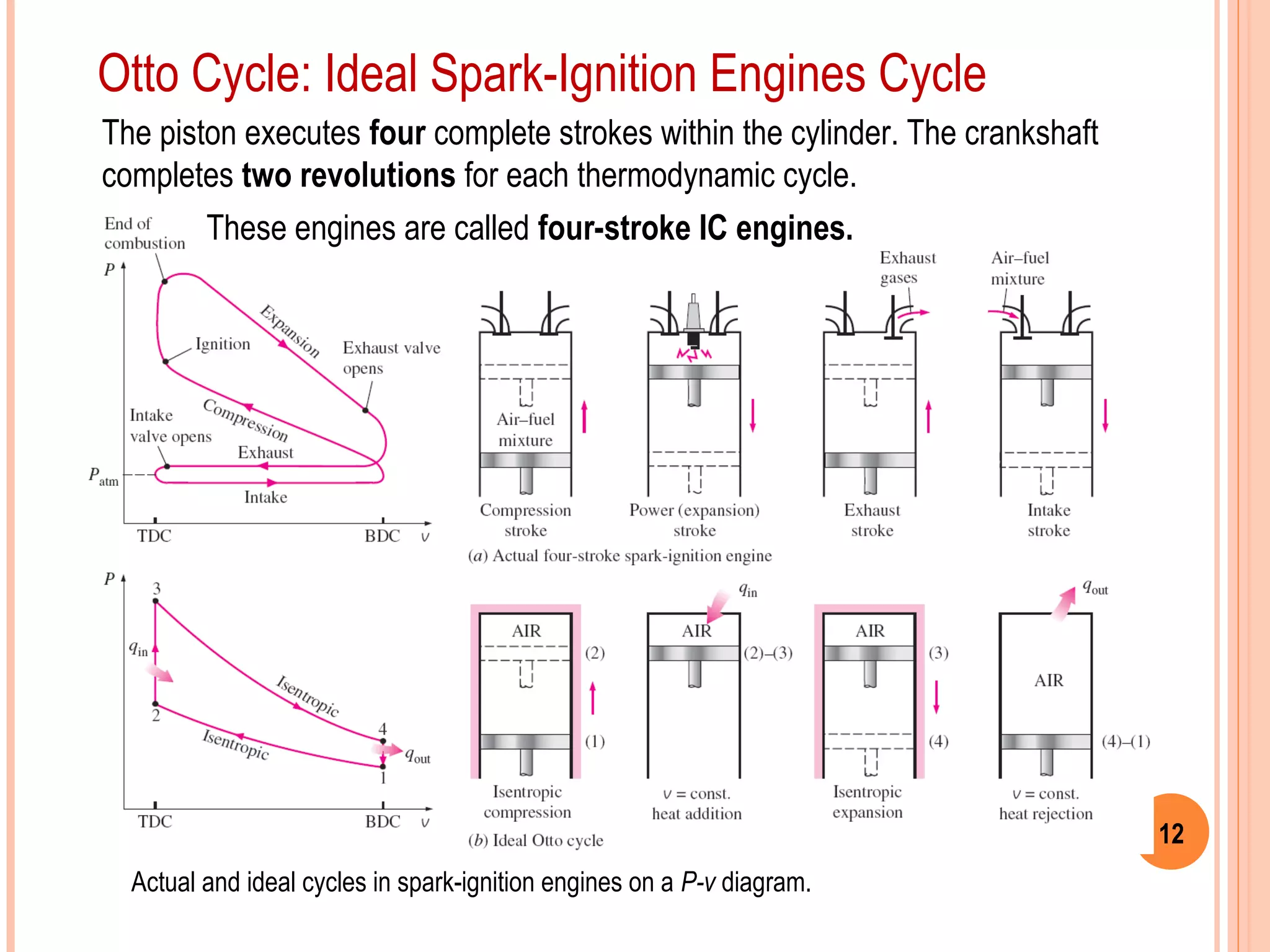
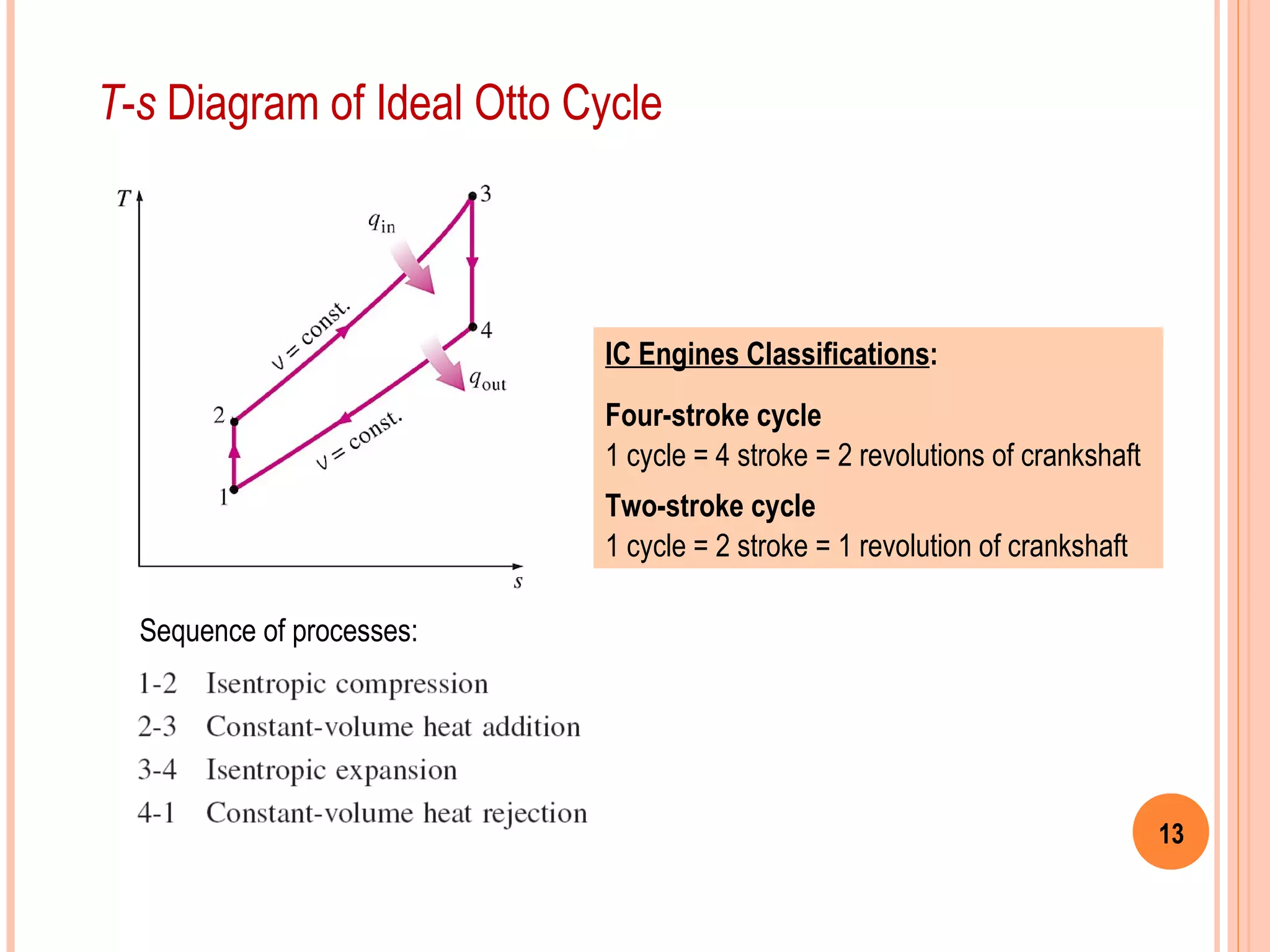
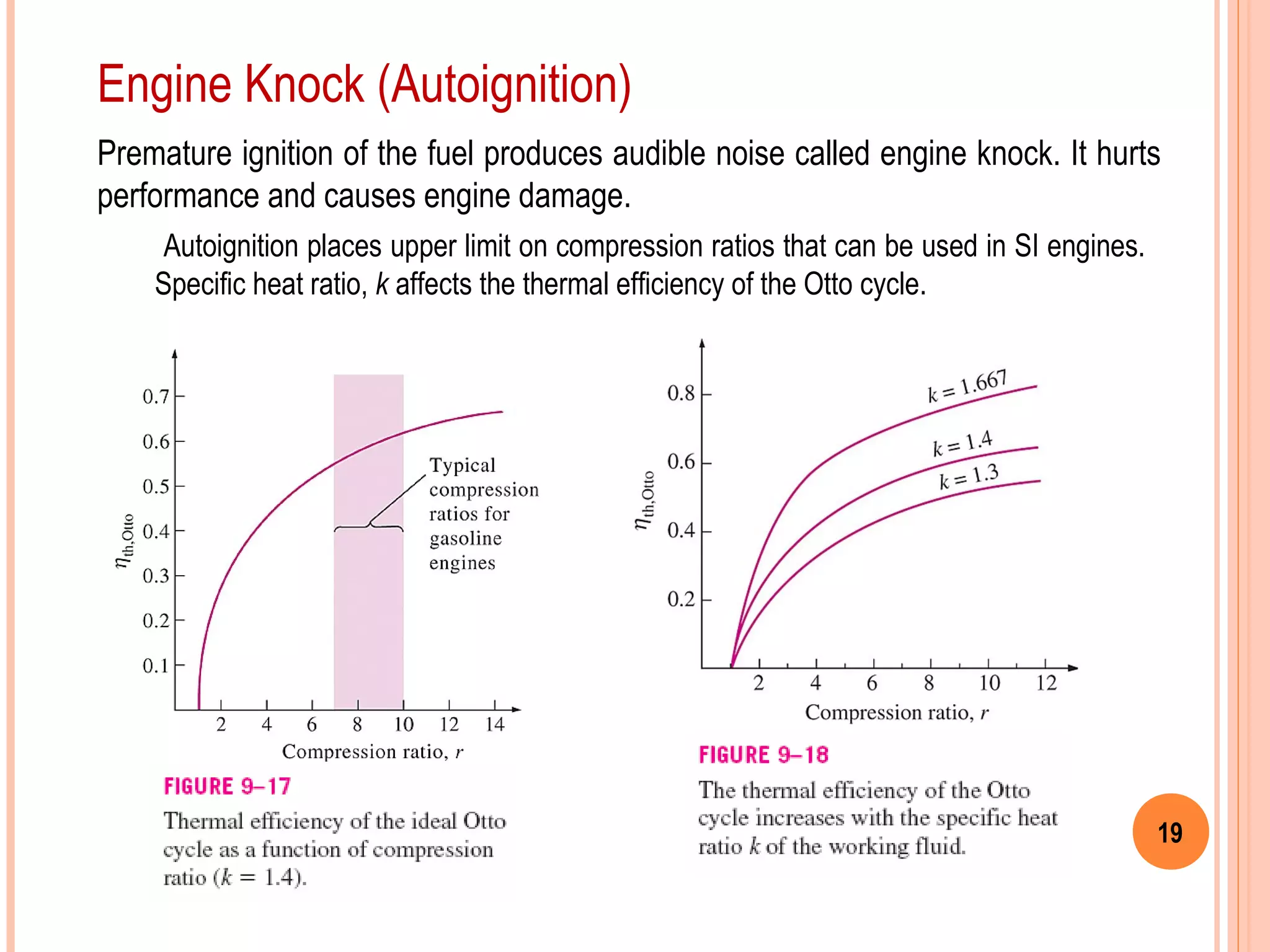
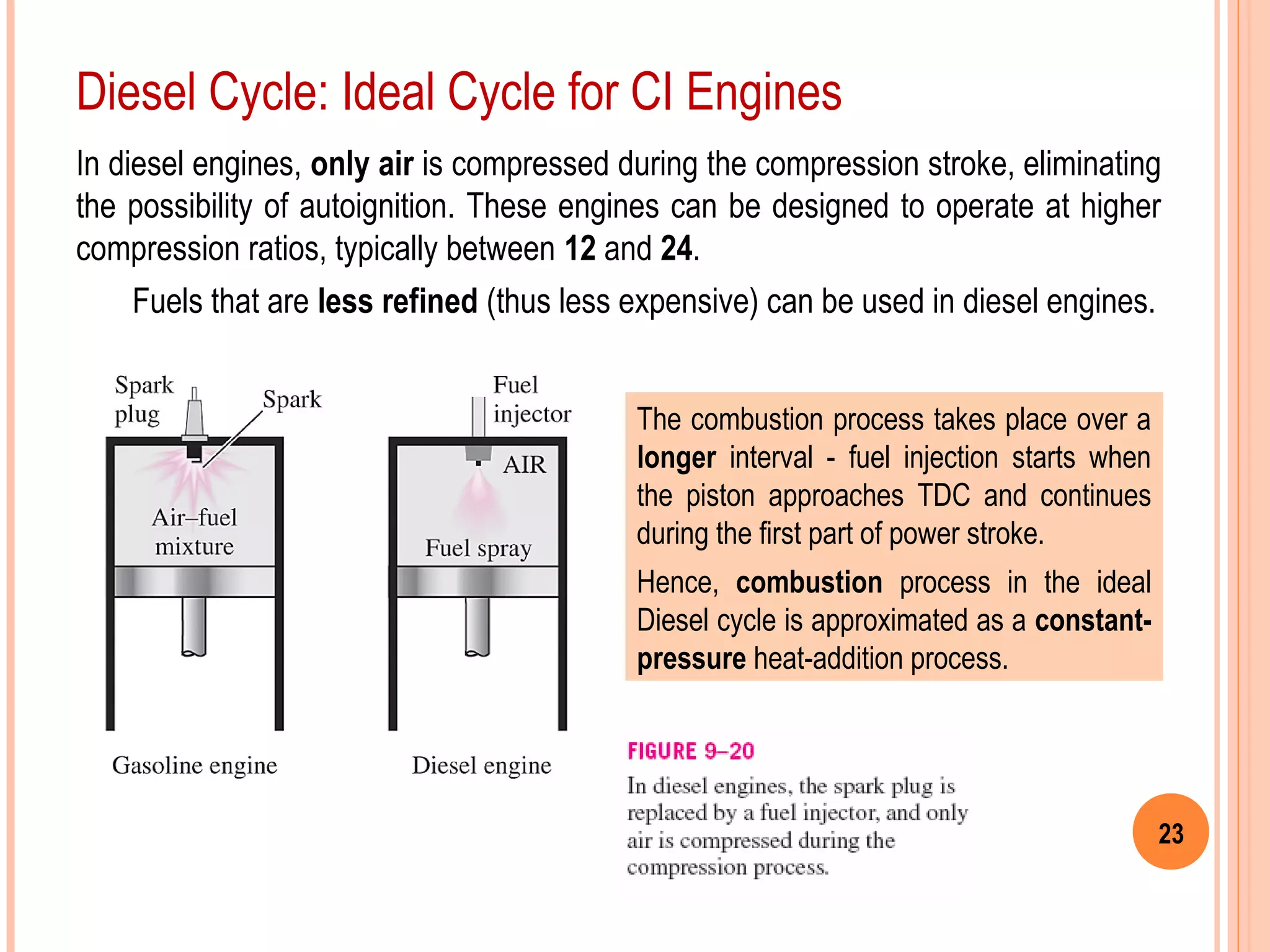
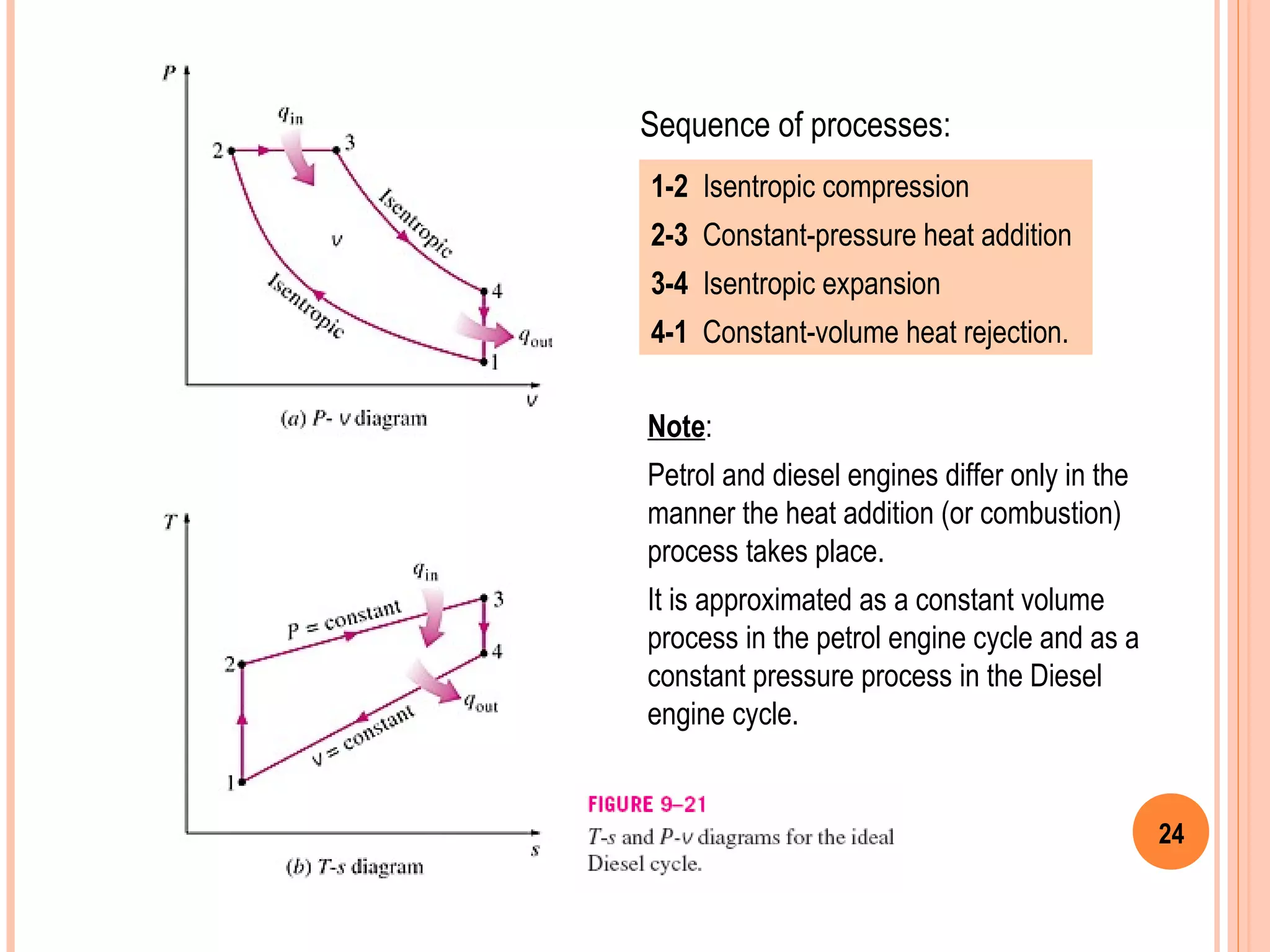
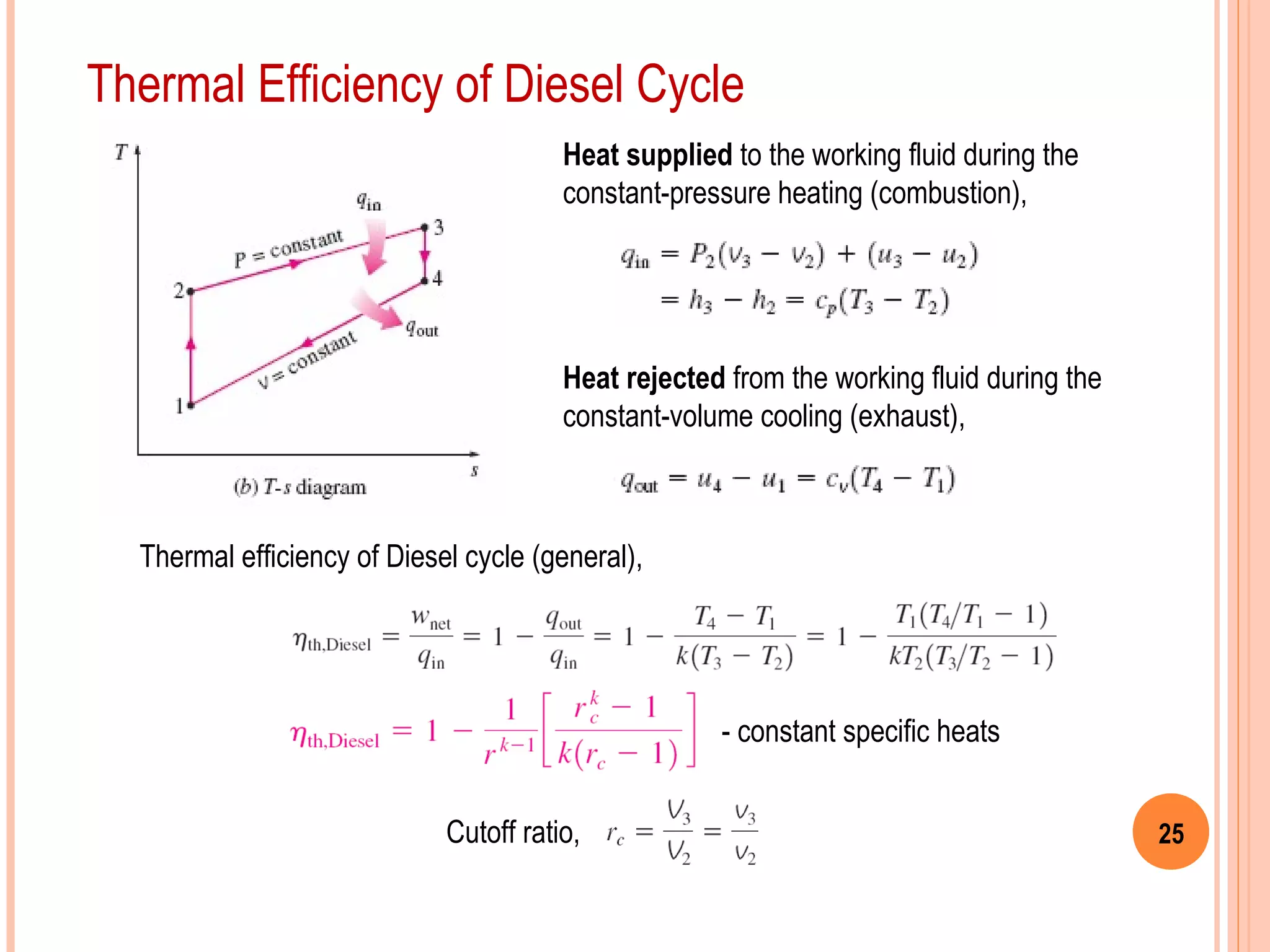
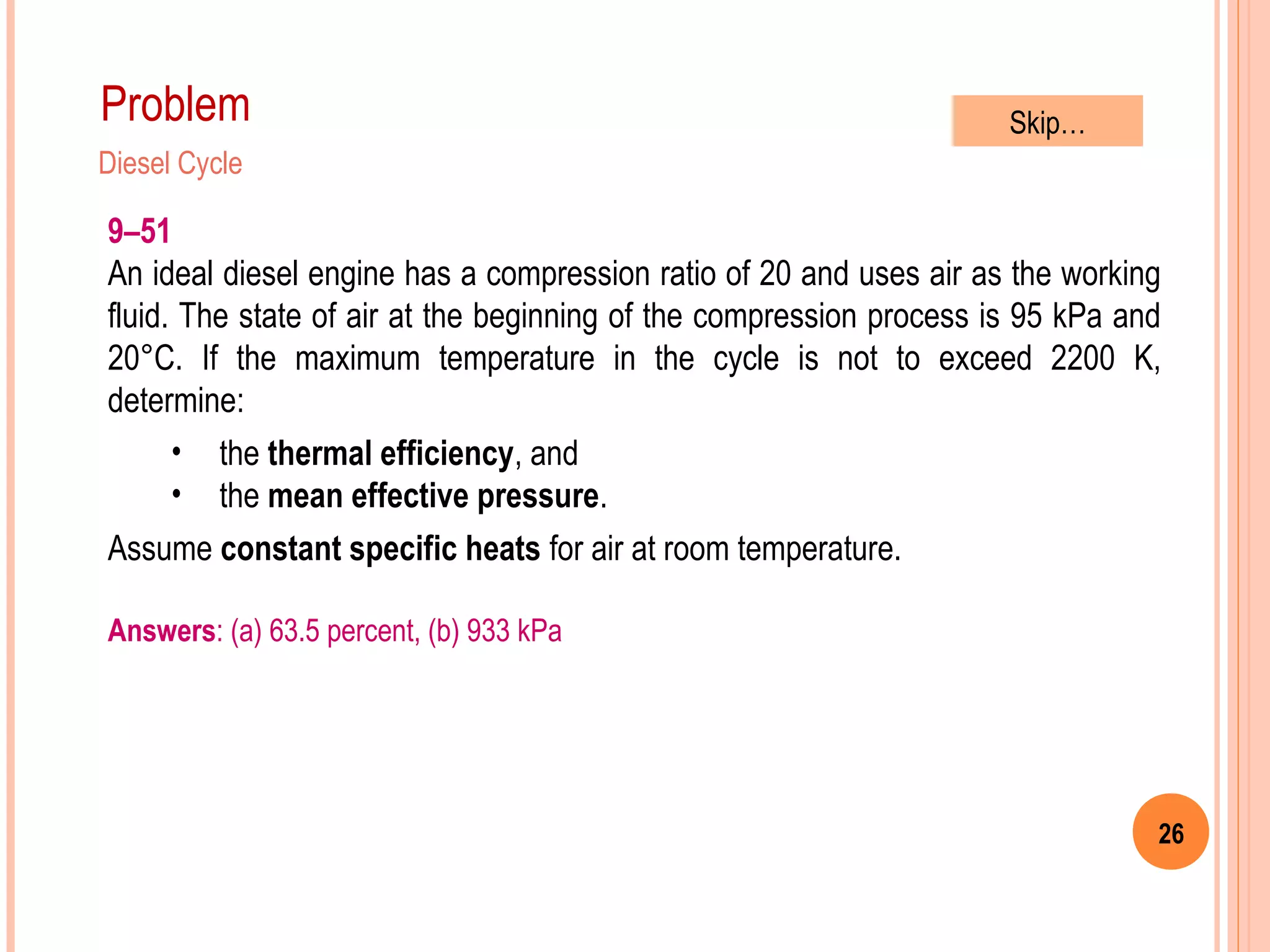
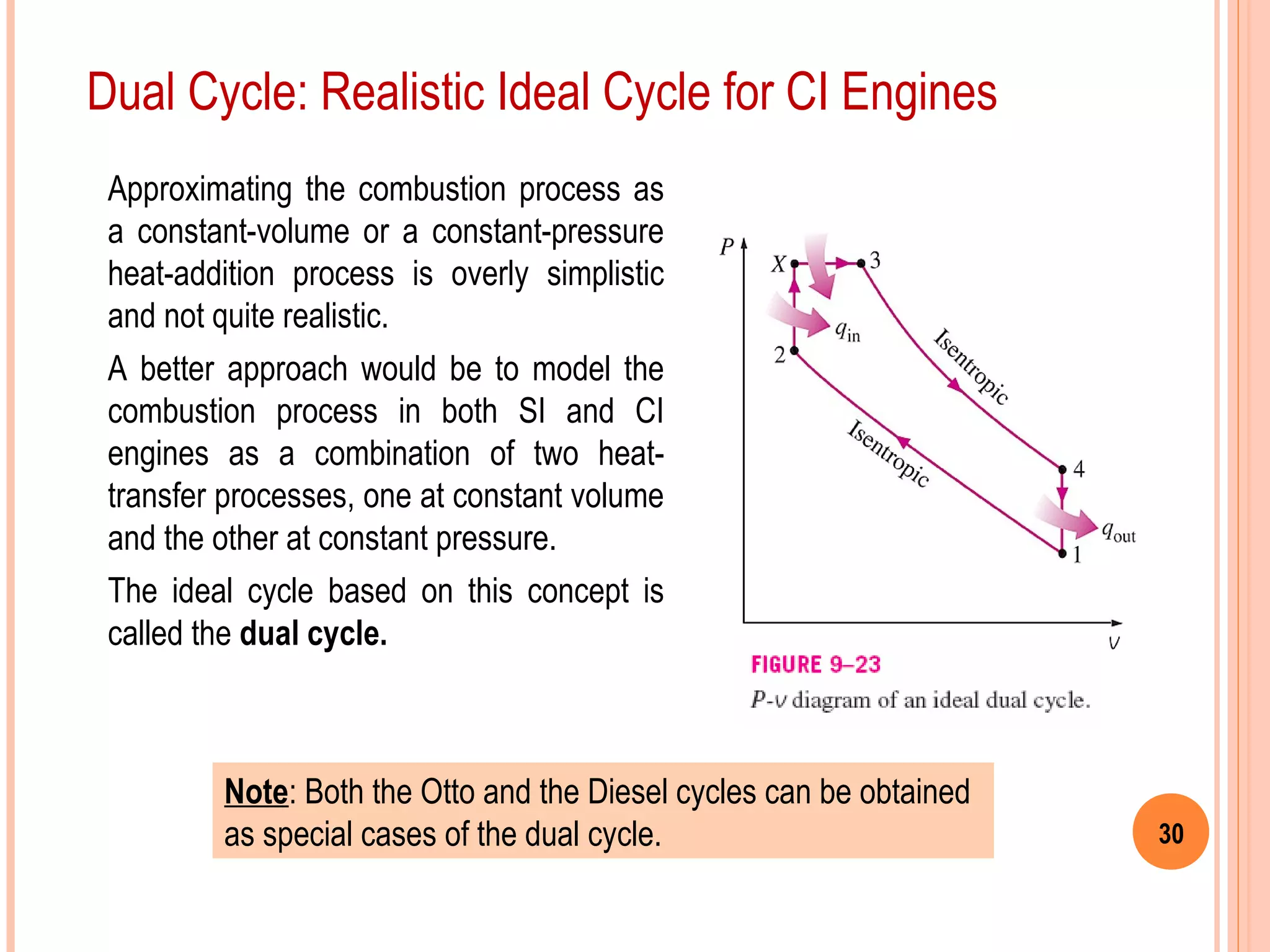
This document provides an overview of gas power cycles and ideal cycles used to model internal combustion engines. It begins by outlining the objectives and basic considerations for analyzing power cycles. Idealizations used include assuming internally reversible, quasi-equilibrium processes and negligible heat transfer. The Carnot, Otto, Diesel, and dual cycles are described as ideal models for heat engines. Sample problems are provided for calculating values like temperature, work, efficiency and mean effective pressure for the Otto and Diesel cycles. Limitations of the ideal cycles are noted, along with characteristics of reciprocating engines.