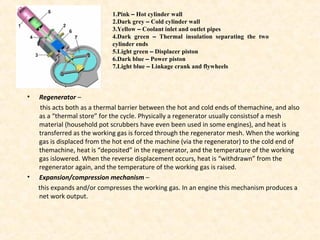
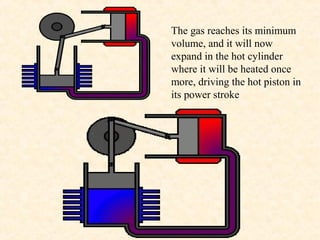
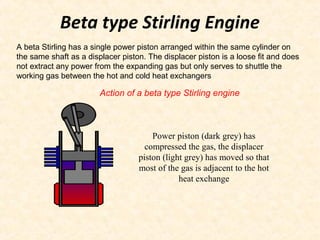
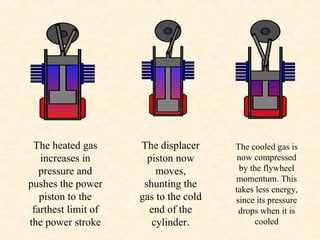
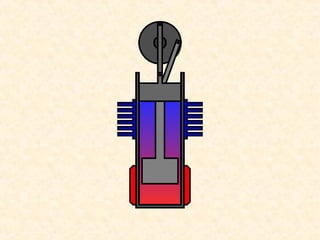
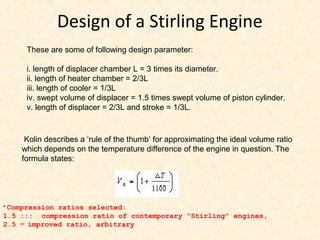
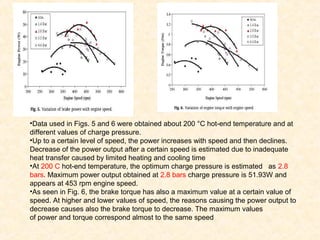
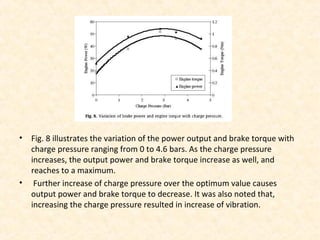
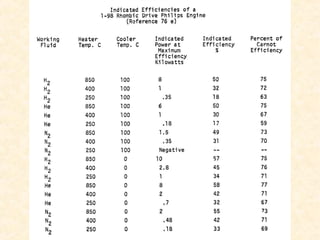
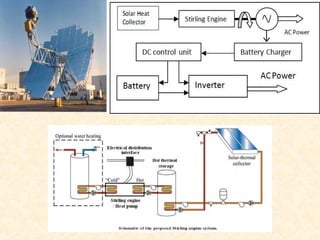
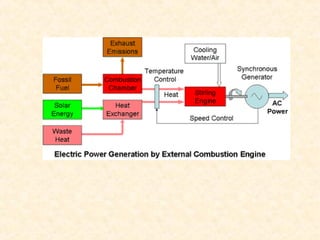
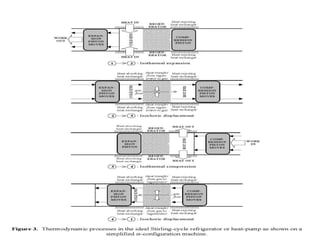
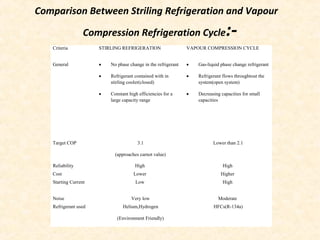
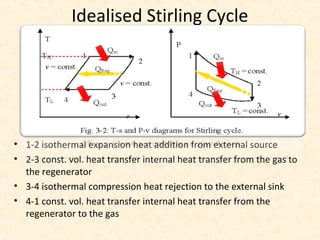
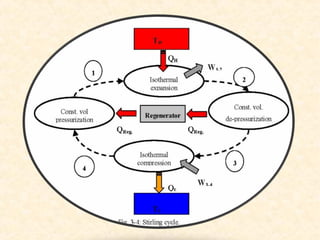
The document discusses the history and working principles of the Stirling engine, an external combustion engine invented in 1816 by Robert Stirling as a safer alternative to steam engines. It describes the ideal Stirling cycle of isothermal expansion and compression processes separated by constant volume heat transfer. The key components of Stirling engines are identified as the working gas, heat exchangers, displacer mechanism, regenerator, and expansion/compression mechanism. Different types of Stirling engines - alpha and beta - are also summarized. Applications highlighted include using solar-powered Stirling engines for water pumping in rural areas.

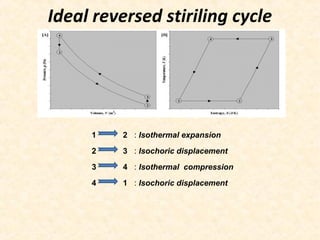
![Comparison of Carnot and Stiriling cycle[4]:-
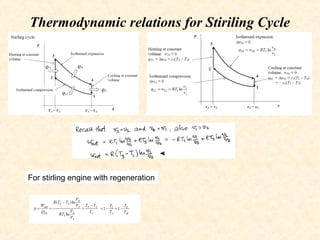
The ideal Stirling cycle has three theoretical advantages
• The thermal efficiency of the cycle with ideal regeneration is equal to the Carnotcycle.
• The second advantage, over the Carnot cycle, is obtained by substitution of two
isentropic processes with two constant-volume processes. This results in increasing
the p–v diagram area
• Compared with all reciprocal piston heat engines working at the same temperature
limits, the same volume ratios, the same mass of ideal working fluid, the same external
pressure, and mechanism of the same overall effectiveness, the ideal Stirling engine has
the maximum possible mechanical efficiency](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stirlingcycleitsapplications-140326111034-phpapp02/85/Stirling-cycle-its-applications-8-320.jpg)