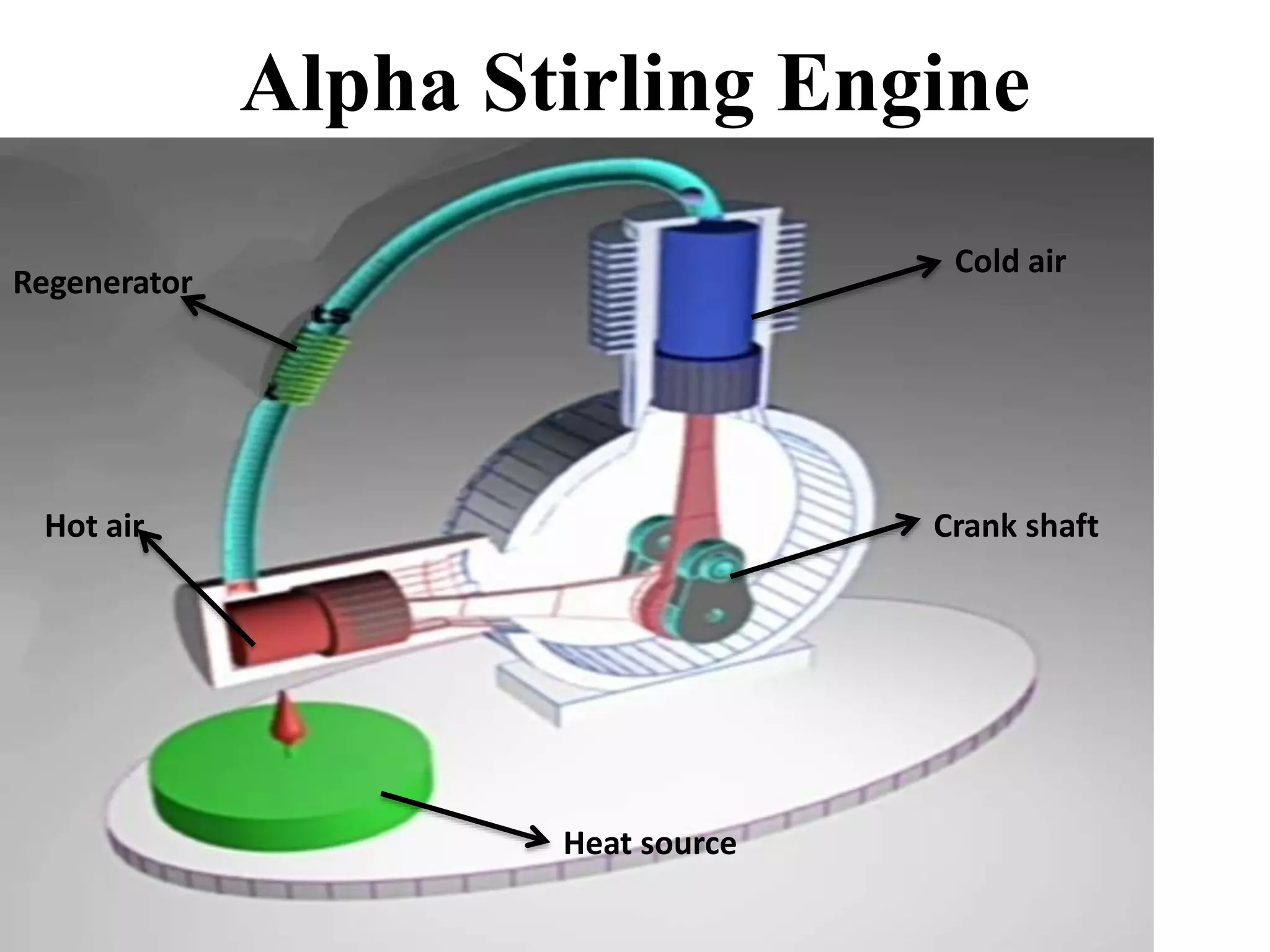
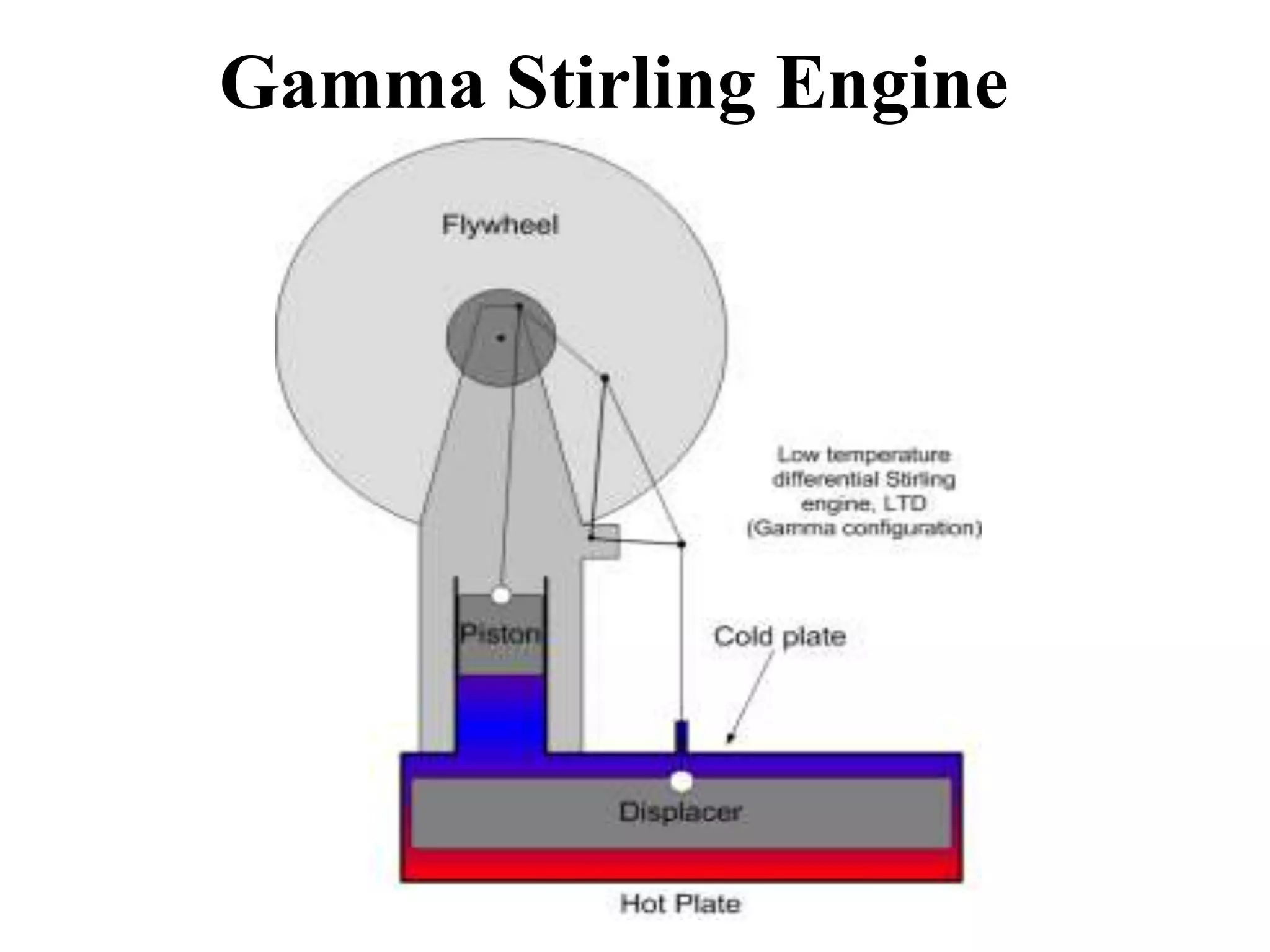
The document summarizes the Stirling engine, a heat engine that converts heat into mechanical work. It discusses the types of Stirling engines including the alpha, beta, and gamma. The key components are described as the regenerator, power piston, displacer, crankshaft, and flywheel. Applications include electricity generation, heating and cooling, and marine propulsion. Advantages are high efficiency and ability to use various heat sources, while disadvantages include high initial costs and inability to instantly change power output. In conclusion, Stirling engines offer applications but are expensive to build and rarely used commercially for power generation.