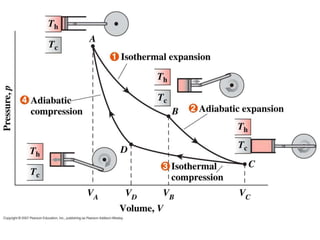
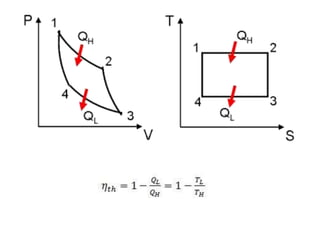
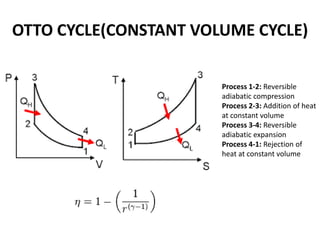
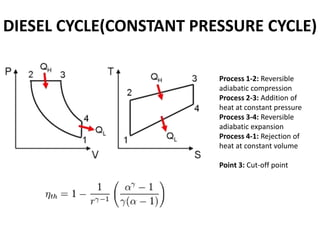
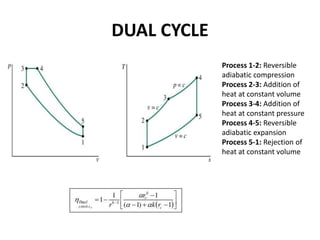
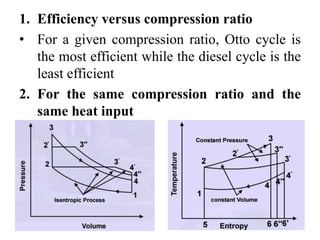
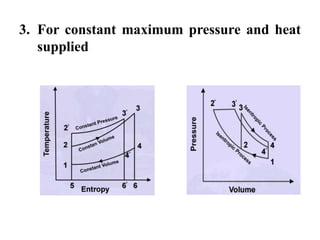
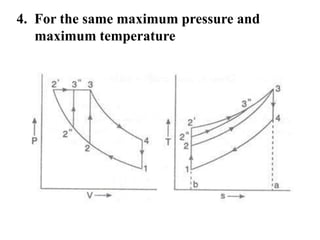
This document presents information on gas power cycles. It discusses how gas cycles have the working fluid remain in the gaseous phase throughout, while vapor cycles involve both vapor and liquid phases. It also describes common assumptions made in analyzing gas cycles, such as treating air as an ideal gas. Specific gas power cycles are then outlined, including the Carnot, Otto, Diesel, and Dual cycles. The key processes and characteristics of each cycle are defined. Finally, the document compares the cycles based on factors like compression ratio, maximum pressure, heat input/output, and efficiency.