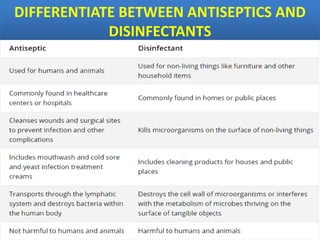
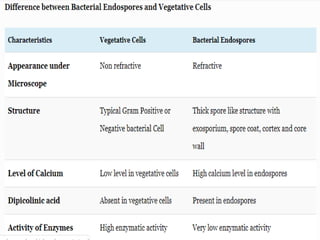
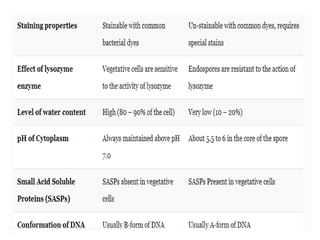
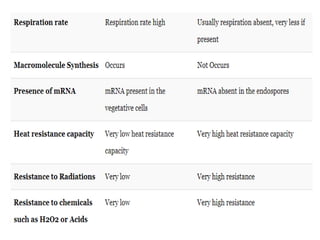
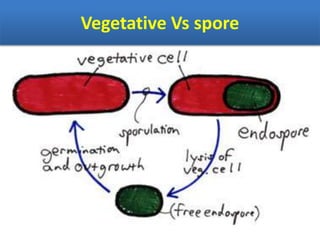
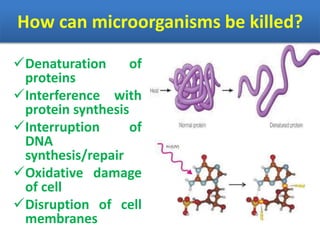
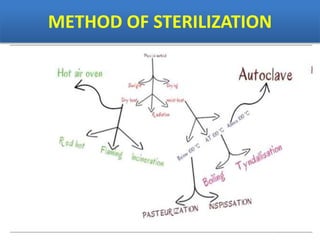
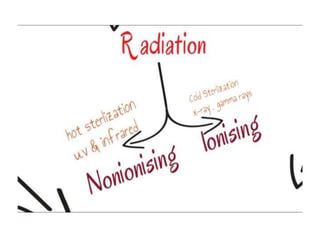
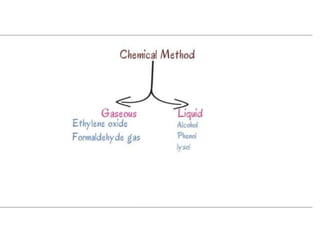
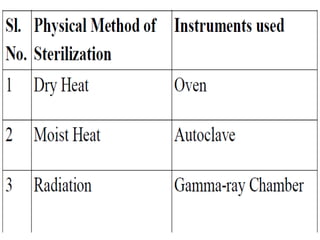
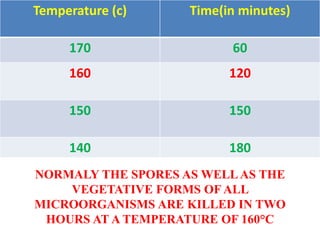
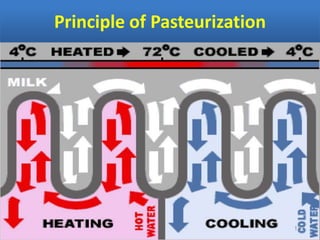
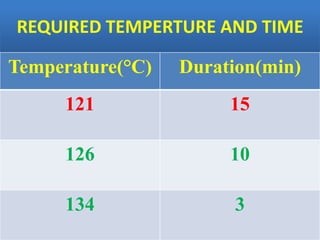
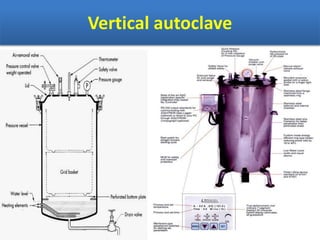
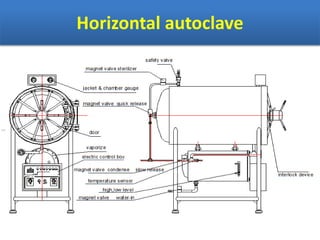
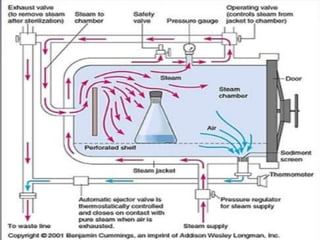
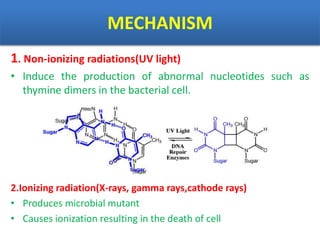
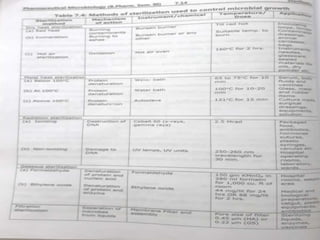
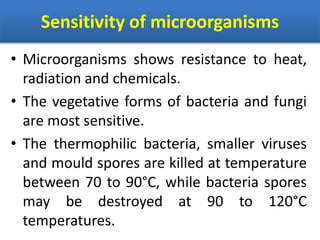
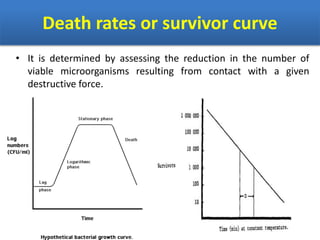
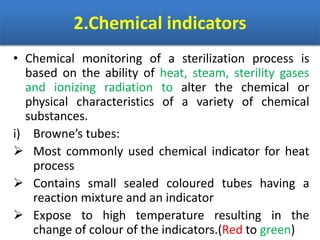
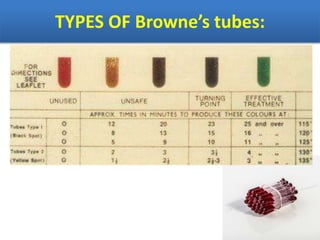
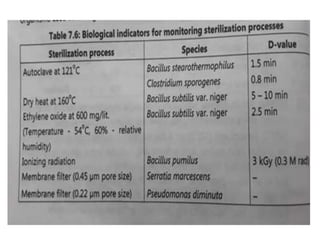
Sterilization is important to prevent contamination and transmission of pathogenic microorganisms. The goal of sterilization is to remove or destroy all microorganisms, including bacterial spores. There are physical and chemical methods of sterilization. Physical methods include dry heat sterilization using hot air ovens at temperatures over 160°C, and moist heat sterilization using autoclaves above 100°C, which is more effective at killing both vegetative cells and bacterial spores. Autoclaves apply high-pressure steam to sterilize materials for over 15 minutes at 121°C. Sterilization is crucial in healthcare, pharmaceutical, food and other industries to prevent infection and spoilage.