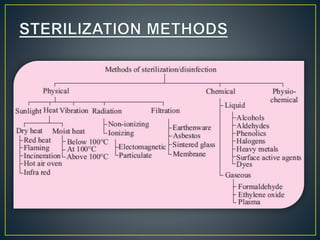
The document discusses various sterilization methods including thermal (dry and moist heat), radiation, filtration, and chemical. It provides details on key sterilization techniques such as autoclaving, which uses pressurized steam to achieve high temperatures for sterilizing materials. The document also defines important sterilization terms and concepts like D-value, which is the time required to reduce microbial counts by 90%. Overall, the document provides a comprehensive overview of common sterilization procedures and their mechanisms of action to eliminate microorganisms.