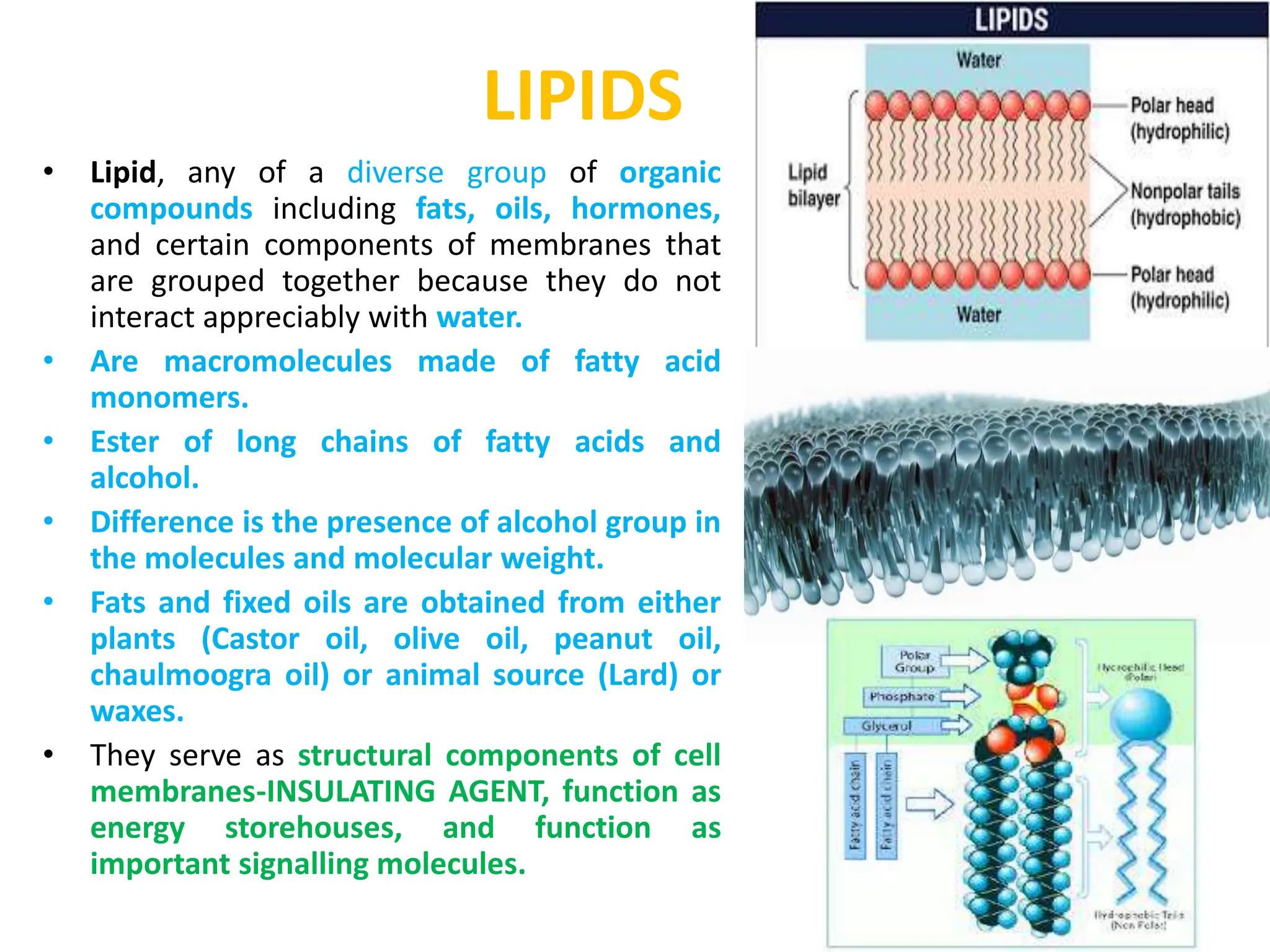
Lipids are a diverse group of organic compounds that do not interact with water. They include fats, oils, hormones, and components of cell membranes. Lipids are macromolecules made of fatty acid monomers esterified to an alcohol. They serve important structural and energy storage functions in cells and also function as signaling molecules. Lipids are classified based on their structure and saturation levels. Saturated fats are solid at room temperature and contain single bonds, while unsaturated fats contain one or more double bonds and remain liquid. Several plant and animal sources of lipids are described including their composition, characteristics, and common uses.