Filtration is a sterilization method that removes microorganisms from liquids and gases without exposing them to heat. It works by passing the substance through a membrane with pores small enough to block microbes. Key points:
- Filtration is preferred for heat-sensitive substances like antibiotics and vaccines.
- It physically removes microbes that are larger than the pore size, but may not remove viruses.
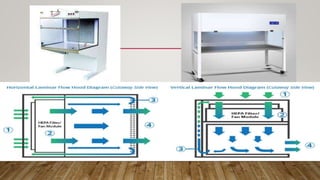
- Various types of filters exist for different applications, including membrane filters, HEPA filters, and candle filters.
- Filtration is commonly used in pharmaceutical and biological research to sterilize protein solutions.