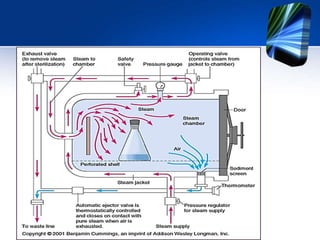
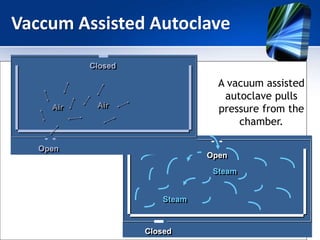
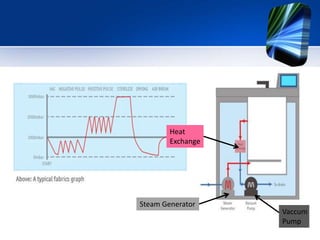
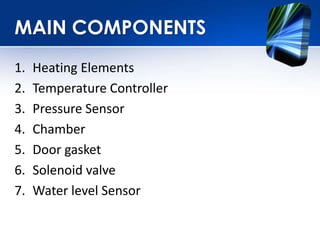
The autoclave uses steam under pressure to sterilize laboratory equipment and supplies. It operates by generating saturated steam at high temperatures, typically 121°C, which is able to destroy all microbial life, including bacterial spores. There are two main types - horizontal autoclaves that use downward displacement of air, and vacuum-assisted autoclaves that remove air via vacuum before introducing steam. Proper loading and maintenance are required to ensure effective sterilization.