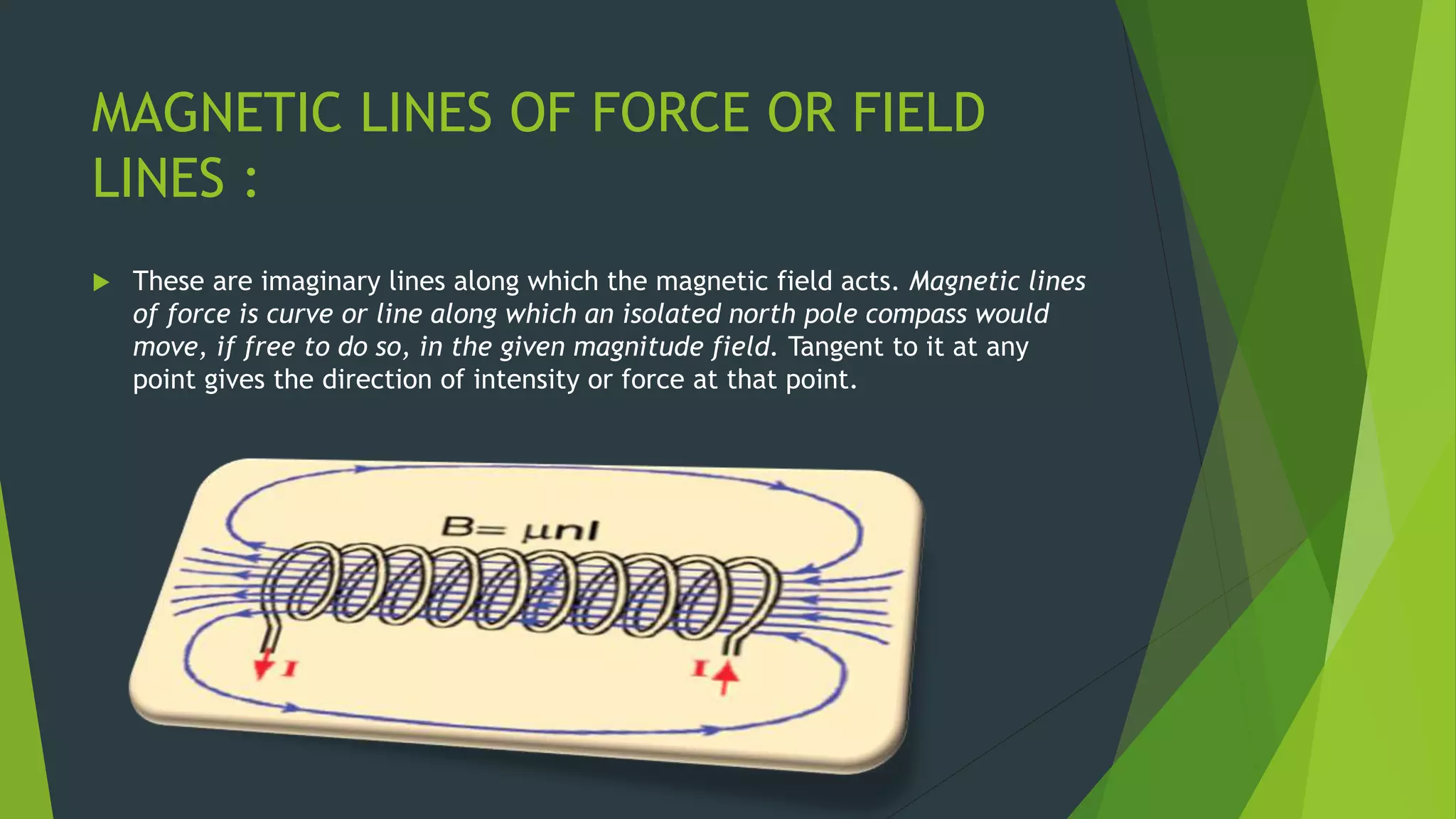
Magnetic effects can be produced by electric currents. When a current flows through a conductor, it creates a magnetic field around the conductor. Three key relationships govern magnetic fields: (1) like magnetic poles repel and opposite poles attract, (2) the strength of a magnetic field depends on the amount of current and number of turns in a coil, and (3) changing magnetic fields can induce electric currents in nearby conductors based on Lenz's law. Electromagnets and transformers take advantage of these relationships to manipulate magnetic fields for applications like motors, generators, and power transmission.