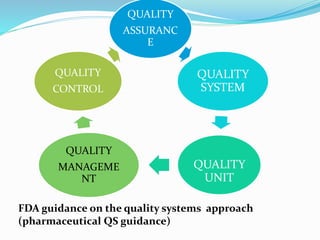
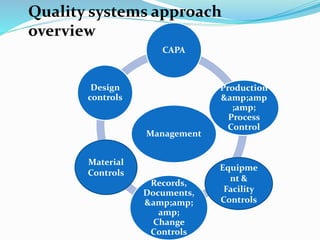
This document outlines the role of quality systems and audits in pharmaceutical manufacturing, detailing regulations, management responsibilities, and the importance of a coordinated quality management approach. It emphasizes the commitment of top management to quality, resource management, and objectives based on the SMART framework. Additionally, it addresses the preparation and execution of quality audits, corrective actions, and continuous improvement measures within the quality management system.