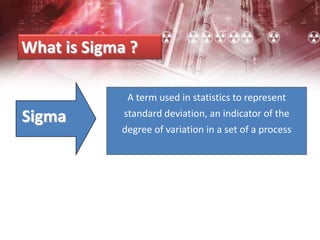
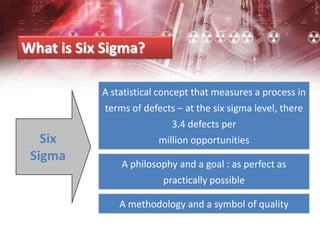
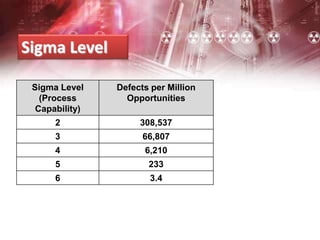
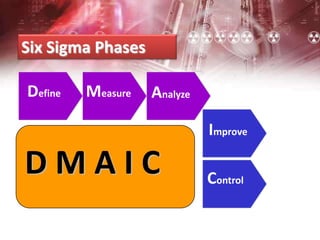
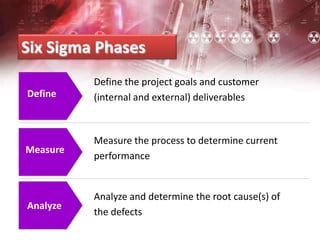
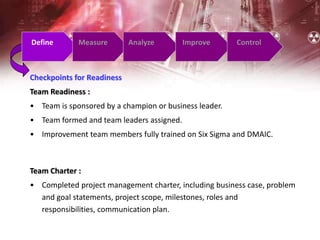
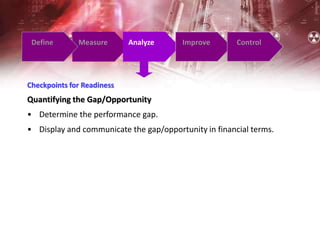
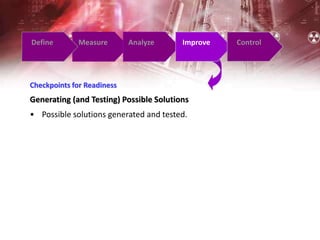
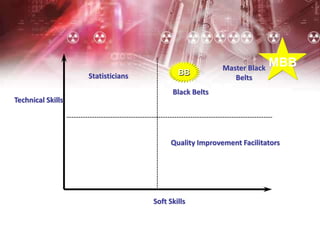
The document provides an overview of Six Sigma management. It defines Six Sigma as a statistical concept that measures quality in terms of defects, with the goal of 3.4 defects per million opportunities. It describes the Six Sigma phases of Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control (DMAIC). Key tools for Six Sigma include process mapping, design of experiments, measurement system analysis, and control plans. Critical roles include Champions, Master Black Belts, Black Belts, and Green Belts. Implementing Six Sigma can help reduce costs and improve customer satisfaction, quality, and competitive advantage.