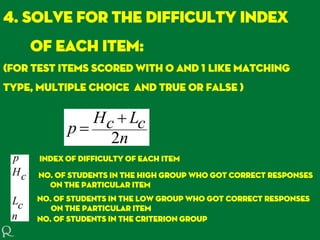
Item analysis evaluates the effectiveness of test items, helping to identify the difficulty level and discriminating power of questions based on student performance. An effective item should have a difficulty index between 0.20 and 0.80, and a discrimination index closer to +1 indicates better differentiability between high and low-performing students. Items that do not meet these criteria, or for which distractors are ineffective, should be revised or eliminated to enhance test quality.