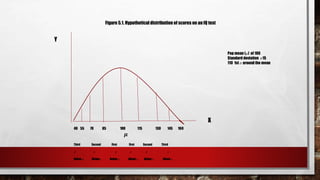
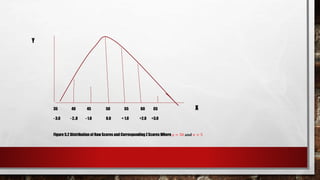
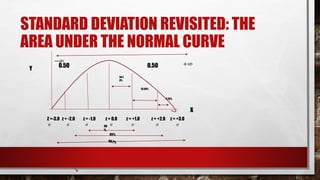
This document discusses standardization and converting raw scores to standardized scores. It explains that standardization involves consistent measurement and interpretation to allow comparison. It then defines several standardized tests used for education and careers. Next, it describes how raw scores are converted to standardized z-scores by calculating the number of standard deviations a score is from the mean. This normalization process allows comparison of scores from different tests or distributions. The key properties of z-scores are explained. Formulas for calculating z-scores from sample or population data are provided. Finally, it illustrates how z-scores can be used to interpret an individual's performance relative to a population.