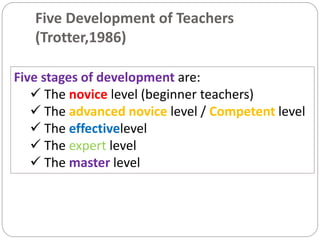
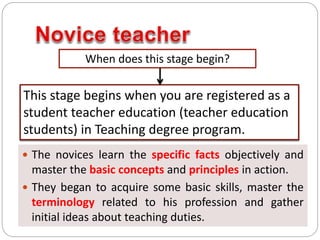
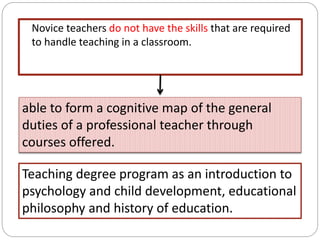
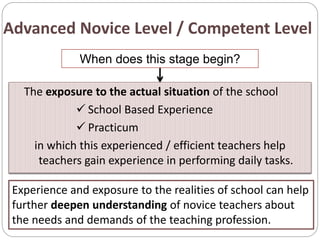
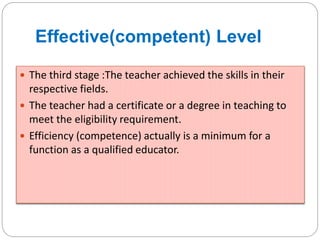
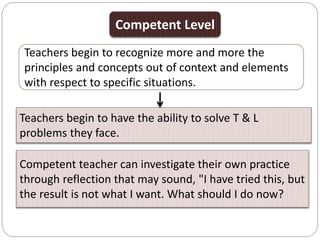
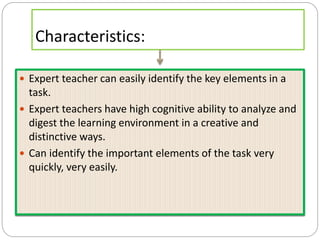
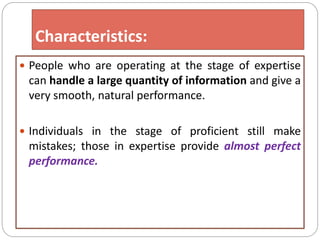
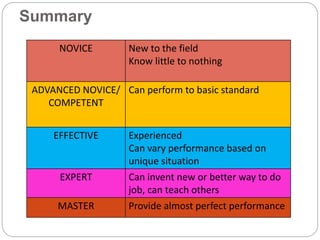
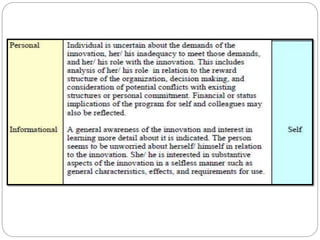
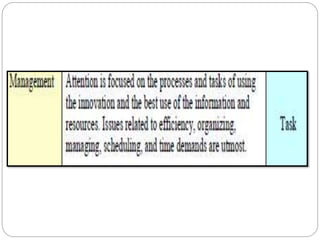
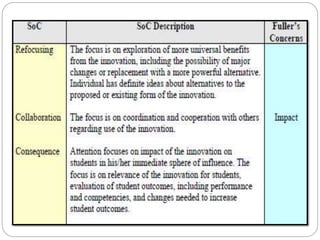
This document outlines five stages of teacher development: novice, advanced novice/competent, effective, expert, and master. The novice stage refers to beginning teachers with little experience. Advanced novice teachers gain experience and skills in the classroom. Competent teachers have several years of experience and can problem solve. Expert teachers intuitively understand teaching and can mentor others. Finally, master teachers provide near perfect performance and are widely recognized as superior educators.