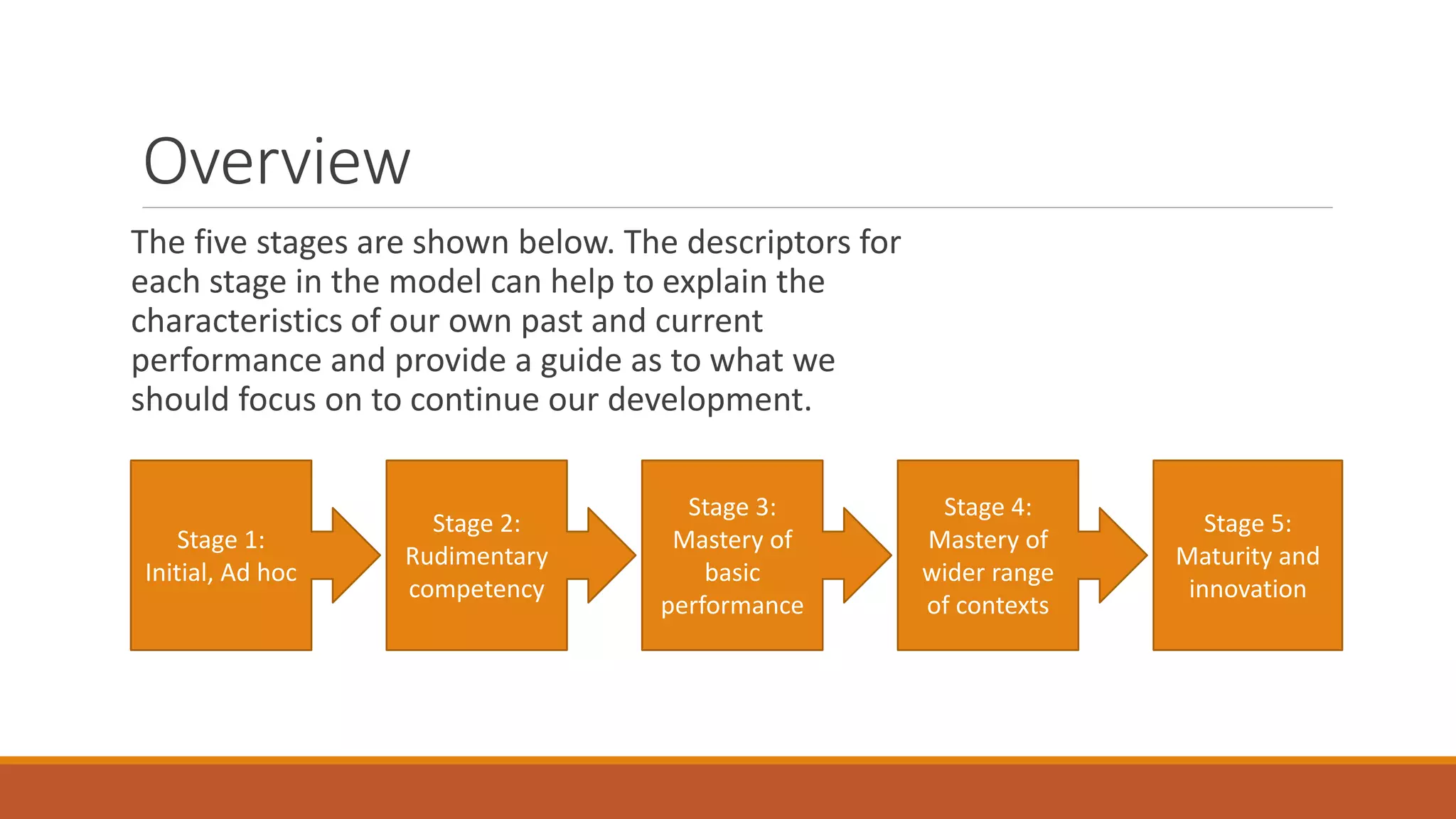
The document presents a five-stage model for developing teaching capabilities, emphasizing the evolution from basic functions to maturity and innovation in the teaching/learning role. It highlights how experience and reflection contribute to personal growth and effectiveness in facilitating student learning. Each stage is characterized by specific traits, from initial, ad hoc practices to mastery and adaptive teaching focused on student satisfaction.