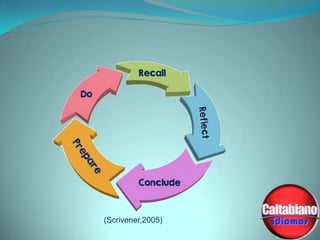
This document discusses the importance of professional development for language teachers. It defines professional development as continuing to develop one's skills throughout their career, as simply gaining experience through years of teaching does not necessarily lead to improvement. The document outlines several important areas of professional development, including obtaining language certificates, teaching certificates, engaging in reflection on one's lessons, attending conferences, and staying informed by reading literature in the field. It also discusses the benefits of activities like keeping a teaching journal, participating in peer observations, and getting involved in teacher associations. Overall, the document emphasizes that professional development is vital for maintaining enthusiasm and engagement in teaching to avoid burnout.