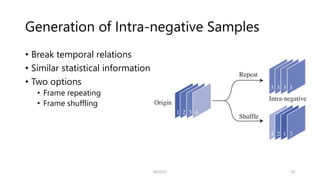
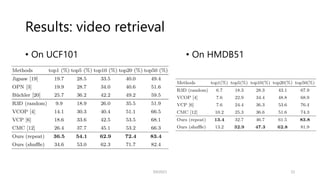
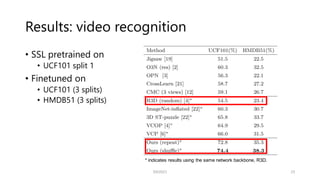
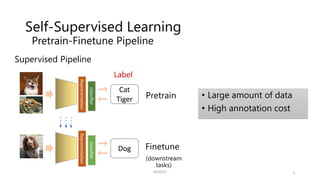
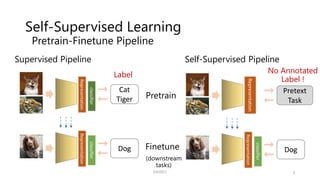
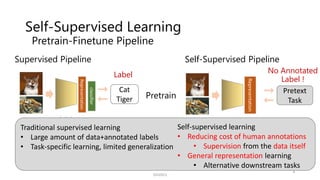
The document explores contrastive self-supervised learning, discussing its methodologies that reduce human annotation costs while promoting general representation learning. It highlights the effectiveness of various frameworks like MoCo and SimCLR, emphasizing their capabilities in distinguishing features among instances and the importance of both positive and negative samples. Additionally, the results demonstrate significant improvements in video tasks through the proposed inter-intra contrastive learning framework.


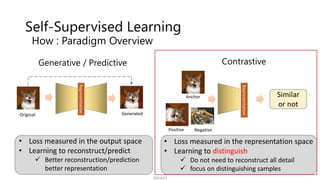
![Self-Supervised Learning
How : Paradigm Overview
SSII2021
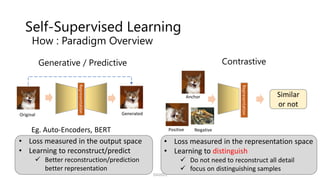
Generative / Predictive
Representation
• Loss measured in the output space
• Learning to reconstruct/predict
Better reconstruction/prediction
better representation
Original Generated
Eg. Auto-Encoders, BERT
Top: Drawing of a dollar bill from memory
Down: Drawing subsequently made with a
dollar bill present. [Image source: Epstein, 2016]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2-04-210605061641/85/SSII2021-OS2-03-7-320.jpg)
![Contrastive Learning
Point: distinguish features among different instances
9
SSII2021
Representation
Positive (𝒙+
)
Negative
(𝐱𝐣, 𝒕𝒉𝒆 𝒐𝒕𝒉𝒆𝒓 𝒔𝒂𝒎𝒑𝒍𝒆𝒔)
Anchor (𝒙)
Positive
Anchor Negative
Anchor
similar dissimilar
InfoNCE Loss [Gutmann+, AISTATS’10]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2-04-210605061641/85/SSII2021-OS2-03-9-320.jpg)
![Contrastive Learning
• MoCo: Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual
representation learning [CVPR’20]
• SimCLR: A Simple Framework for Contrastive Learning
of Visual Representations [ICML’20]
SSII2021 10
Recent related works
Increase negatives
Increase positives](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2-04-210605061641/85/SSII2021-OS2-03-10-320.jpg)
![MoCo[CVPR’20]
Points (Negative samples)
He, Kaiming, et al. "Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning." CVPR2020.
SSII2021
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2-04-210605061641/85/SSII2021-OS2-03-11-320.jpg)
![MoCo[CVPR’20]
He, Kaiming, et al. "Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning." CVPR2020.
SSII2021
12
End-to-end:
• Negative
• All the other samples (-anchor/positive)
• Two encoders
• q: anchor; k:positive/negative
• Benefit from large batch size
• Memory problem](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2-04-210605061641/85/SSII2021-OS2-03-12-320.jpg)
![MoCo[CVPR’20]
He, Kaiming, et al. "Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning." CVPR2020.
SSII2021
13
Memory Bank(MB):
• Negative:
• Embedding stored in MB
• Random sampling from
MB
• Memory bank updating
• Computing cost problem](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2-04-210605061641/85/SSII2021-OS2-03-13-320.jpg)
![MoCo[CVPR’20]
He, Kaiming, et al. "Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning." CVPR2020.
SSII2021
14
Momentum encoder
• Encoder:
• Only positive sample
• Negative:
• Past embeddings of positives
• Queue: save embedded features
• Updating: weight of momentum encoder](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2-04-210605061641/85/SSII2021-OS2-03-14-320.jpg)
![SimCLR[ICML’20]
Points
• Positive samples: data augmentation
• Random crops + color distortion
• Negative samples: larger batch size(end-to-end)
SimCLR:Chen, Ting, et al. "A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations." ICML2020.
SSII2021
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2-04-210605061641/85/SSII2021-OS2-03-15-320.jpg)
![Effect of Recent Works
SSII2021 16
source: [SimCLR: A Simple Framework for Contrastive Learning of Visual Representations]
• Performance approaching
supervised methods
• Limitation:
more time & parameters
• Less labeling cost
• High generalization
(Eg. cross-domain)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2-04-210605061641/85/SSII2021-OS2-03-16-320.jpg)

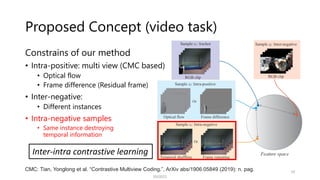
![Inter-intra Contrastive Framework [MM’20]
SSII2021 18
• Intra-positives: same instance, same class
Intra-negatives: same instance, different class
• Inter-positives: different instances, same class
Inter-negatives: different instances
Traditional contrastive learning
IIC: L. TAO, X. Wang, and T. YAMASAKI, “Self-supervised Video Representation Learning Using Inter-
intra Contrastive Framework”, ACMMM2020.
Inter-intra contrastive (IIC) learning framework
makes the most use of data](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2-04-210605061641/85/SSII2021-OS2-03-18-320.jpg)